

怎样使用毛刺滤波器来滤除毛刺和反弹?
描述
可编程逻辑系统通常部署在可能存在噪声的应用中。这种噪声会影响可编程逻辑设计接收的信号。例如,它可能会导致信号故障或跳动,如果处理不当,可能会导致设计和操作出现问题。
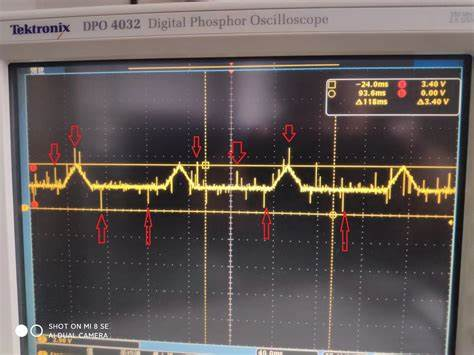
毛刺的持续时间是随机的,并且与时钟沿不同步。因此,它们可能会导致下游信息损坏。
处理此问题的最常见方法是使用毛刺滤波器来滤除毛刺和反弹。
毛刺滤波器核心是使用长度可变的移位寄存器,噪声信号被放到寄存器中,直到移位寄存器的所有值都一致。此时,信号可以视为稳定。当然,我们必须确定潜在毛刺和反弹可能持续多长时间,以确保时钟周期的寄存器大小正确。这就是为什么我们的毛刺滤波器需要非常灵活,并且需要确保其大小能够适合每个应用程序的要求。
滤波器应该能够接收噪声输入并滤除持续时间为多个时钟脉冲的毛刺。
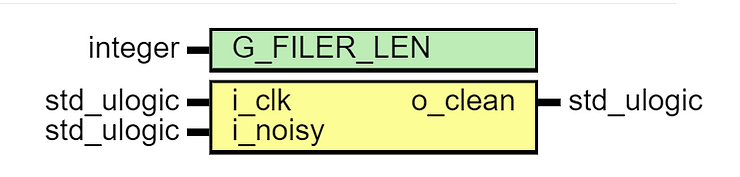
library ieee; use ieee.std_logic_1164.all; use ieee.numeric_std.all; entity glitch_filter is generic( G_FILER_LEN : integer := 8 ); port( i_clk : in std_ulogic; i_noisy : in std_ulogic; o_clean : out std_ulogic ); end glitch_filter; architecture behaviour of glitch_filter is signal s_delay_line : std_ulogic_vector(G_FILER_LEN - 1 downto 0); signal s_delay_and : std_ulogic; signal s_delay_nor : std_ulogic; signal s_output_clean : std_ulogic; begin o_clean <= s_output_clean; --Delay disctete using delay line synchroniser_process : process (i_clk) begin if rising_edge(i_clk) then s_delay_line <= s_delay_line(G_FILER_LEN - 2 downto 0) & i_noisy; end if; end process; --Generate AND and NOR of delay line bits s_delay_and <= '1' when to_01(s_delay_line) = (s_delay_line'range => '1') else '0'; s_delay_nor <= '1' when to_01(s_delay_line) = (s_delay_line'range => '0') else '0'; --Set discrete based on delay line output_process : process (i_clk) begin if rising_edge(i_clk) then if s_delay_nor = '1' then s_output_clean <= '0'; elsif s_delay_and = '1' then s_output_clean <= '1'; end if; end if; end process; end behaviour;
为了测试这个模块,创建一个简单的测试文件,它将随机数量的毛刺注入信号中。在信号改变状态后,许多随机毛刺被输入到信号中。如果滤波器运行正常,则这些毛刺将在毛刺滤波器输出干净的信号。
library ieee; use ieee.std_logic_1164.all; use ieee.numeric_std.all; use ieee.math_real.all; entity glitch_filter_tb is end; architecture bench of glitch_filter_tb is component glitch_filter generic ( G_FILER_LEN : integer ); port ( i_clk : in std_ulogic; i_noisy : in std_ulogic; o_clean : out std_ulogic ); end component; -- Clock period constant clk_period : time := 10 ns; -- Generics constant G_FILER_LEN : integer := 8; -- Ports signal i_clk : std_ulogic :='0'; signal i_noisy : std_ulogic; signal o_clean : std_ulogic; begin i_clk <= not i_clk after (clk_period/2); glitch_filter_inst : glitch_filter generic map ( G_FILER_LEN => G_FILER_LEN ) port map ( i_clk => i_clk, i_noisy => i_noisy, o_clean => o_clean ); uut : process variable glitch_duration : integer; variable seed1 : positive := 1; variable seed2 : positive := 283647823; impure function integer_random(min, max : integer) return integer is variable random : real; begin uniform(seed1, seed2, random); return integer(round(random * real(max - min) + real(min))); end function; begin i_noisy <= '0'; wait until rising_edge(i_clk); wait for G_FILER_LEN * clk_period; test: for i in 0 to 1 loop i_noisy <= '1'; wait until rising_edge(i_clk); glitch_duration := integer_random(1,5); for x in 0 to glitch_duration loop i_noisy <= not i_noisy; wait until rising_edge(i_clk); end loop; i_noisy <= '1'; wait for 20 * clk_period; report "loop high completed" severity note; i_noisy <= '0'; wait until rising_edge(i_clk); glitch_duration := integer_random(1,5); for x in 0 to glitch_duration loop i_noisy <= not i_noisy; wait until rising_edge(i_clk); end loop; i_noisy <= '0'; wait for 20 * clk_period; report "loop low completed" severity note; end loop; report "Simulation complete" severity failure; end process; end;
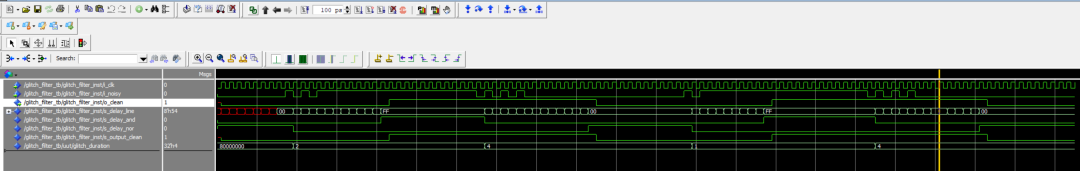
运行仿真后显示在信号状态改变后随机数量的脉冲便增加。检查输出信号表明滤波器已正确滤除输入信号中可能存在的毛刺。
正如在一开始所说的,这样的滤波器对于部署在可能存在电噪声的环境中非常有用。与 BRAM 上的 EDAC 等其他缓解策略相结合,这是可用于实现设计弹性的关键方法之一。
审核编辑:刘清
声明:本文内容及配图由入驻作者撰写或者入驻合作网站授权转载。文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表电子发烧友网立场。文章及其配图仅供工程师学习之用,如有内容侵权或者其他违规问题,请联系本站处理。
举报投诉
-
TPA3110D2无信号输入时,输出336kHZ的正弦波信号有明显的毛刺,如何滤除毛刺?2024-11-04 781
-
I2C噪声毛刺滤波2024-10-08 903
-
emi滤波器的主要作用是滤除多少频率的干扰2024-08-25 2824
-
双面无毛刺冲裁如何实现(一种消除毛刺的加工方法)2023-12-12 1646
-
什么是毛刺?毛刺的大小和方向 如何测量毛刺的尺寸?2023-12-07 8528
-
FPGA | 竞争冒险和毛刺问题2023-11-02 1108
-
在 FlexIO上进行毛刺滤波的方法2023-10-19 1884
-
电感的毛刺现象是什么意思?如何解决感应毛刺?2023-08-15 6519
-
怎样去设计一个使用时序逻辑对单bit信号进行毛刺滤除操作的电路2021-08-19 2251
-
毛刺的滤波方法2019-06-04 4086
-
引入输入滤波器来滤除噪声设计2018-07-05 3360
-
电路从SDA和SCL线路中滤除毛刺的解决方法及过程2018-06-29 19837
-
波形滤除毛刺2017-04-11 6875
全部0条评论

快来发表一下你的评论吧 !

