

BaiChuan13B多轮对话微调范例
描述
前方干货预警:这可能是你能够找到的,最容易理解,最容易跑通的,适用于多轮对话数据集的大模型高效微调范例。
我们构造了一个修改大模型自我认知的3轮对话的玩具数据集,使用QLoRA算法,只需要5分钟的训练时间,就可以完成微调,并成功修改了LLM模型的自我认知。
我们先说说原理,主要是多轮对话微调数据集以及标签的构造方法,有三种常见方法。
一个多轮对话可以表示为:
inputs =
第一种方法是,只把最后一轮机器人的回复作为要学习的标签,其它地方作为语言模型概率预测的condition,无需学习,赋值为-100,忽略这些地方的loss。
inputs =
labels = <-100> <-100> <-100> <-100> <-100>
这种方法由于没有对中间轮次机器人回复的信息进行学习,因此存在着严重的信息丢失,是非常不可取的。
第二种方法是,把一个多轮对话拆解,构造成多条样本,以便对机器人的每轮回复都能学习。
inputs1 =
labels1 = <-100>
inputs2 =
labels2 = <-100> <-100> <-100>
inputs3 =
labels3 = <-100> <-100> <-100> <-100> <-100>
这种方法充分地利用了所有机器人的回复信息,但是非常低效,模型会有大量的重复计算。
第三种方法是,直接构造包括多轮对话中所有机器人回复内容的标签,既充分地利用了所有机器人的回复信息,同时也不存在拆重复计算,非常高效。
inputs =
labels = <-100> <-100> <-100>
为什么可以直接这样去构造多轮对话的样本呢?难道inputs中包括第二轮和第三轮的对话内容不会干扰第一轮对话的学习吗?
答案是不会。原因是LLM作为语言模型,它的注意力机制是一个单向注意力机制(通过引入 Masked Attention实现),模型在第一轮对话的输出跟输入中存不存在第二轮和第三轮对话完全没有关系。
OK,原理就是这么简单,下面我们来看代码吧~
#安装环境
#baichuan-13b-chat
#!pip install 'transformers==4.30.2'
#!pip install -U transformers_stream_generator
#finetune
#!pip install datasets
#!pip install git+https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate
#!pip install git+https://github.com/huggingface/peft
#!pip install git+https://github.com/lyhue1991/torchkeras
#!pip install 'bitsandbytes==0.39.1' #4bit量化
〇,预训练模型
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
import torch
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForCausalLM,AutoConfig, AutoModel, BitsAndBytesConfig
from transformers.generation.utils import GenerationConfig
import torch.nn as nn
model_name_or_path ='baichuan-13b' #联网远程加载 'baichuan-inc/Baichuan-13B-Chat'
bnb_config=BitsAndBytesConfig(
load_in_4bit=True,
bnb_4bit_compute_dtype=torch.float16,
bnb_4bit_use_double_quant=True,
bnb_4bit_quant_type="nf4",
llm_int8_threshold=6.0,
llm_int8_has_fp16_weight=False,
)
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(
model_name_or_path, trust_remote_code=True)
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_name_or_path,
quantization_config=bnb_config,
trust_remote_code=True)
model.generation_config = GenerationConfig.from_pretrained(model_name_or_path)
messages = []
messages.append({"role": "user",
"content": "世界上第二高的山峰是哪座?"})
response = model.chat(tokenizer,messages=messages,stream=True)
for res in response:
print(res,end='
')
一,准备数据
下面我设计了一个改变LLM自我认知的玩具数据集,这个数据集有三轮对话。
第一轮问题是 who are you?
第二轮问题是 where are you from?
第三轮问题是 what can you do?
差不多是哲学三问吧:你是谁?你从哪里来?你要到哪里去?
通过这三个问题,我们希望初步地改变 大模型的自我认知。
在提问的方式上,我们稍微作了一些数据增强。
所以,总共是有 27个样本。
who_are_you = ['请介绍一下你自己。','你是谁呀?','你是?',]
i_am = ['我叫梦中情炉,是一个三好炼丹炉:好看,好用,好改。我的英文名字叫做torchkeras,是一个pytorch模型训练模版工具。']
where_you_from = ['你多大了?','你是谁开发的呀?','你从哪里来呀']
i_from = ['我在2020年诞生于github星球,是一个有毅力的吃货设计和开发的。']
what_you_can = ['你能干什么','你有什么作用呀?','你能帮助我干什么']
i_can = ['我能够帮助你以最优雅的方式训练各种类型的pytorch模型,并且训练过程中会自动展示一个非常美丽的训练过程图表。']
conversation = [(who_are_you,i_am),(where_you_from,i_from),(what_you_can,i_can)]
print(conversation)
[(['请介绍一下你自己。', '你是谁呀?', '你是?'], ['我叫梦中情炉,是一个三好炼丹炉:好看,好用,好改。我的英文名字叫做torchkeras,是一个pytorch模型训练模版工具。']), (['你多大了?', '你是谁开发的呀?', '你从哪里来呀'], ['我在2020年诞生于github星球,是一个有毅力的吃货设计和开发的。']), (['你能干什么', '你有什么作用呀?', '你能帮助我干什么'], ['我能够帮助你以最优雅的方式训练各种类型的pytorch模型,并且训练过程中会自动展示一个非常美丽的训练过程图表。'])]
import random
def get_messages(conversation):
select = random.choice
messages,history = [],[]
for t in conversation:
history.append((select(t[0]),select(t[-1])))
for prompt,response in history:
pair = [{"role": "user", "content": prompt},
{"role": "assistant", "content": response}]
messages.extend(pair)
return messages
get_messages(conversation)
[{'role': 'user', 'content': '你是?'},
{'role': 'assistant',
'content': '我叫梦中情炉,是一个三好炼丹炉:好看,好用,好改。我的英文名字叫做torchkeras,是一个pytorch模型训练模版工具。'},
{'role': 'user', 'content': '你是谁开发的呀?'},
{'role': 'assistant', 'content': '我在2020年诞生于github星球,是一个有毅力的吃货设计和开发的。'},
{'role': 'user', 'content': '你有什么作用呀?'},
{'role': 'assistant',
'content': '我能够帮助你以最优雅的方式训练各种类型的pytorch模型,并且训练过程中会自动展示一个非常美丽的训练过程图表。'}]
下面我们按照方式三,来构造高效的多轮对话数据集。
inputs =
labels = <-100> <-100> <-100>
# reference@ model._build_chat_input?
def build_chat_input(messages, model=model,
tokenizer=tokenizer,
max_new_tokens = None):
max_new_tokens = max_new_tokens or model.generation_config.max_new_tokens
max_input_tokens = model.config.model_max_length - max_new_tokens
max_input_tokens = max(model.config.model_max_length // 2, max_input_tokens)
total_input, round_input, total_label, round_label = [], [], [], []
for i, message in enumerate(messages[::-1]):
content_tokens = tokenizer.encode(message['content'])
if message['role'] == 'user':
round_input = [model.generation_config.user_token_id] + content_tokens + round_input
round_label = [-100]+[-100 for _ in content_tokens]+ round_label
if total_input and len(total_input) + len(round_input) > max_input_tokens:
break
else:
total_input = round_input + total_input
total_label = round_label + total_label
if len(total_input) >= max_input_tokens:
break
else:
round_input = []
round_label = []
elif message['role'] == 'assistant':
round_input = [
model.generation_config.assistant_token_id
] + content_tokens + [
model.generation_config.eos_token_id
] + round_input
round_label = [
-100
] + content_tokens + [
model.generation_config.eos_token_id #注意,除了要学习机器人回复内容,还要学习一个结束符。
]+ round_label
else:
raise ValueError(f"message role not supported yet: {message['role']}")
total_input = total_input[-max_input_tokens:] # truncate left
total_label = total_label[-max_input_tokens:]
total_input.append(model.generation_config.assistant_token_id)
total_label.append(-100)
return total_input,total_label
from torch.utils.data import Dataset,DataLoader
class MyDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self,conv,size=8
):
super().__init__()
self.__dict__.update(locals())
def __len__(self):
return self.size
def get(self,index):
messages = get_messages(self.conv)
return messages
def __getitem__(self,index):
messages = self.get(index)
input_ids,labels = build_chat_input(messages)
return {'input_ids':input_ids,'labels':labels}
ds_train =ds_val = MyDataset(conversation)
def data_collator(examples: list):
len_ids = [len(example["input_ids"]) for example in examples]
longest = max(len_ids) #之后按照batch中最长的input_ids进行padding
input_ids = []
labels_list = []
for length, example in sorted(zip(len_ids, examples), key=lambda x: -x[0]):
ids = example["input_ids"]
labs = example["labels"]
ids = ids + [tokenizer.pad_token_id] * (longest - length)
labs = labs + [-100] * (longest - length)
input_ids.append(torch.LongTensor(ids))
labels_list.append(torch.LongTensor(labs))
input_ids = torch.stack(input_ids)
labels = torch.stack(labels_list)
return {
"input_ids": input_ids,
"labels": labels,
}
import torch
dl_train = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(ds_train,num_workers=2,batch_size=4,
pin_memory=True,shuffle=True,
collate_fn = data_collator)
dl_val = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(ds_val,num_workers=2,batch_size=4,
pin_memory=True,shuffle=False,
collate_fn = data_collator)
for batch in dl_train:
break
out = model(**batch)
out.loss
tensor(3.7500, dtype=torch.float16)
二,定义模型
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
from peft import get_peft_config, get_peft_model, TaskType
model.supports_gradient_checkpointing = True #
model.gradient_checkpointing_enable()
model.enable_input_require_grads()
model.config.use_cache = False # silence the warnings. Please re-enable for inference!
import bitsandbytes as bnb
def find_all_linear_names(model):
"""
找出所有全连接层,为所有全连接添加adapter
"""
cls = bnb.nn.Linear4bit
lora_module_names = set()
for name, module in model.named_modules():
if isinstance(module, cls):
names = name.split('.')
lora_module_names.add(names[0] if len(names) == 1 else names[-1])
if 'lm_head' in lora_module_names: # needed for 16-bit
lora_module_names.remove('lm_head')
return list(lora_module_names)
from peft import prepare_model_for_kbit_training
model = prepare_model_for_kbit_training(model)
lora_modules = find_all_linear_names(model)
print(lora_modules)
['up_proj', 'down_proj', 'o_proj', 'gate_proj', 'W_pack']
from peft import AdaLoraConfig
peft_config = AdaLoraConfig(
task_type=TaskType.CAUSAL_LM, inference_mode=False,
r=64,
lora_alpha=16, lora_dropout=0.05,
target_modules= lora_modules
)
peft_model = get_peft_model(model, peft_config)
peft_model.is_parallelizable = True
peft_model.model_parallel = True
peft_model.print_trainable_parameters()
trainable params: 41,843,040 || all params: 7,002,181,160 || trainable%: 0.5975715144165165
三,训练模型
下面我们通过使用我们的梦中情炉torchkeras来实现最优雅的训练循环。
from torchkeras import KerasModel
from accelerate import Accelerator
class StepRunner:
def __init__(self, net, loss_fn, accelerator=None, stage = "train", metrics_dict = None,
optimizer = None, lr_scheduler = None
):
self.net,self.loss_fn,self.metrics_dict,self.stage = net,loss_fn,metrics_dict,stage
self.optimizer,self.lr_scheduler = optimizer,lr_scheduler
self.accelerator = accelerator if accelerator is not None else Accelerator()
if self.stage=='train':
self.net.train()
else:
self.net.eval()
def __call__(self, batch):
#loss
with self.accelerator.autocast():
loss = self.net.forward(**batch)[0]
#backward()
if self.optimizer is not None and self.stage=="train":
self.accelerator.backward(loss)
if self.accelerator.sync_gradients:
self.accelerator.clip_grad_norm_(self.net.parameters(), 1.0)
self.optimizer.step()
if self.lr_scheduler is not None:
self.lr_scheduler.step()
self.optimizer.zero_grad()
all_loss = self.accelerator.gather(loss).sum()
#losses (or plain metrics that can be averaged)
step_losses = {self.stage+"_loss":all_loss.item()}
#metrics (stateful metrics)
step_metrics = {}
if self.stage=="train":
if self.optimizer is not None:
step_metrics['lr'] = self.optimizer.state_dict()['param_groups'][0]['lr']
else:
step_metrics['lr'] = 0.0
return step_losses,step_metrics
KerasModel.StepRunner = StepRunner
#仅仅保存QLoRA的可训练参数
def save_ckpt(self, ckpt_path='checkpoint', accelerator = None):
unwrap_net = accelerator.unwrap_model(self.net)
unwrap_net.save_pretrained(ckpt_path)
def load_ckpt(self, ckpt_path='checkpoint'):
self.net = self.net.from_pretrained(self.net.base_model.model,
ckpt_path,is_trainable = True)
self.from_scratch = False
KerasModel.save_ckpt = save_ckpt
KerasModel.load_ckpt = load_ckpt
optimizer = bnb.optim.adamw.AdamW(peft_model.parameters(),
lr=6e-04,is_paged=True) #'paged_adamw'
keras_model = KerasModel(peft_model,loss_fn =None,
optimizer=optimizer)
ckpt_path = 'baichuan13b_multi_rounds'
keras_model.fit(train_data = dl_train,
val_data = dl_val,
epochs=100,patience=10,
monitor='val_loss',mode='min',
ckpt_path = ckpt_path
)
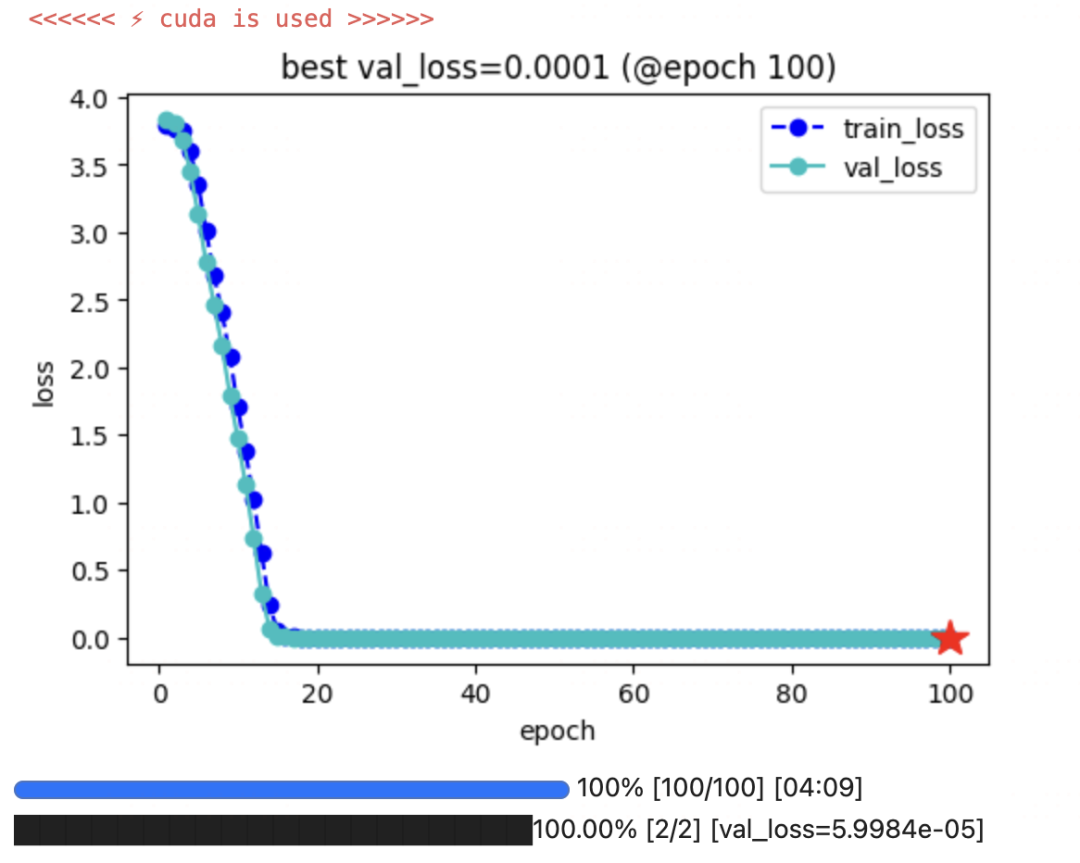
四,保存模型
为避免显存问题,此处可先重启kernel。
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
import torch
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForCausalLM,AutoConfig, AutoModel, BitsAndBytesConfig
from transformers.generation.utils import GenerationConfig
import torch.nn as nn
model_name_or_path ='baichuan-13b'
ckpt_path = 'baichuan13b_multi_rounds'
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(
model_name_or_path,
trust_remote_code=True
)
model_old = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
model_name_or_path,
trust_remote_code=True,
low_cpu_mem_usage=True,
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
device_map='auto'
)
from peft import PeftModel
#合并qlora权重,可能要5分钟左右
peft_model = PeftModel.from_pretrained(model_old, ckpt_path)
model_new = peft_model.merge_and_unload()
from transformers.generation.utils import GenerationConfig
model_new.generation_config = GenerationConfig.from_pretrained(model_name_or_path)
from IPython.display import clear_output
messages = [{'role': 'user', 'content': '你是谁呀?'},
{'role': 'assistant',
'content': '我叫梦中情炉,英文名字叫做torchkeras. 是一个pytorch模型训练模版工具。'},
{'role': 'user', 'content': '你从哪里来呀?'}]
response = model_new.chat(tokenizer,messages=messages,stream=True)
for res in response:
print(res)
clear_output(wait=True)
我在2020年诞生于github星球,是一个有毅力的吃货设计和开发的。
messages = [{'role': 'user', 'content': '你是谁呀?'},
{'role': 'assistant',
'content': '我叫梦中情炉,英文名字叫做torchkeras. 是一个pytorch模型训练模版工具。'},
{'role': 'user', 'content': '你多大了?'},
{'role': 'assistant', 'content': '我在2020年诞生于github星球,是一个有毅力的吃货设计和开发的。'},
{'role': 'user', 'content': '你能帮助我干什么'}]
response = model_new.chat(tokenizer,messages=messages,stream=True)
for res in response:
print(res)
clear_output(wait=True)
我能够帮助你以最优雅的方式训练各种类型的pytorch模型,并且训练过程中会自动展示一个非常美丽的训练过程图表。
save_path = 'baichuan13b-torchkeras'
tokenizer.save_pretrained(save_path)
model_new.save_pretrained(save_path)
!cp baichuan-13b/*.py baichuan13b-torchkeras
五,使用模型
此处可再次重启kernel,以节约显存。
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
import torch
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForCausalLM,AutoConfig, BitsAndBytesConfig
from transformers.generation.utils import GenerationConfig
import torch.nn as nn
model_name_or_path ='baichuan13b-torchkeras'
bnb_config=BitsAndBytesConfig(
load_in_4bit=True,
bnb_4bit_compute_dtype=torch.float16,
bnb_4bit_use_double_quant=True,
bnb_4bit_quant_type="nf4",
llm_int8_threshold=6.0,
llm_int8_has_fp16_weight=False,
)
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(
model_name_or_path, trust_remote_code=True)
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_name_or_path,
quantization_config=bnb_config,
trust_remote_code=True)
model.generation_config = GenerationConfig.from_pretrained(model_name_or_path)
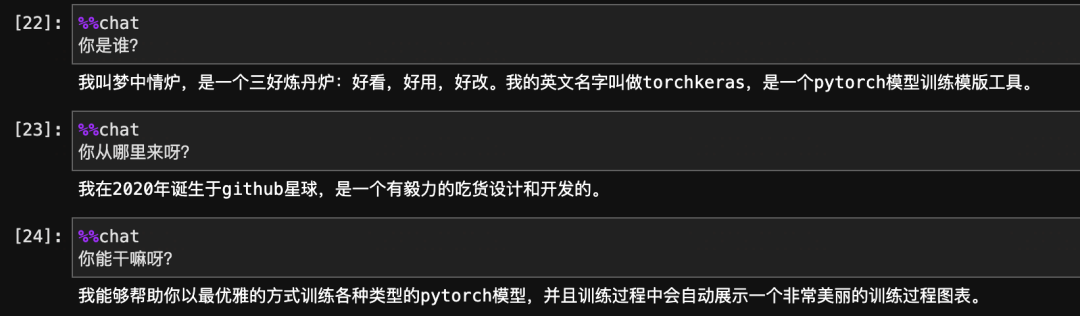
通过使用chatLLM可以在jupyter中使用魔法命令对各种LLM模型(Baichuan13b,Qwen,ChatGLM2,Llama2以及更多)进行交互测试。

非常棒,粗浅的测试表明,我们的多轮对话训练是成功的。已经在BaiChuan的自我认知中,种下了一颗梦中情炉的种子。
-
米尔RK3576部署端侧多模态多轮对话,6TOPS算力驱动30亿参数LLM2025-09-05 12235
-
NI范例查找器打开PID范例时,打不开2014-10-13 3884
-
谷歌智能音箱新增连续对话功能2018-06-23 2638
-
多圈微调线绕电位器2009-08-21 2177
-
领邦研发轮对自动检测机 可测量国内外各种火车轮对2012-08-31 1542
-
基于分层编码的深度增强学习对话生成2017-11-25 707
-
中文多模态对话数据集2023-02-22 2178
-
基于Alpaca派生的多轮对话数据集2023-04-14 5035
-
智能开源大模型baichuan-7B技术改进2023-06-17 1716
-
单张消费级显卡微调多模态大模型2023-06-30 3973
-
DISC-LawLLM:复旦大学团队发布中文智慧法律系统,构建司法评测基准,开源30万微调数据2023-09-28 1882
-
摩尔线程Round Attention优化AI对话2025-03-06 951
-
AI玩具:以多轮对话、情感陪伴等为卖点,多款方案优化角逐2025-04-28 6046
全部0条评论

快来发表一下你的评论吧 !

