

STM32 SPI读写W25Q64(三)
接口/总线/驱动
1159人已加入
描述
GPIO口模拟SPI读写W25Q64的基本内容已经跟大家介绍完了,今天跟大家介绍下如何通过串口接收文件并保存到W25Q64中。
由于文件是通过串口中断接收的,如果只定义一个缓冲区,有可能缓冲区的内容在写入W25Q64时就被串口中断接收到的内容覆盖,造成数据丢失,所以通过定义两个缓冲区,分时进行接收和保存数据。
串口中断及变量定义
u8 Usart1_buf[2][USART1_BUF_SIZE] = {0};
u8 Usart1_OK = 0;
u16 cnt = 0;
u8 recStart = 0;
u8 timeout = 0;
u8 pos = 0;
void USART1_IRQHandler()
{
recStart = 1;
timeout = 0;
if((USART1- >SR & (1< < 5)) != 0) //接收中断
{
Usart1_buf[pos][cnt] = USART1- >DR;
cnt++;
if(cnt == USART1_BUF_SIZE)
{
Usart1_OK = 1;
cnt = 0;
pos++;
pos%=2;
}
}
else
USART1- >SR = 0;
}
主函数通过判断接收中断存储串口中断缓冲区数据到W25Q64。并判断接收数据是否超时作为文件接收完成的标志。接收完成后将保存到W25Q64的内容全部读取并打印到串口。
#include "stm32f4xx.h"
#include "led.h"
#include "core_cm4.h"
#include "usart.h"
#include "delay.h"
#include "stdio.h"
#include "W25Q64.h"
int main()
{
u32 add = 0;
u16 i = 0;
NVIC_SetPriorityGrouping(5); //4层嵌套,4个响应优先级
Usart1_Init(115200);
W25Q64_Init();
printf("擦除扇区0、1......rn");
W25Q64_SectorErase(0);
W25Q64_SectorErase(4096);
printf("擦除完成,请发文件!rn");
while(1)
{
if(Usart1_OK == 1)
{
Usart1_OK = 0;
if(pos == 0) //写缓冲区1
W25Q64_PageProgram(add,Usart1_buf[1],256);
else if(pos == 1) //写缓冲区0
W25Q64_PageProgram(add,Usart1_buf[0],256);
add += 256;
}
// //判断是否超时
if(recStart == 1)
{
Systick_Delayms(5);
timeout++;
if(timeout >10)
{
recStart = 0;
timeout = 0;
//存储最后一次接收到数据
W25Q64_PageProgram(add,Usart1_buf[pos],cnt);
printf("文件接收完毕!rn");
add = 0;
for(i=0;i< 24;i++)
{
W25Q64_ReadBytes(add,Usart1_buf[0],USART1_BUF_SIZE-1);
Usart1_buf[0][USART1_BUF_SIZE-1] = '�';
printf("%s",(const char *)Usart1_buf[0]);
add += USART1_BUF_SIZE-1;
}
}
}
}
}
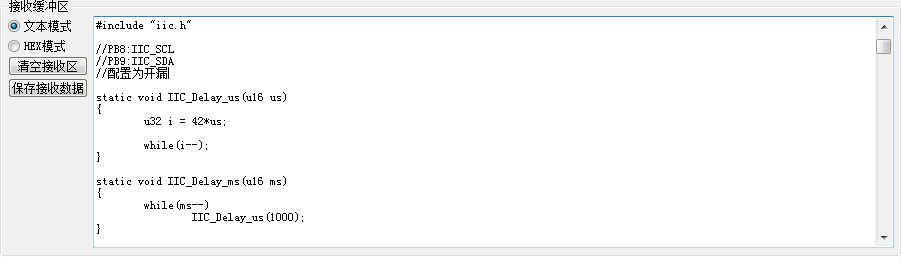
编译后将程序烧入开发板,打开串口助手发送一个iic.c文件,发送完成后,串口助手接收到的内容和iic.c文件内容完全一致,串口接收文件并保存到W25Q64成功。
声明:本文内容及配图由入驻作者撰写或者入驻合作网站授权转载。文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表电子发烧友网立场。文章及其配图仅供工程师学习之用,如有内容侵权或者其他违规问题,请联系本站处理。
举报投诉
-
Air780E开发板SPI接口:实现W25Q64读写不是事儿!2024-11-02 1483
-
STM32 SPI读写W25Q64(二)2023-07-22 10092
-
STM32驱动W25Q64读写数据资料2023-04-12 952
-
W25Q64中文数据手册2022-06-28 3906
-
请问STM32 SPI 读写 W25Q64接上逻辑分析仪后读取失败是为什么?2022-02-17 2147
-
介绍W25Q64和驱动函数2022-01-26 1733
-
问题贴 STM32 SPI 读写 W25Q64 接上逻辑分析仪后读取失败2021-12-22 1133
-
W25Q64是什么?怎样去使用W25Q64呢2021-12-20 4128
-
STM32L4+HAL+QSPI+DMA读写W25Q64/1282021-12-04 1834
-
STM32入门开发: 介绍SPI总线、读写W25Q64(FLASH)(硬件+模拟时序)2021-12-02 1467
-
【STM32Cube-18】使用硬件QSPI读写SPI Flash(W25Q64)2021-12-01 2445
-
w25Q64的中文手册2017-10-19 4193
-
w25Q64中文手册2017-10-16 9179
全部0条评论

快来发表一下你的评论吧 !

