

嵌入式Linux设备如何添加开机启动文件
嵌入式技术
描述
1. 前言
嵌入式 Linux 设备通常会使用 sysvinit 或 systemd 两种方式中的一种作为开机启动的方式。xilinx petalinux 2021.2 默认使用 sysvinit。
在说明如何添加开机启动文件之前,先说一下 sysvinit 设备中,开机程序被启动的过程。
整体过程:
/sbin/init + /etc/inittab
-- > /etc/init.d/rcS
-- > /etc/init.d/rc S
-- > /etc/init.d/rc 5
下面,咱们一个一个地说(着急的可以直接拉到最后看答案)。
2. /sbin/init
系统启动时,文件系统挂载完毕后会首先执行 /sbin/init 程序,它就是 系统中进程号为 1 的进程对应的程序 ,是系统中所有进程的祖先。
系统启动 log:
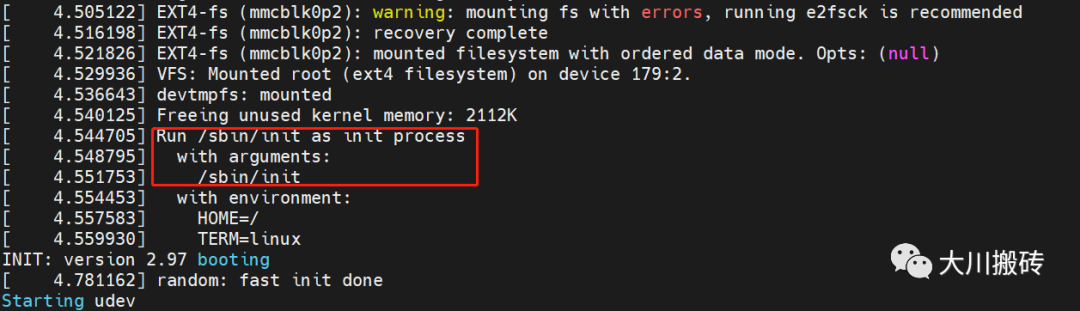
init 进程信息:
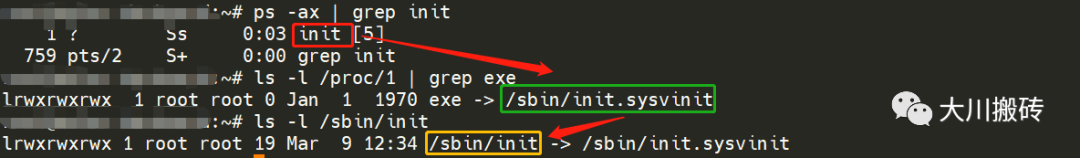
3. /etc/inittab
/etc/inittab 是一个配置文件,程序 /sbin/init 根据该文件的内容对系统进行操作,比如设置系统的运行级别(runlevel),运行各级别下所需启动的程序等等。
这篇文章不对 inittab 文件内容进行分析。当前,我们只需知道:
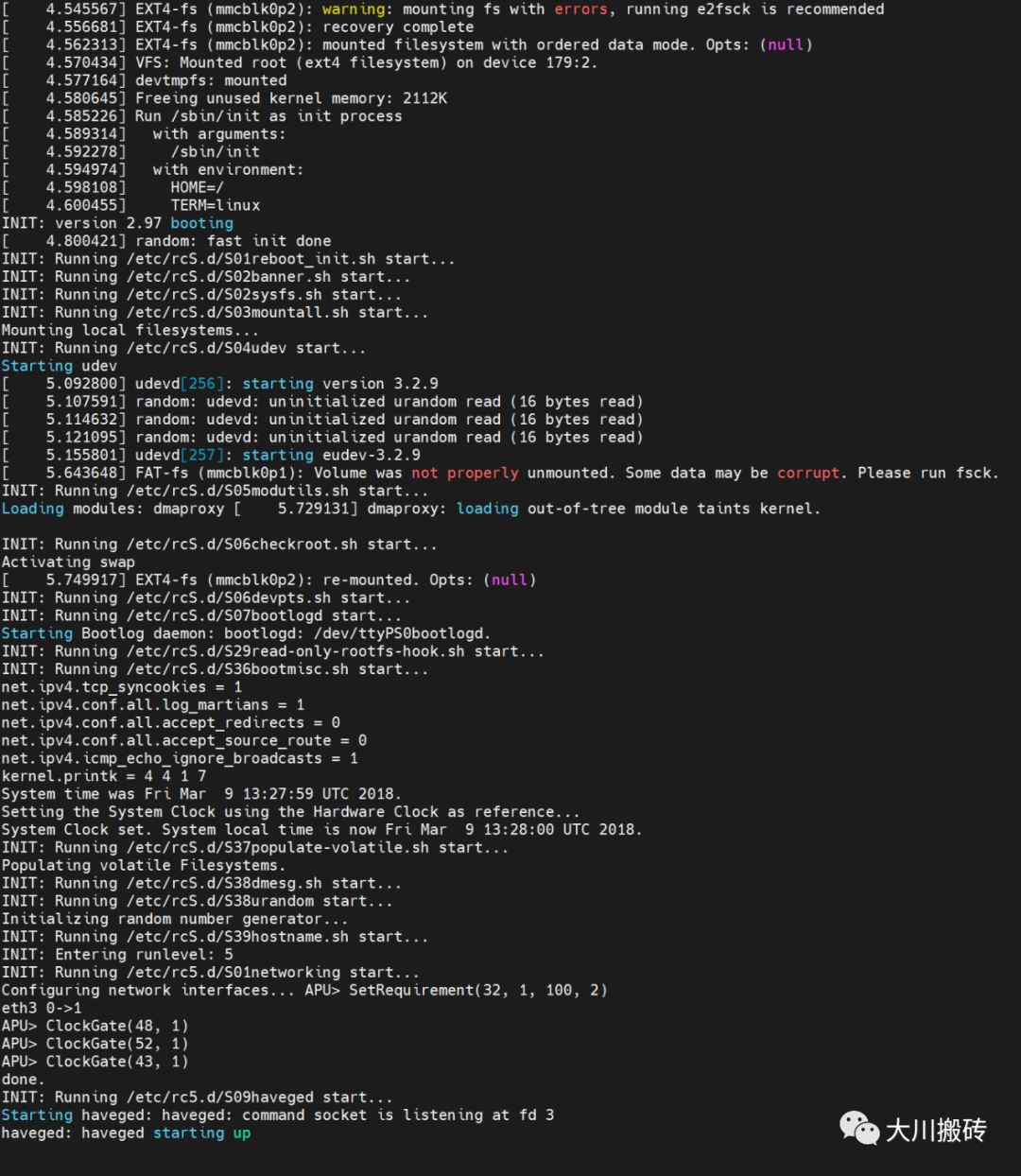
/sbin/init 会首先执行 /etc/init.d/rcS ,然后执行 /etc/init.d/rc 5 。
4. /etc/init.d/rcS
这个脚本主要用于挂载文件系统,比如 sysfs 。该脚本中,首先执行 /etc/default/rcS ,设置一些环境变量,然后执行 exec /etc/init.d/rc S——执行 /etc/rcS.d/ 目录下的文件。
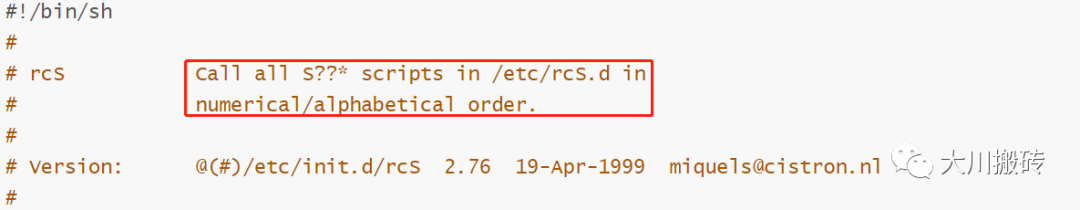
rcS 文件内容:
#!/bin/sh
#
# rcS Call all S??* scripts in /etc/rcS.d in
# numerical/alphabetical order.
#
# Version: @(#)/etc/init.d/rcS 2.76 19-Apr-1999 miquels@cistron.nl
#
PATH=/sbin:/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin
runlevel=S
prevlevel=N
umask 022
export PATH runlevel prevlevel
# Make sure proc is mounted
#
[ -d "/proc/1" ] || mount /proc
#
# Source defaults.
#
. /etc/default/rcS
#
# Trap CTRL-C &c only in this shell so we can interrupt subprocesses.
#
trap ":" INT QUIT TSTP
#
# Call all parts in order.
#
exec /etc/init.d/rc S
4.1 /etc/default/rcS
这个文件会设置一些环境变量,后面执行的脚本会用到。比如,我们可以将该文件中 VERBOSE 的值改为 very 。这样,在系统启动时我们就可以看到 /etc/init.d/rc 执行的详细过程了。
文件内容:
#
# Defaults for the boot scripts in /etc/rcS.d
#
# Time files in /tmp are kept in days.
TMPTIME=0
# Set to yes if you want sulogin to be spawned on bootup
SULOGIN=no
# Set to no if you want to be able to login over telnet/rlogin
# before system startup is complete (as soon as inetd is started)
DELAYLOGIN=no
# Assume that the BIOS clock is set to UTC time (recommended)
UTC=yes
# Set VERBOSE to "no" if you would like a more quiet bootup.
VERBOSE=no
# Set EDITMOTD to "no" if you don't want /etc/motd to be edited automatically
EDITMOTD=no
# Whether to fsck root on boot
ENABLE_ROOTFS_FSCK=no
# Set FSCKFIX to "yes" if you want to add "-y" to the fsck at startup.
FSCKFIX=yes
# Set TICKADJ to the correct tick value for this specific machine
#TICKADJ=10000
# Enable caching in populate-volatile.sh
VOLATILE_ENABLE_CACHE=yes
# Indicate whether the rootfs is intended to be read-only or not.
# Setting ROOTFS_READ_ONLY to yes and rebooting will give you a read-only rootfs.
# Normally you should not change this value.
ROOTFS_READ_ONLY=no
VERBOSE=very :
4.2 exec /etc/init.d/rc S
/etc/init.d/rc ,这个是最主要的文件,各个运行级别下的开机启动程序的执行就发生在这个文件中。
比如,当前执行的是 /etc/init.d/rc S,那么就会执行 /etc/rcS.d/ 目录下的程序。
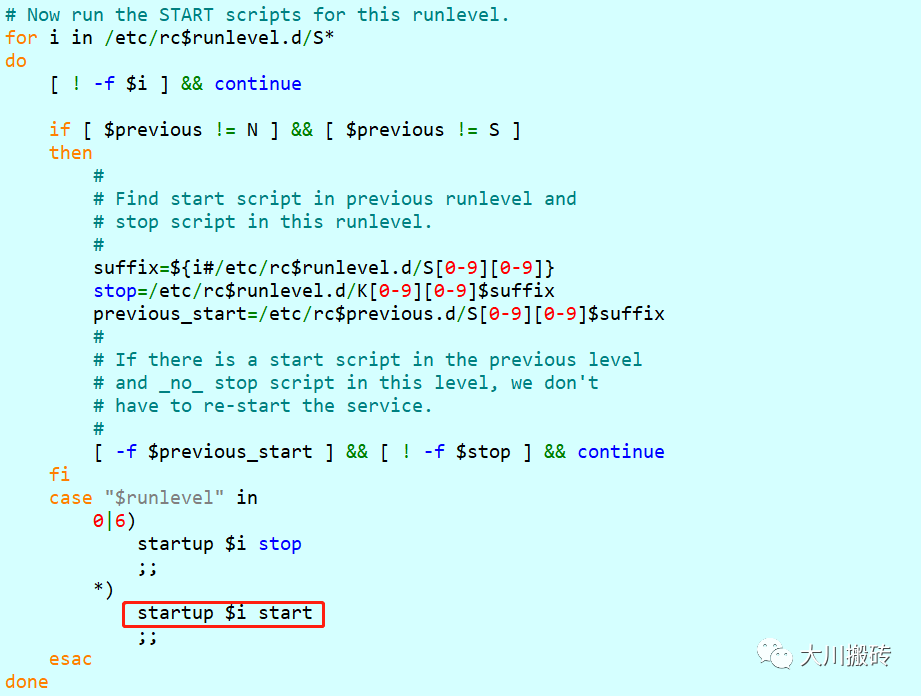
5. exec /etc/init.d/rc 5
和 exec /etc/init.d/rc S 类似,exec /etc/init.d/rc 5 会执行 /etc/rc5.d/ 目录下的程序。通常情况下, 这个目录下的文件在系统启动的最后阶段执行 。所以, 我们的启动文件也应当放在这个目录下 。
6. 启动文件添加规则
6.1 软链接
如果使用 ls -al 命令查看 /etc/rcX.d/ 目录下的文件,你就会发现,这些目录下的文件都是软链接,链接到 /etc/init.d/ 目录下的对应文件。
所以,我们也 应当将我们的文件放在 /etc/init.d/ 目录下,然后在 /etc/rcX.d/ 目录下创建软链接 。
6.2 数字和名称
/etc/rcX.d/ 目录下的文件名可以分为 3 部分——S[序号][文件名称]。
S :start,表示需要开机运行的程序,与之对应的是 K ——kill,表示开机需要停止的程序;
序号 :一个两位的数字,范围为 01~99,表示启动的顺序, 数值小的优先启动 ;
文件名称 :英文名称(我没见过中文的),也表示启动顺序,按照 a~z 的顺序启动。如果两个文件有相同的序号,那么就按照文件名称中字母的顺序进行启动;
比如,在 /etc/rc5.d/ 目录下有两个文件,分别为 S99atest 和 S99btest。那么,系统启动时会 优先执行 S10atest 。
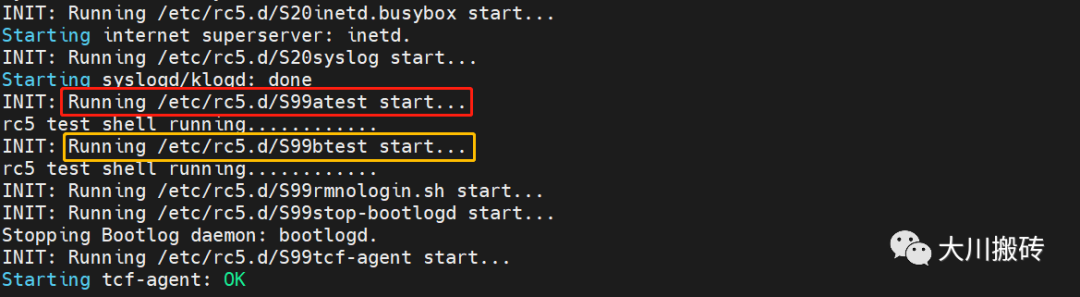
其实,在 /etc/init.d/rcS 文件开头的注释部分已经表明了文件的启动顺序:
7. 总结
啰里吧嗦一大堆,添加开机启动文件时只需按照以下步骤即可:
- 将需要开机启动程序的启动命令写在一个脚本中,比如 test-auto-run.sh ;(虽然可以直接使用可执行程序,但还是建议使用脚本的方式)
- 将 test-auto-run.sh 放在 /etc/init.d/ 目录下;
- 在 /etc/rc5.d/ 目录下创建 test-auto-run.sh 文件的软链接;
- 根据程序的启动时机对软链接进行命名 。比如,想要最后启动程序,那么就命名为 S99zxxxx 。
-
RK3399 Android如何添加开机启动shell脚本?2022-03-07 2018
-
嵌入式Linux设备如何在运作2021-11-05 722
-
嵌入式Linux专题(一)——嵌入式Linux系统构成及启动流程2021-11-02 914
-
嵌入式linux和物联网,嵌入式Linux或RTOS:用于物联网2021-11-01 1206
-
嵌入式Linux开发有哪些内容?2021-10-28 966
-
【嵌入式】构建嵌入式Linux系统(uboot、内核、文件系统)2021-10-20 1262
-
基于Bootsplash打造嵌入式Linux启动画面2019-07-03 3647
-
学习嵌入式linux系统开发,文件类型一定要分清2018-07-05 1254
-
详解嵌入式linux文件类型2018-06-11 1199
-
详解嵌入式linux 启动信息2017-10-30 852
-
嵌入式Linux快速启动技术综述张全胜2017-03-14 766
-
嵌入式Linux的USB驱动添加及应用2009-04-15 524
全部0条评论

快来发表一下你的评论吧 !

