

Linux如何获取进程的基地信息
嵌入式技术
描述
1. 问题
执行程序时,与程序同目录下存在一 config/ 目录,其中存放了 json 格式的配置文件。进行部署时需要将程序和 config/ 目录放在同一位置。那么,问题来了,如何保证不管这个程序部署到什么位置,不管以什么方式运行,程序自己都能访问到配置文件呢?
解决问题之前,先说一下进程的工作目录——Current Working Directory。
2. 什么是进程的工作目录
进程的工作目录是指进程的调用者在启动进程对应的程序时, 调用者所在的目录 。比如说,在 /home/sdc/ 目录下有一个可执行程序 hello-world。如果在根目录下启动 hello-world,那么 hello-world 进程的工作目录为根目录 / 。如果在 /home/sdc 目录下启动 hello-world,那么其工作目录为 /home/sdc。
Linux C 中,有两个函数可以获取进程工作目录:getcwd() 和 readlink()。
2.1 getcwd()
man 3 getcwd():https://man7.org/linux/man-pages/man2/getcwd.2.html
#include < unistd.h >
char *getcwd(char *buf, size_t size);
该函数将获取到的进程工作目录的绝对路径存储在形参 buf 中。同时也会返回一个指针,指针指向的内容和 buf 存储的内容相同。如果路径的长度比 size 大,那么该函数返回为 NULL。
2.2 readlink()
man 2 readlink:https://www.man7.org/linux/man-pages/man2/readlink.2.html
#include < unistd.h >
ssize_t readlink(const char *pathname, char *buf, size_t bufsiz);
该函数用于获取符号链接所指的文件。借助 /proc/self/cwd,即 pathname = "/proc/self/cwd",readlink() 即可获得当前进程的工作目录。
该函数同样将进程工作目录的绝对路径存储在形参 buf 中,并返回存储的路径长度。但是,buf 中存储路径不带字符串结束符 '�'。而且,如果返回的长度和 bufsiz 相同,那么路径信息很可能被截取了。
2.3 简单例程
hello-world.c:
#include < stdio.h >
#include < stdlib.h >
#include < string.h >
#include < unistd.h >
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
char work_dir[64] = {0};
int dir_size = 0;
getcwd(work_dir, sizeof(work_dir)))
printf("getcwd:%sn", work_dir);
memset(work_dir, 0, sizeof(work_dir));
dir_size = readlink("/proc/self/cwd", work_dir, sizeof(work_dir));
work_dir[dir_size] = '�';
printf("readlink:%sn", work_dir);
return 0;
}
执行结果:

3. 获取进程对应程序的绝对路径
如果想要解决文章开头提出的问题,那么进程需要获取程序所在的绝对路径。该功能通过 readlink(const char *pathname, char *buf, size_t bufsiz)实现。不过 pathname 不再是 /proc/self/cwd,而是 /proc/self/exe 。
开箱即用代码 :
#include < stdio.h >
#include < stdlib.h >
#include < string.h >
#include < unistd.h >
#include < stdint.h >
#include < fcntl.h >
#define CONFIG_FILENAME "./config/psl.json"
//get current process elf absolute path
static int32_t curr_elf_abs_path_get(int8_t *path_buf, int32_t buf_size)
{
ssize_t len = 0;
int32_t i = 0;
len = readlink("/proc/self/exe", path_buf, buf_size);
if(-1 == len)
{
perror("readlinkn");
return -1;
}
if(len == buf_size)
{
printf("Warn:path may be truncatedn");
}
//from last to head, find first '/'
for(i = len; i > 0; i--)
{
if(path_buf[i] == '/')
{
path_buf[i + 1] = '�';
break;
}
}
return 0;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int8_t elf_path[128] = {0};
int8_t config_file_path[256] = {0};
int fd = -1;
int32_t i = 0;
int32_t ret = 0;
ret = curr_elf_abs_path_get(elf_path, sizeof(elf_path));
if(0 != ret)
{
printf("get exe path failedn");
return -1;
}
printf("current process exe absolute path:%sn", elf_path);
sprintf(config_file_path, "%s%s", elf_path, CONFIG_FILENAME);
fd = open(config_file_path, O_RDWR);
if(-1 == fd)
{
perror("open");
return -1;
}
printf("open %s successn", config_file_path);
close(fd);
return 0;
}
CMakeLists.txt:
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.12)
project(exe-abs-path C)
set(CMAKE_VERBOSE_MAKEFILE ON)
add_executable(${PROJECT_NAME} main.c)
执行结果:
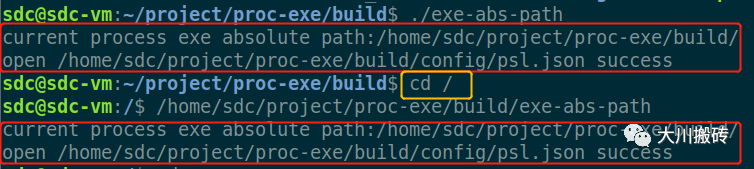
4. 总结
我当然可以借助 shell 脚本解决该问题。可是,我还是喜欢让程序自己”实现“该功能,这样我在部署和使用时会方便很多。
5. 说明
/proc/self/ 目录中存放了当前进程的很多有用信息。
/proc/self/fd/:进程打开的文件描述符;
/proc/self/cmdline:进程被执行时,命令行中输入的命令;
/proc/self/task:进程中包含的线程 id;
/proc/self/environ:进程运行时的环境变量信息。
-
Linux开发_Linux下进程编程2022-09-17 2010
-
Linux如何获取写文件的进程号2022-10-08 1118
-
Linux系统和进程信息笔记2023-03-06 605
-
Linux 查看进程和删除进程2016-04-24 3233
-
Linux下的进程结构2017-05-27 2990
-
Linux进程管理2009-04-28 381
-
LINUX 进程源代码分析2010-02-09 443
-
Linux守护进程详解2017-10-18 851
-
Linux和UNIX可以用什么命令查看运行中进程的相关信息2019-01-20 6932
-
Linux进程管理:什么是进程?进程的生命周期2019-02-15 8863
-
Linux进程的概念说明2020-07-14 1063
-
用来获取linux系统信息的shell脚本2021-08-25 5887
-
如何获取Linux所有进程信息2023-10-07 977
-
linux查看weblogic进程2023-12-05 3062
-
鸿蒙语言基础类库:ohos.process 获取进程相关的信息2024-07-08 1172
全部0条评论

快来发表一下你的评论吧 !

