

 C++之STL算法(二)
C++之STL算法(二)
描述
1.sort排序算法
sort(const _RanIt _First, const _RanIt _Last, _Pr _Pred) --默认为升序排序
形参:_First、_Last --容器的起始和结束迭代器
_Pred --排序规则,默认为从小到大
示例:
#include < iostream >
#include < vector >
#include < algorithm >
using namespace std;
class Print
{
public:
void operator()(int val)
{
cout < < val < < " ";
}
};
void test()
{
vector< int >vtr;
vtr.push_back(rand()%50);
vtr.push_back(rand() % 50);
vtr.push_back(rand() % 50);
vtr.push_back(rand() % 50);
vtr.push_back(rand() % 50);
vtr.push_back(rand() % 50);
for_each(vtr.begin(), vtr.end(), Print());
cout < < endl;
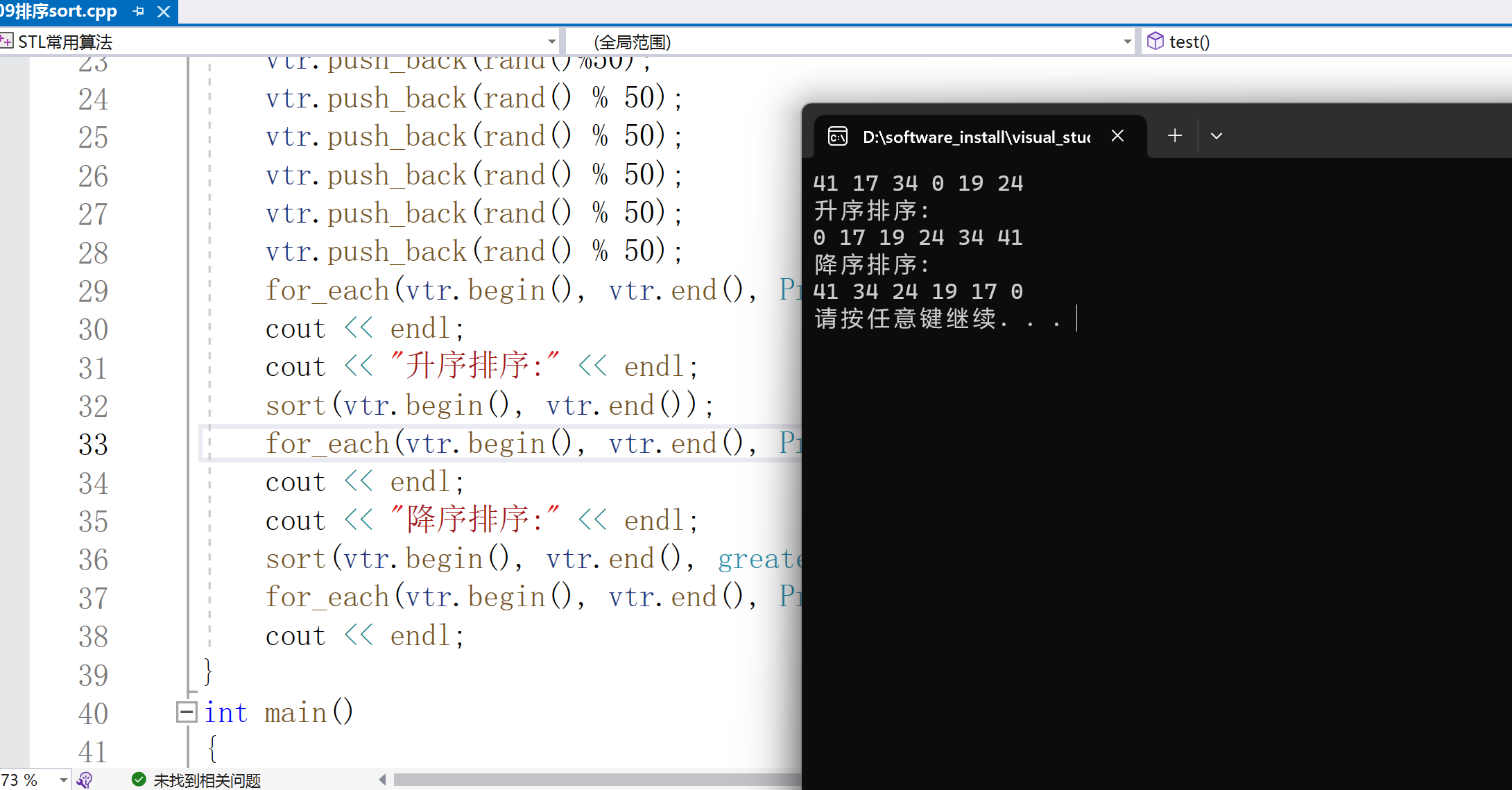
cout < < "升序排序:" < < endl;
sort(vtr.begin(), vtr.end());
for_each(vtr.begin(), vtr.end(), Print());
cout < < endl;
cout < < "降序排序:" < < endl;
sort(vtr.begin(), vtr.end(), greater< int >());
for_each(vtr.begin(), vtr.end(), Print());
cout < < endl;
}
int main()
{
test();
system("pause");
}
2.random_shuffle打乱顺序(洗牌)
打乱有序数列,重新洗牌:
void random_shuffle(_RanIt _First, _RanIt _Last);
形参:_First、_Last --起始和结束迭代器
#include < iostream >
using namespace std;
#include < vector >
#include < algorithm >
#include < map >
#include < ctime >
class Person
{
friend class Print;
public:
Person() {}
Person(string name, int age) :name(name), age(age) {
}
bool operator< (const Person p)const
{
if (age == p.age)
{
return name < p.name;
}
return age < p.age;
}
string name;
int age;
};
class Print
{
public:
void operator()(int val)
{
cout < < val < < " ";
}
void operator()(Person& p)
{
cout < < "姓名:" < < p.name < < "t年龄:" < < p.age < < endl;
}
};
void test()
{
vector< int >vtr;
vtr.resize(10);
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
vtr[i] = i;
}
for_each(vtr.begin(), vtr.end(), Print());
cout < < endl;
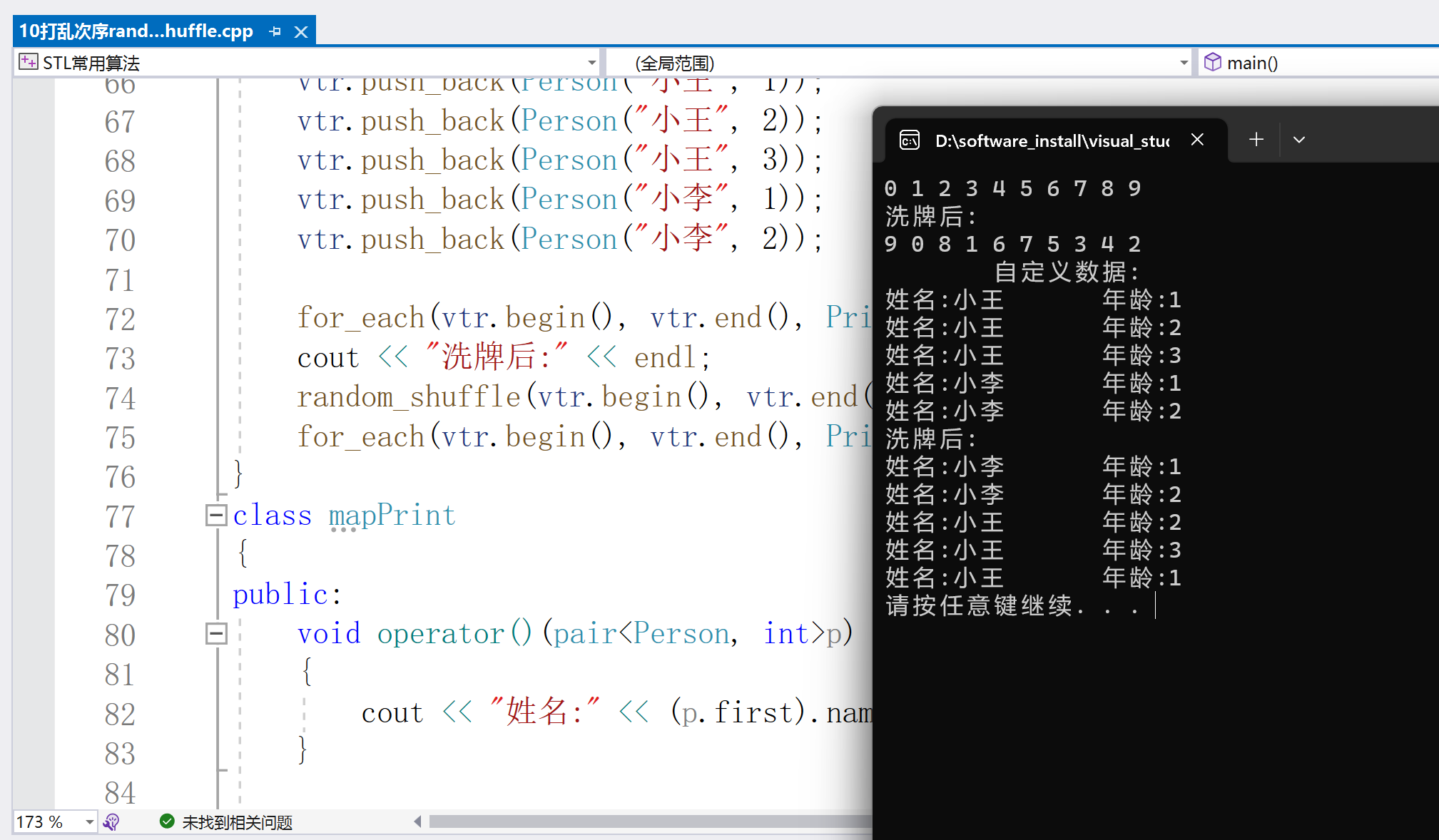
cout < < "洗牌后:" < < endl;
random_shuffle(vtr.begin(), vtr.end());
for_each(vtr.begin(), vtr.end(), Print());
cout < < endl;
}
void test02()
{
cout < < "t自定义数据:" < < endl;
vector< Person >vtr;
vtr.push_back(Person("小王", 1));
vtr.push_back(Person("小王", 2));
vtr.push_back(Person("小王", 3));
vtr.push_back(Person("小李", 1));
vtr.push_back(Person("小李", 2));
for_each(vtr.begin(), vtr.end(), Print());
cout < < "洗牌后:" < < endl;
random_shuffle(vtr.begin(), vtr.end());
for_each(vtr.begin(), vtr.end(), Print());
}
class mapPrint
{
public:
void operator()(pair< Person, int >p)
{
cout < < "姓名:" < < (p.first).name < < "t年龄:" < < (p.first).age < < "t得分:" < < p.second < < endl;
}
};
int main()
{
srand(time(NULL));//random_shuffle底层需要随机数种子,否则每次生成结果一样
test();
test02();
system("pause");
}
3.merge合并容器
容器合并:
merge()实现吧两个容器合并在一起,存放到第三个容器中。
注意:merge()合并一定要保证容器元素有序,默认是从小到大的顺序。
merge(_InIt1 _First1, _InIt1 _Last1, _InIt2 _First2, _InIt2 _Last2, _OutIt _Dest) -- >默认从小到大
merge(_InIt1 _First1, _InIt1 _Last1, _InIt2 _First2, _InIt2 _Last2, _OutIt _Dest, _Pr _Pred) -- >重载版本,支持自定义排序规则
_First1、_Last1 --第一个容器的起始和结束迭代器
_Last2、_Dest --第二个元素的起始和结束迭代器
_Dest --要存储的新容器起始迭代器
_Pred --谓词,设定排序规则
谓词:
函数对象返回中为bool类;
函数对象形参只有一个 -- > 一元谓词
函数对象形参有两个 -- > 二元谓词
示例:
#include < iostream >
#include < algorithm >
#include < vector >
#include < map >
using namespace std;
class Print
{
public:
void operator()(int val)
{
cout < < val < < " ";
}
};
void test01()
{
vector< int >v1;
vector< int >v2;
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
v1.push_back(i);
}
v2.push_back(2);
v2.push_back(16);
v2.push_back(12);
v2.push_back(14);
sort(v2.begin(), v2.end(), less< int >());
vector< int >v3;
v3.resize(v1.size() + v2.size());
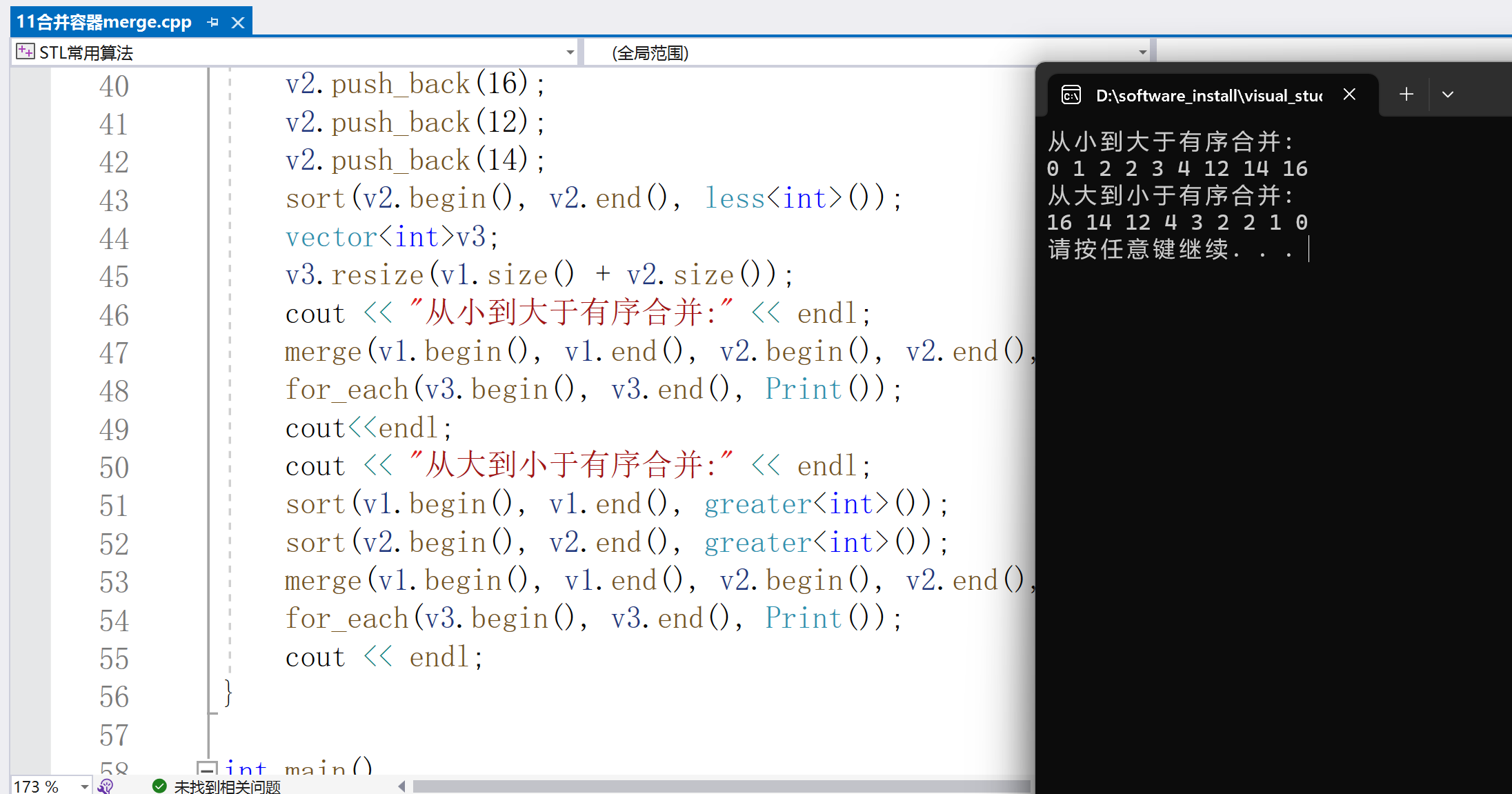
cout < < "从小到大于有序合并:" < < endl;
merge(v1.begin(), v1.end(), v2.begin(), v2.end(), v3.begin());
for_each(v3.begin(), v3.end(), Print());
cout< ());
sort(v2.begin(), v2.end(), greater< int >());
merge(v1.begin(), v1.end(), v2.begin(), v2.end(), v3.begin(),greater< int >());
for_each(v3.begin(), v3.end(), Print());
cout < < endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
system("pause");
}
;>
4.reverse元素反转
函数功能: 元素反转,将容器中的元素前后颠倒
reverse(const _BidIt _First, const _BidIt _Last)
形参:_First、_Last --起始和结束迭代器
#include < iostream >
#include < vector >
#include < algorithm >
using namespace std;
class Person
{
public:
Person() {}
Person(string name, int age) :name(name), age(age) {
}
Person(const Person& p)
{
this- >age = p.age;
name = p.name;
}
bool operator< ( Person p)const
{
if (age == p.age)return name < p.name;
return age < p.age;
}
string name;
int age;
};
class Print
{
public:
void operator()(Person p)
{
cout < < "姓名:" < < p.name < < "t年龄:" < < p.age < < endl;
}
};
void test()
{
vector< Person >vtr;
vtr.push_back(Person("小王",18));
vtr.push_back(Person("小刘", 15));
vtr.push_back(Person("小林", 20));
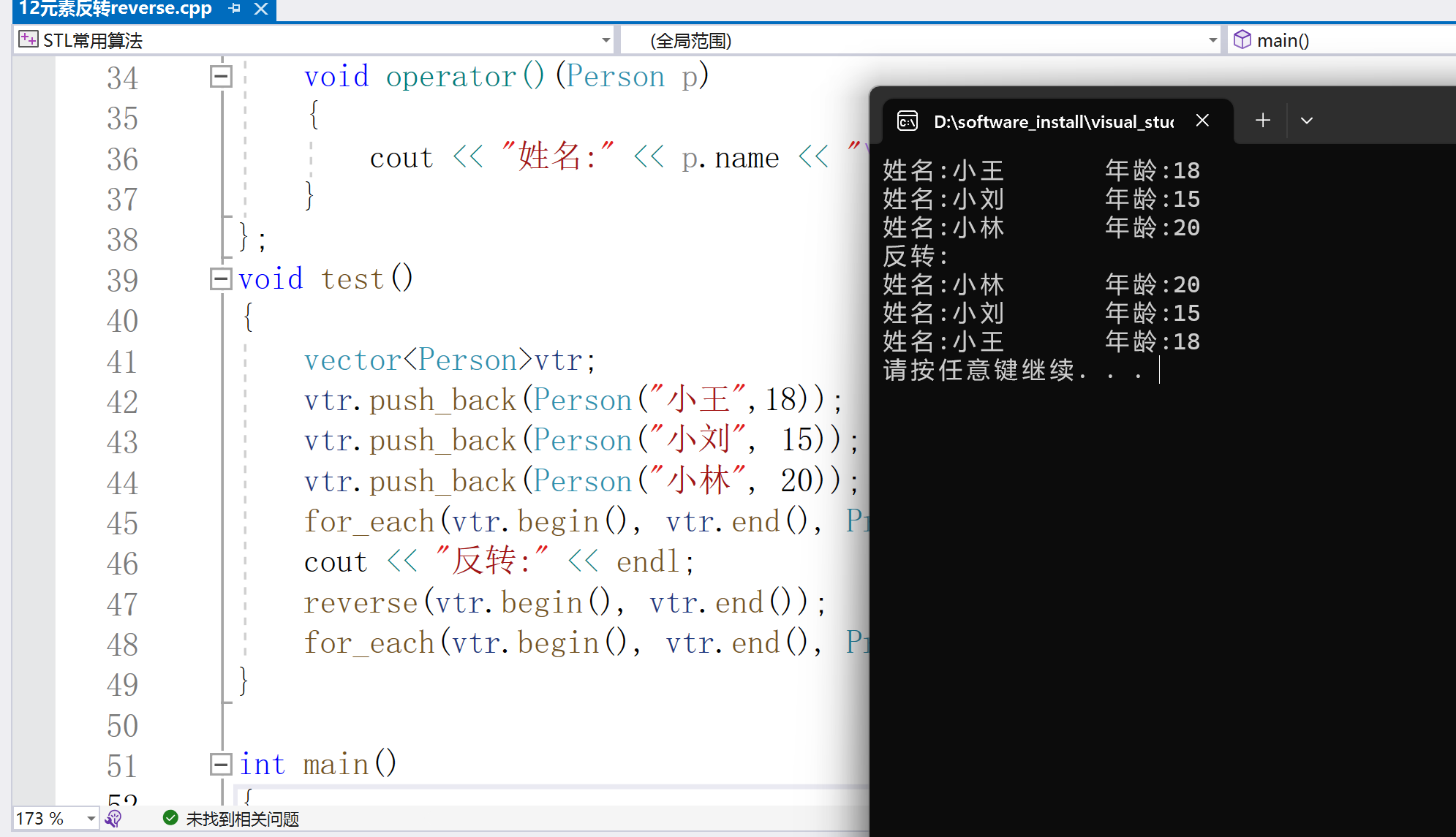
for_each(vtr.begin(), vtr.end(), Print());
cout < < "反转:" < < endl;
reverse(vtr.begin(), vtr.end());
for_each(vtr.begin(), vtr.end(), Print());
}
int main()
{
test();
system("pause");
}
5.copy元素拷贝
_OutIt copy(_InIt _First, _InIt _Last, _OutIt _Dest)
形参:_First、_Last --原容器的起始和结束位置
_Dest --目标容器的起始位置
该函数功能类似于重载运算符=功能
#include < iostream >
#include < algorithm >
#include < vector >
void test()
{
std::vector< std::string >vtr, vtr2;
vtr.push_back("C++");
vtr.push_back("copy算法");
vtr.push_back("学习");
vtr.push_back("案例");
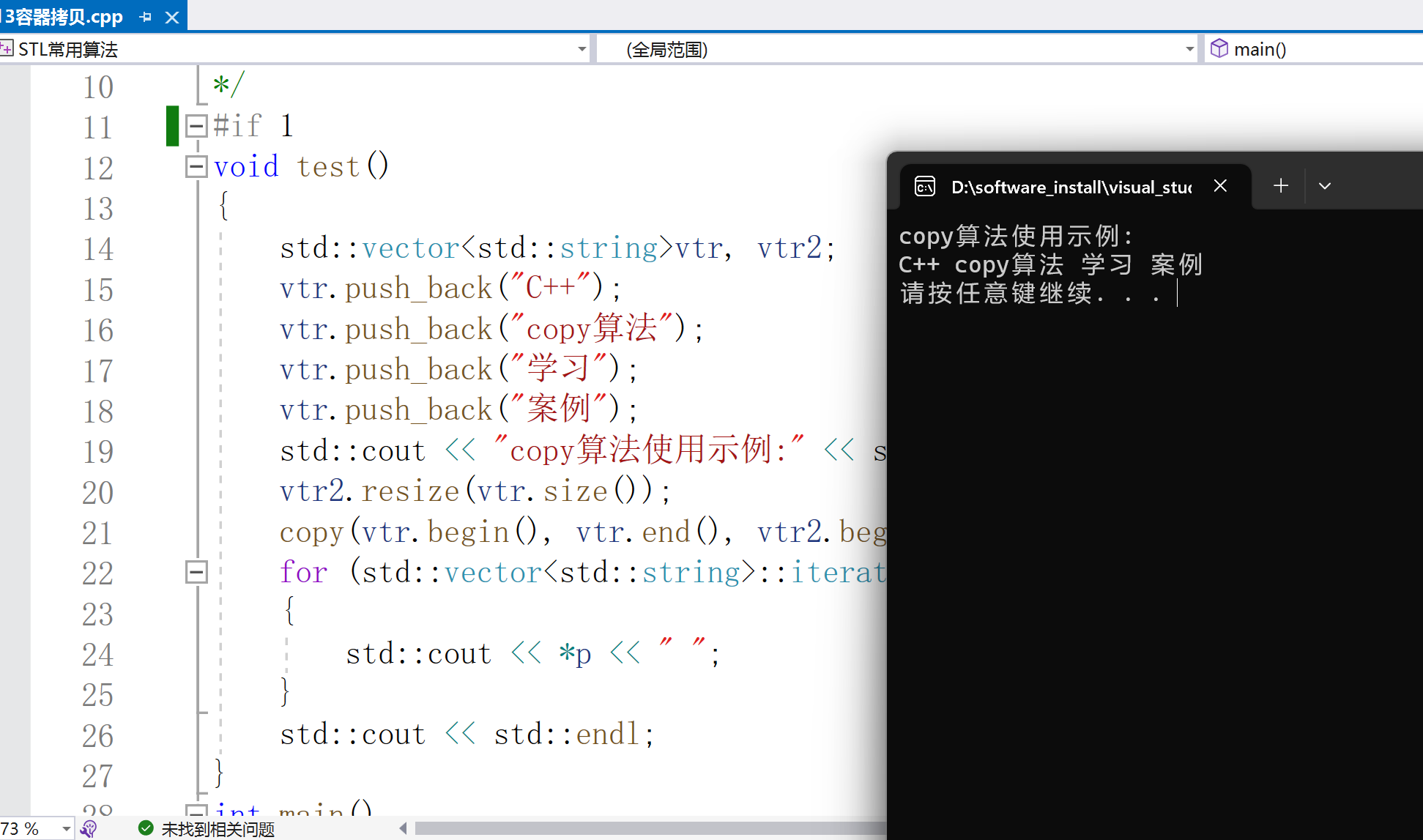
std::cout < < "copy算法使用示例:" < < std::endl;
vtr2.resize(vtr.size());
copy(vtr.begin(), vtr.end(), vtr2.begin());//copy函数类似于赋值操作,vtr2=vtr1
for (std::vector< std::string >::iterator p = vtr2.begin(); p != vtr2.end(); p++)
{
std::cout < < *p < < " ";
}
std::cout < < std::endl;
}
int main()
{
test();
system("pause");
}
6.replace元素替换
元素替换
void replace(const _FwdIt _First, const _FwdIt _Last, const _Ty& _Oldval, const _Ty& _Newval)
形参:_First、_Last --要替换的数据区间
_Oldval --要替换的内容
_Newval --替换后的内容
#include < vector >
#include < iostream >
using namespace std;
#include < algorithm >
using namespace std;
class Print
{
public:
void operator()(int val)
{
cout < < val < < " ";
}
};
void test()
{
vector< int >vtr;
vtr.push_back(10);
vtr.push_back(10);
vtr.push_back(30);
vtr.push_back(10);
vtr.push_back(35);
vtr.push_back(10);
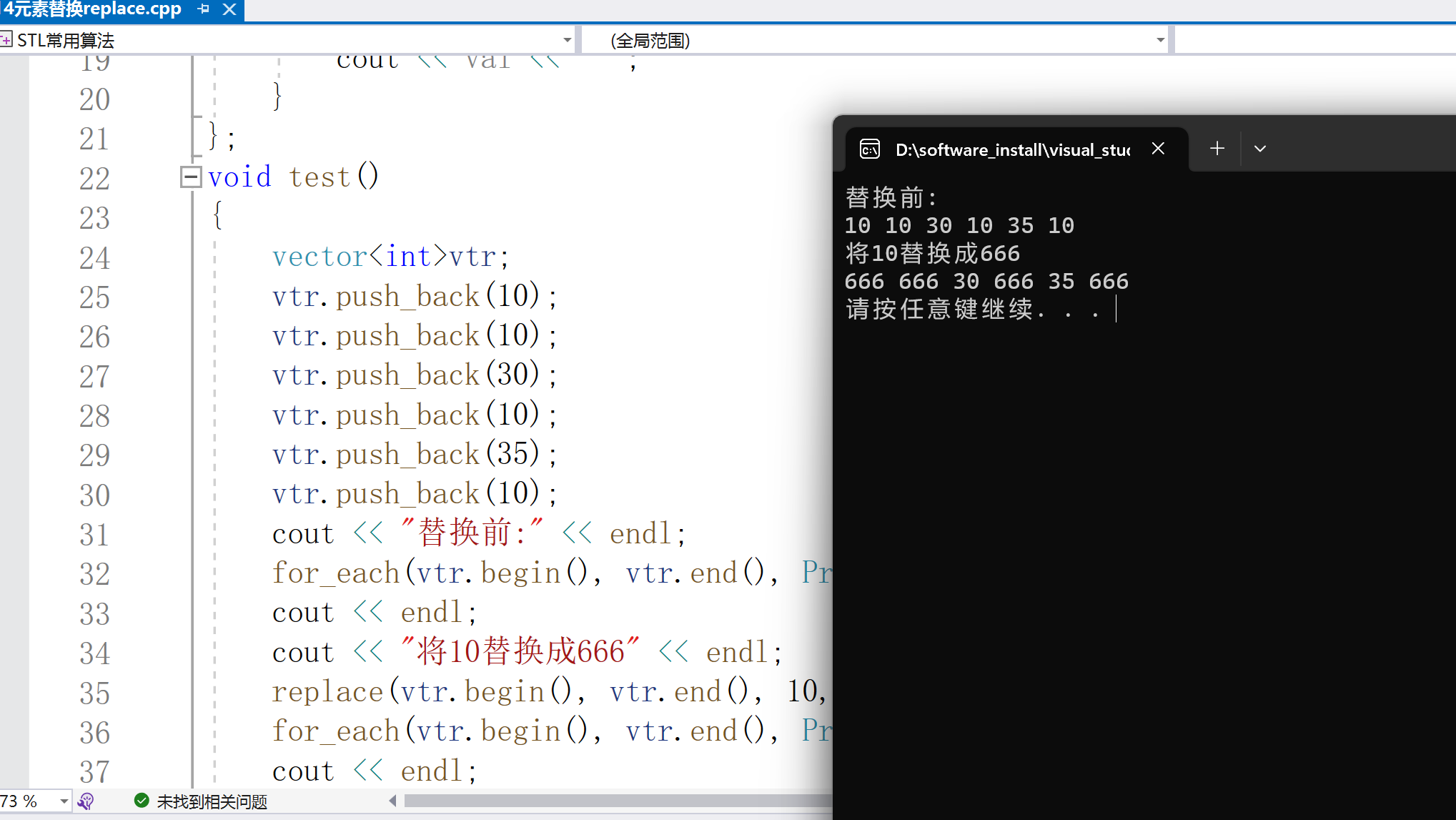
cout < < "替换前:" < < endl;
for_each(vtr.begin(), vtr.end(), Print());
cout < < endl;
cout < < "将10替换成666" < < endl;
replace(vtr.begin(), vtr.end(), 10, 666);
for_each(vtr.begin(), vtr.end(), Print());
cout < < endl;
}
int main()
{
test();
system("pause");
}
7.条件替换replace_if
条件替换
replace_if(const _FwdIt _First, const _FwdIt _Last, _Pr _Pred, const _Ty& _Val)
形参:_First、_Last --要替换的区间
_Pred --谓词,替换条件
_Val --替换后的值
示例:
#include < iostream >
#include < vector >
#include < functional >
#include < algorithm >
using namespace std;
class Myreplace
{
public:
bool operator()(int val)
{
return val >= 30;
}
};
void test()
{
vector< int >vtr;
vtr.push_back(10);
vtr.push_back(10);
vtr.push_back(30);
vtr.push_back(10);
vtr.push_back(50);
vtr.push_back(10);
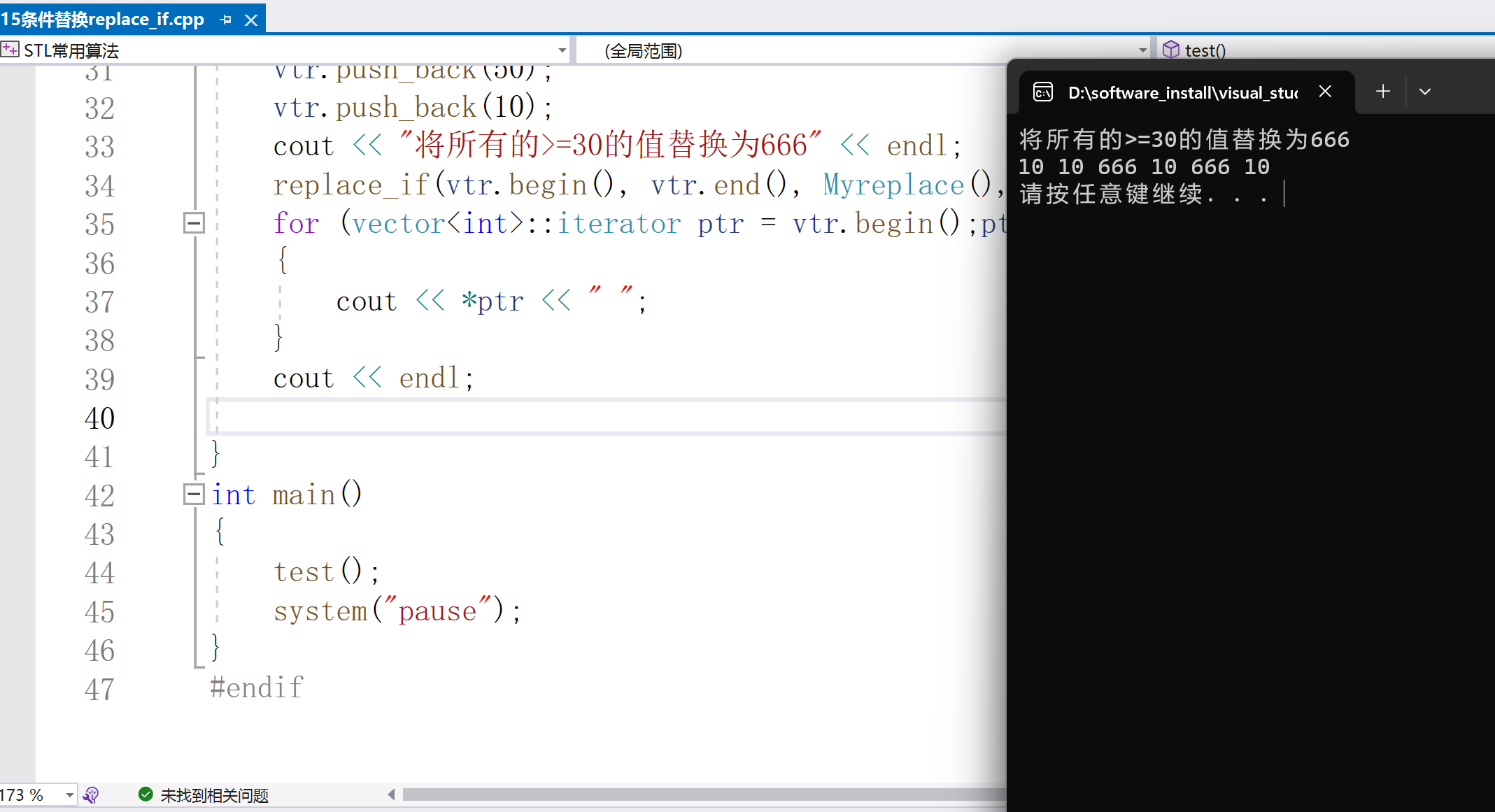
cout < < "将所有的 >=30的值替换为666" < < endl;
replace_if(vtr.begin(), vtr.end(), Myreplace(), 666);
for (vector< int >::iterator ptr = vtr.begin();ptr != vtr.end();ptr++)
{
cout < < *ptr < < " ";
}
cout < < endl;
}
int main()
{
test();
system("pause");
}
8.容器互换swap
容器元素互换:
swap(container v1,container v2);
将v1和v2的容器元素进行互换,类似于成员函数swap();
#include < iostream >
using namespace std;
#include < algorithm >
#include < vector >
class Print
{
public:
void operator()(int val)
{
cout < < val < < " ";
}
};
void test()
{
vector< int >vtr1 = { 10,20,30,50 };
vector< int >vtr2 = { 10,29,88 };
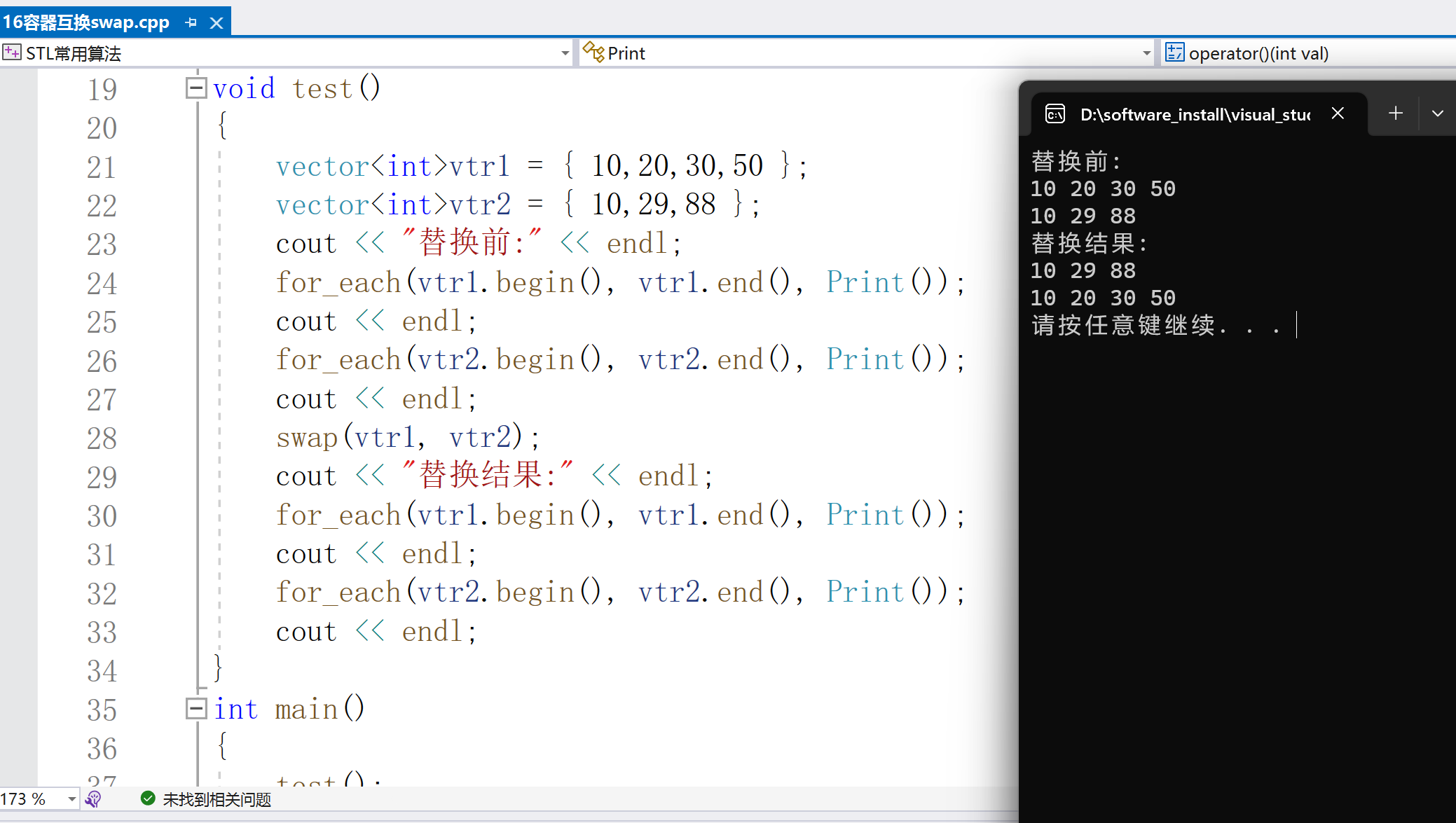
cout < < "替换前:" < < endl;
for_each(vtr1.begin(), vtr1.end(), Print());
cout < < endl;
for_each(vtr2.begin(), vtr2.end(), Print());
cout < < endl;
swap(vtr1, vtr2);
cout < < "替换结果:" < < endl;
for_each(vtr1.begin(), vtr1.end(), Print());
cout < < endl;
for_each(vtr2.begin(), vtr2.end(), Print());
cout < < endl;
}
int main()
{
test();
system("pause");
}
声明:本文内容及配图由入驻作者撰写或者入驻合作网站授权转载。文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表电子发烧友网立场。文章及其配图仅供工程师学习之用,如有内容侵权或者其他违规问题,请联系本站处理。
举报投诉
-
C++编程思想第二卷_刁成嘉译2011-10-21 849
-
c语言入门知识之STL篇2023-03-10 1699
-
c++之STL算法(三)2023-07-18 3001
-
C++之文件操作2023-07-21 1726
-
C++零基础教程之STL集合类算法,轻松上手C++ STL电子学习 2023-01-14
-
密码编码学(加密方法的C与C++实现) pdf第二版2008-09-25 714
-
C++ STL的概念及举例2010-08-30 1629
-
STL算法在GIS中的应用2011-06-28 779
-
C++课程资料详细资料合集包括了:面向对象程序设计与C++,算法,函数等2018-07-09 1301
-
C语言教程:STL-for-each算法2021-09-17 711
-
STL的概述2023-01-20 2228
-
C++之STL库中的容器2023-02-21 2065
-
C++ STL基本概念是什么2023-02-27 2200
-
C++入门之通用算法2023-05-17 1340
-
STL内容介绍2023-11-13 1935
全部0条评论

快来发表一下你的评论吧 !

