

使用Raspberry Pi Pico W和MicroPython开发物联网应用
电子说
描述
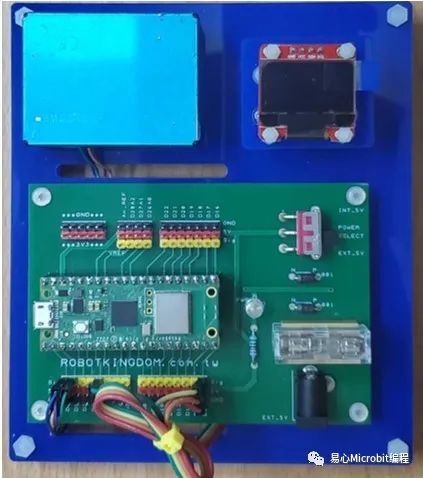

当我们提及物联网(IoT, Internet of Things)开发,可能首先想到的是Arduino或是ESP8266这样的微控制器开发板。然而,Raspberry Pi的微控制器开发板——Raspberry Pi Pico W,也是一个很好的选择。
在本项目中,将会介绍如何使用Raspberry Pi Pico W和MicroPython,并用Thonny IDE的平台来撰写程序。
Raspberry Pi Pico W 简介
Raspberry Pi Pico W是由RaspberryPi基金会出品的微控制器开发板。它配备了一个RP2040微控制器,有264KB的内部RAM,并且支持MicroPython程序语言,这让我们可以更方便地开发物联网应用。
使用上和Raspberry Pi Pico没有多大差别,只是Raspberry Pi Pico W 还支持Wi-Fi 802.11n无线网络和蓝牙,更多Raspberry Pi Pico相关介绍连结如下:
Raspberry Pi Pico family
Raspberry Pi Pico介绍(含使用ArduinoIDE和扩充板)
MicroPython简介
MicroPython是一种针对微控制器和受限环境设计的Python 3 程序语言编译程序和执行环境。这种程序语言实现了Python 3的大部分语法和特性,并对于开发板所需的低功耗和实时响应有进一步优化。MicroPython提供了丰富的API,可以直接控制微控制器的GPIO、I2C、SPI等各种硬件资源。
Thonny IDE简介
Thonny是一个专为Python初学者设计的集成开发环境(IDE)。它的介界面简单,功能强大,对于学习Python语言非常有帮助。而且,Thonny IDE 也支持 MicroPython,我们可以直接在Thonny IDE中编写MicroPython 程序,并上传到Raspberry Pi Pico W上执行。
请由 Thonny 官方网站下载 Thonny。
电路接线图
本次项目分享如何透过Thonny IDE来撰写MicroPython程序,并使用PMS5003粉尘传感器取得数值和经由Raspberry Pi Pico W的Wi-Fi功能取得目前台湾时间,并显示在OLED中。
以下介绍Raspberry Pi Pico W、Raspberry Pi Pico W扩充板、OLED、PMS5003接线图。
Raspberry Pi Pico与扩充板接法(扩充板可兼容于Raspberry Pi Pico W)
https://cavedu.gitbook.io/cavedu/raspberry_pi_pico_info/pico_breakout

Raspberry Pi Pico W扩充板与OLED接线图
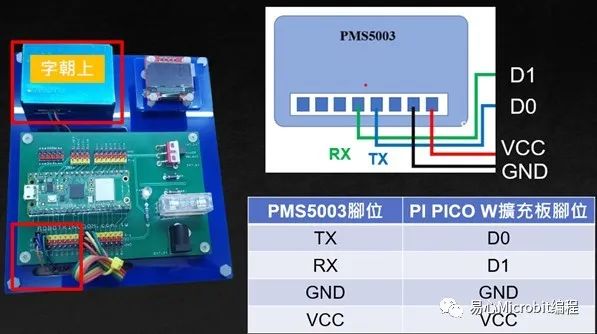
Raspberry Pi Pico W扩充板与PMS5003接线图
接下来使用 Thonny IDE 来编写程序,请先下载 Raspberry Pi Pico W 的 uf2 韧体档,除非有更新版本的韧体,否则更新只要一次即可。
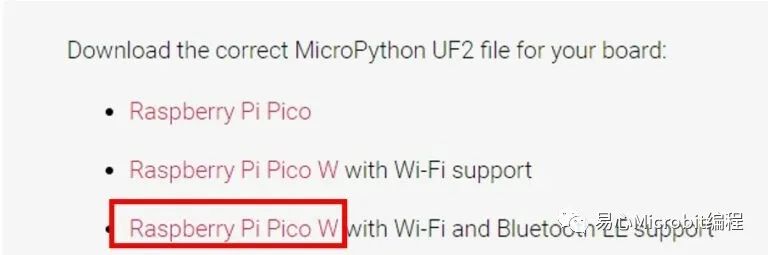
如何上传Raspberry Pi Pico W的uf2檔
按住 Raspberry Pi Pico W 的 BOOTSET 按钮时,插上USB连接到计算机。
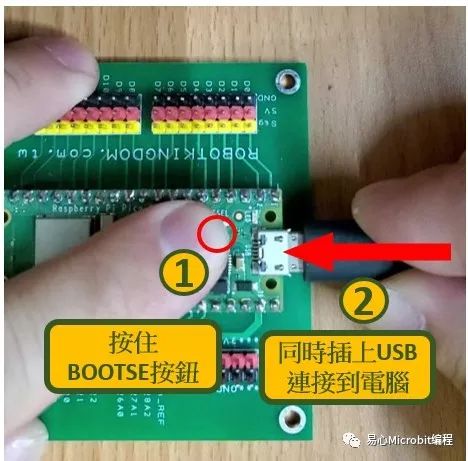
Raspberry Pi Pico W 会被计算机辨识为一个磁盘,将 uf2 韧体档拖放到其中就会自动更新韧体。
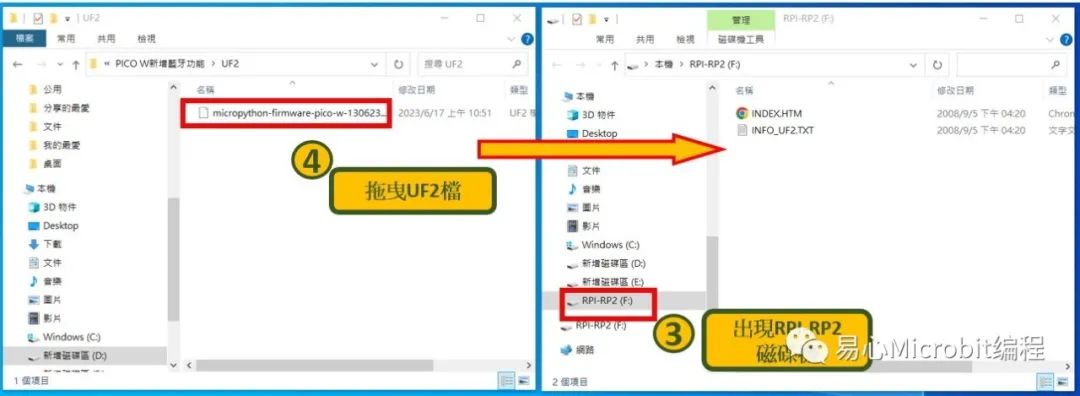
Raspberry Pi Pico W连接Thonny IDE
●将Thonny IDE下载至计算机,并解压缩后开启,请选择执行>设定直译器
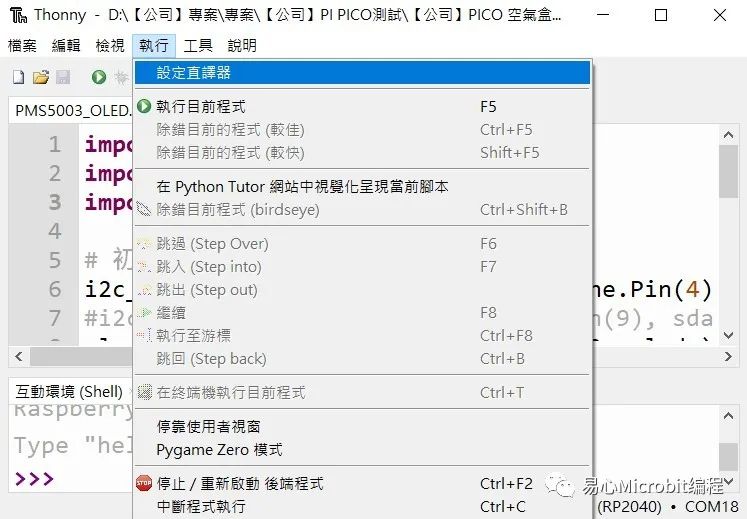
●选Micro Python (RP2040)
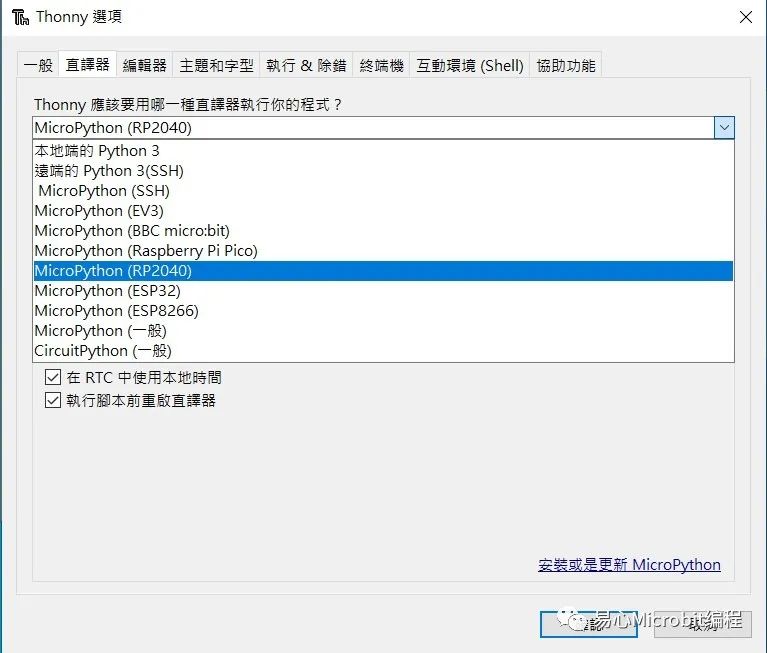
●端口选择USB序列装置(COM X)
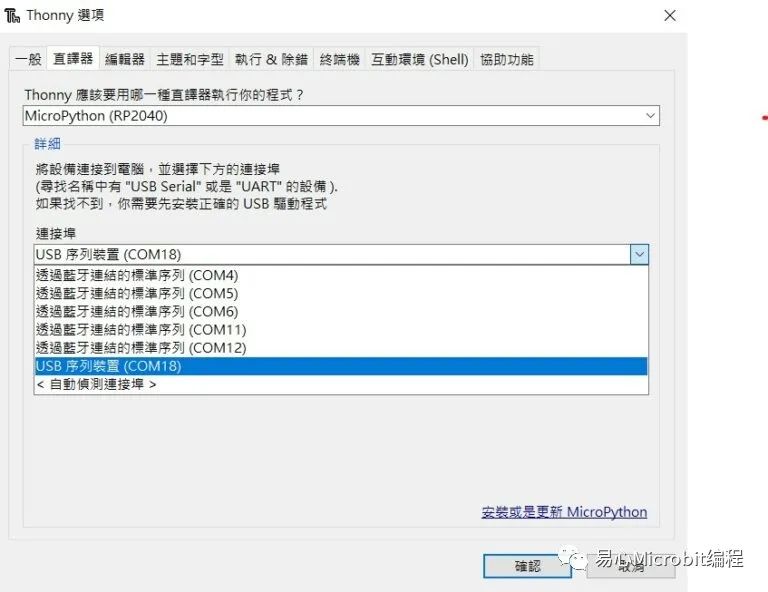
[注] COM号要记住,后续上传程序需要正确指定 COM 号,概念如同 Aduino IDE
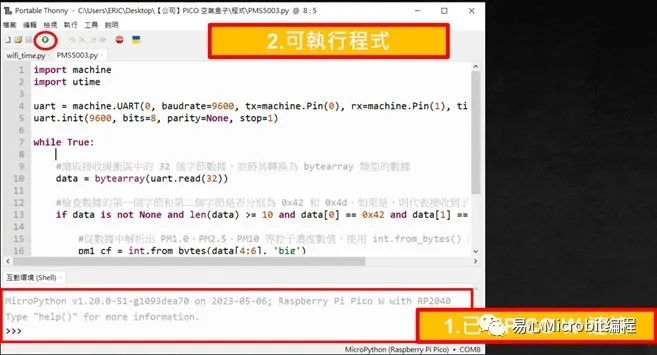
●确认是否抓到 Raspberry Pi Pico W
检查 Thonny IDE 下方的互动环境(Shell),如果没有红字错误讯息即可上传程序,这时候还没写,继续看下去吧。
汇入OLED函式库至 Raspberry Pi Pico W
本项目需要透过 OLED 显示模块来显示数值,故需要先汇入OLED 函式库
1. 下载 OLED 函式库,档名ssd1306.py到您的计算机
2. 在 Thonny IDE 中安装套件
我们可由 Thonny IDE 呼叫系统命令行来安装 python 套件,请由工具–> 开启系统命令行
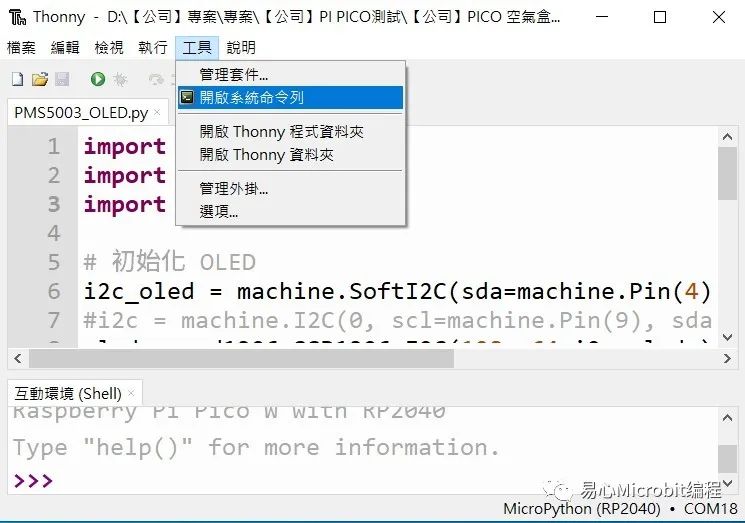
开启系统命令行,如下图
3. 安装 adafruit-ampy 套件
为了顺利执行程序,我们需要安装 adafruit-ampy 套件,用于透过串行端口与 CircuitPython 或 MicroPython 开发板互动,
安装方式就是一般的 pip 指令,相当简单:
4. 汇入OLED函式库到RaspberryPi Pico W
cd module_library
ampy --port COMX put ssd1306.py
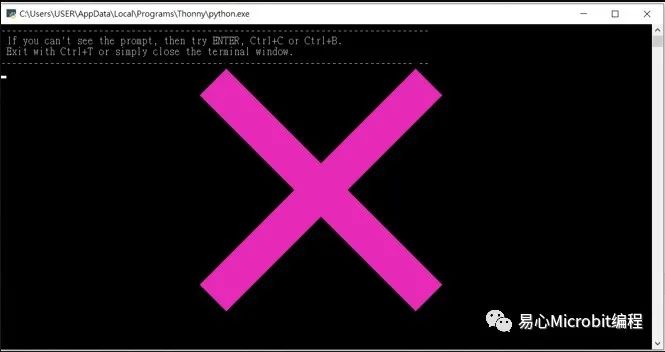
[注]请注意,并不是开启下方的窗口,若出现下方窗口,则要再按一次开启系统命令行。
5. 如何查看已汇入的函式库
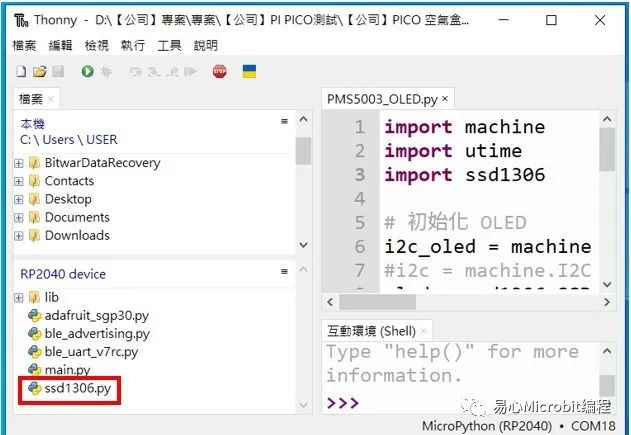
在 Thonny IDE 中,点选检视 -> 档案,可以查看Raspberry Pi Pico W中汇入的档案
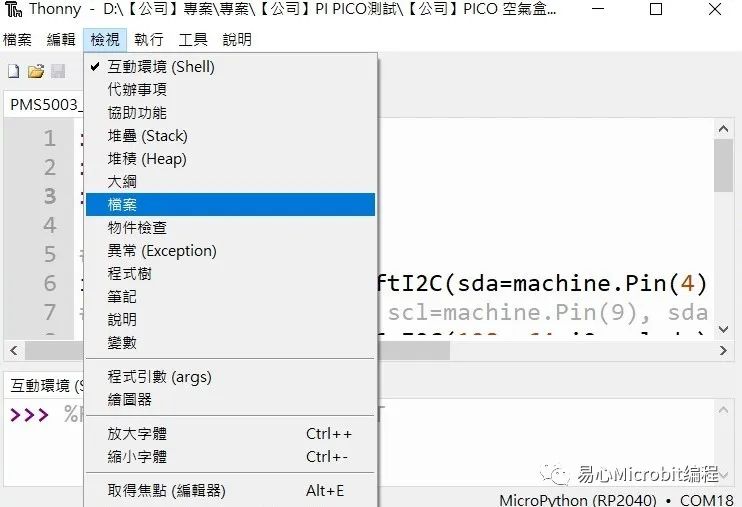
确认已汇入先前所操作的档案
执行程序
本专题有两个程序 (或下载原始码,或由以下复制也可以):
在 OLED 显示时间(
OLED_wifitime.py
)
在 OLED 显示 PMS5003 粉尘传感器数值(
PMS5003_OLED.py
)
OLED_wifitime.py
import machine
import utime
import ssd1306
from time import sleep
import network
import ntptime
import urequests
i2c = machine.SoftI2C(scl=machine.Pin(15),sda=machine.Pin(4))
oled_width = 128
oled_height = 64
oled = ssd1306.SSD1306_I2C(oled_width,oled_height, i2c)
# 初始化 UART
uart = machine.UART(0, baudrate=9600,tx=machine.Pin(0), rx=machine.Pin(1), timeout=1000)
uart.init(9600, bits=8, parity=None,stop=1)
# 初始化WiFi
sta_if = network.WLAN(network.STA_IF)
sta_if.active(True)
wifi_ssid = "XXXXX"
wifi_password = "XXXXXXX"
sta_if.connect(wifi_ssid, wifi_password)
# 显示WiFi连接状态
oled.fill(0)
oled.text('WiFi:', 0, 0)
if sta_if.isconnected():
oled.text('connected', 40, 0)
else:
oled.text('connceting', 40, 0)
oled.show()
#设定时区
TIME_ZONE = 8
# 取得NTP时间
#ntptime.settime()
for i in range(5):
try:
ntptime.settime()
break
except OSError:
print('Error connecting to NTP server, retrying...')
utime.sleep(5)
else:
print('Could not connect to NTP server after 5 retries.')
# 等待一段时间
utime.sleep(3)
while True:
t= utime.localtime(utime.time() + TIME_ZONE * 3600)
oled.fill(0)
oled.text(str("%d/%02d/%02d" % (t[0], t[1], t[2])), 0, 0)
oled.text(str("%02d:%02d:%02d" % (t[3], t[4], t[5])), 0, 16)
oled.show()
utime.sleep(1)
PMS5003_OLED.py
import machine
import utime
import ssd1306
from time import sleep
i2c = machine.SoftI2C(scl=machine.Pin(15),sda=machine.Pin(4))
oled_width = 128
oled_height = 64
oled = ssd1306.SSD1306_I2C(oled_width,oled_height, i2c)
# 初始化 UART
uart = machine.UART(0, baudrate=9600,tx=machine.Pin(0), rx=machine.Pin(1), timeout=1000)
uart.init(9600, bits=8, parity=None,stop=1)
while True:
#读取 PMS5003 数据
data = bytearray(uart.read(32))
# 判断是否为正确的PMS5003 资料
if data is not None and len(data) >= 10 and data[0] == 0x42 anddata[1] == 0x4d:
pm1_cf = int.from_bytes(data[4:6], 'big')
pm25_cf = int.from_bytes(data[6:8], 'big')
pm10_cf = int.from_bytes(data[8:10], 'big')
#清除 OLED
oled.fill(0)
# 显示 PMS5003 数据
oled.text("PM1.0: %d ug/m3" % pm1_cf, 0, 22)
oled.text("PM2.5: %d ug/m3" % pm25_cf, 0, 38)
oled.text("PM10 : %d ug/m3" % pm10_cf, 0, 54)
# 更新 OLED
oled.show()
utime.sleep(1)
实际展示
执行程序之后,可在 OLED 显示模块上看到相关信息,恭喜成功啰!


审核编辑:汤梓红
- 相关推荐
- 热点推荐
- 微控制器
- 物联网
- 开发板
- Arduino
- Micropython
-
Raspberry Pi Pico 22024-11-25 2243
-
远程编程Raspberry Pi Pico2023-06-16 701
-
Arduino Raspberry Pi Pico/RP2040以太网:W5100S EVB Pico2023-06-14 912
-
基于树莓派Raspberry Pi Pico的自动浇花系统2022-12-27 1666
-
使用Raspberry Pi Pico的LED序列2022-11-14 763
-
Raspberry Pi Pico:使用PIO驱动伺服2022-11-04 1323
-
Raspberry Pi 4/3B的Pico开发板2022-07-26 1596
-
使用MicroPython在Raspberry Pi上通过双核编程的多线程控制LED2022-07-25 8893
-
适用于Raspberry Pi 4的Raspberry Pi Pico开发板2022-07-22 1754
-
使用raspberry pi Pico的原因2022-02-07 1655
-
raspberry pi Pico使用MicroPython变砖后的解决方法2021-12-04 1046
-
微控制器开发板Raspberry Pi Pico2021-10-29 1966
-
Raspberry Pi Pico是什么2021-07-14 1777
-
基于Raspberry Pi Pico开发先进的家庭自动化系统2021-04-27 3589
全部0条评论

快来发表一下你的评论吧 !

