

基于java开发的缓存框架jetcache简介
描述
0. 引言
在实际应用中,并不是单一的使用本地缓存或者redis,更多是组合使用来满足不同的业务场景,于是如何优雅的组合本地缓存和远程缓存就成了我们要研究的问题,而这一点,阿里开源的jetcache组件帮我们实现了
1. jetcache简介
jetcache是阿里开源的基于java开发的缓存框架,支持多种缓存类型:本地缓存、分布式缓存、多级缓存。能够满足不同业务场景的缓存需求。
jetcache具有上手简单、性能高效、拓展性强的特点。支持缓存预热 、缓存key前缀等功能。结合spring-cache使用,可以实现十分优雅的缓存类型切换
2. jetcache使用
1、引入依赖,这里我们使用sringboot项目框架,同时使用redis作为远程缓存。于是我们引入jetcache-starter-redis依赖,这里我的springboot版本为2.6.13
如果是非springboot项目可以参考官网说明配置

com.alicp.jetcache jetcache-starter-redis 2.7.0 redis.clients jedis 4.3.1
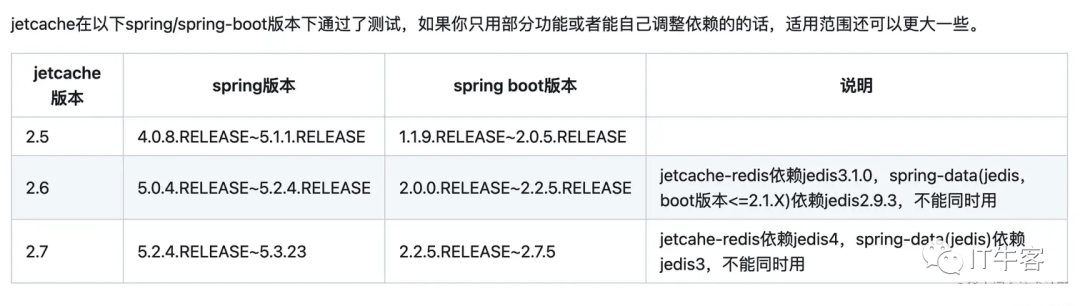
对应的版本说明如下:springboot与jetcache版本关系
2、修改配置文件,配置redis地址和线程数
jetcache: # 统计间隔,0表示不统计,开启后定期在控制台输出缓存信息 statIntervalMinutes: 15 # 是否把cacheName作为远程缓存key前缀 areaInCacheName: false # 本地缓存配置 local: default: # default表示全部生效,也可以指定某个cacheName # 本地缓存类型,其他可选:caffeine/linkedhashmap type: linkedhashmap keyConvertor: fastjson # 远程缓存配置 remote: default: # default表示全部生效,也可以指定某个cacheName type: redis # key转换器方式n keyConvertor: fastjson broadcastChannel: projectA # redis序列化方式 valueEncoder: java valueDecoder: java # redis线程池 poolConfig: minIdle: 5 maxIdle: 20 maxTotal: 50 # redis地址与端口 host: 127.0.0.1 port: 6379
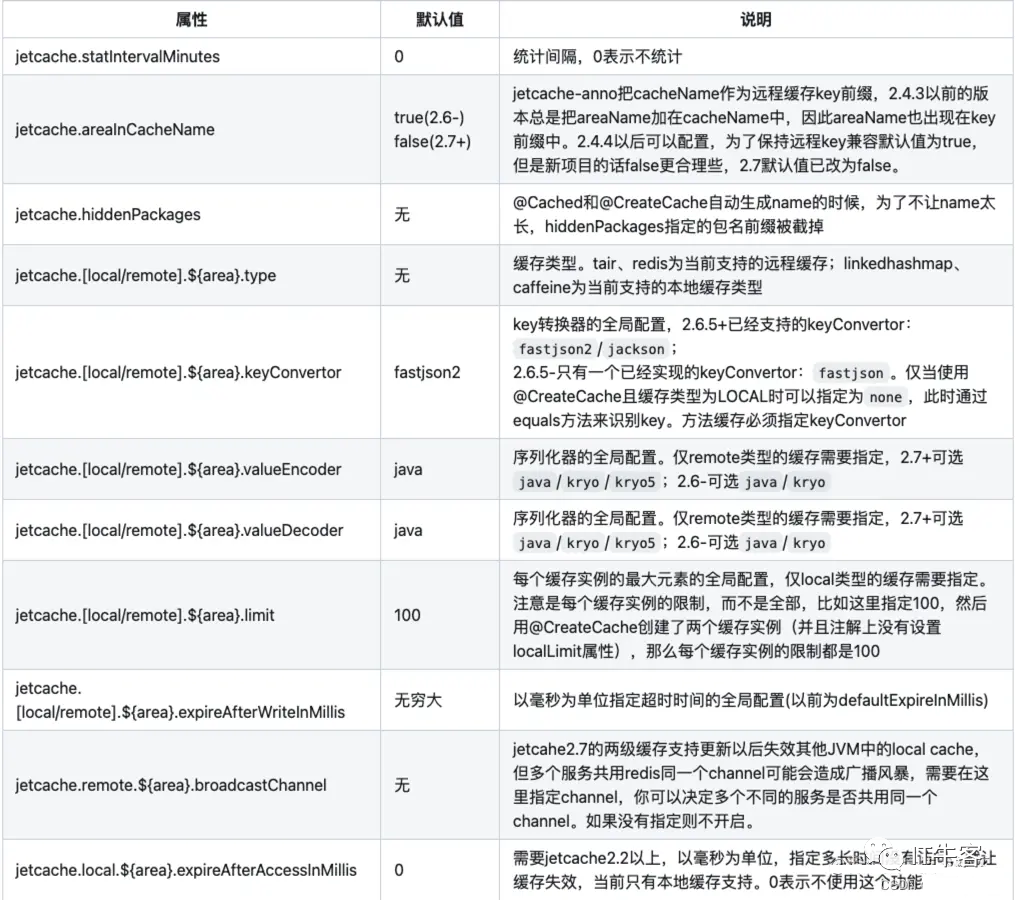
更详细的参数配置
3、启动类添加注解@EnableCreateCacheAnnotation,开启缓存,添加@EnableMethodCache(basePackages = "com.example.jetcachedemo")注解,配置缓存方法扫描路径
4、使用缓存可以通过三种方式:
方式一(推荐)AOP模式:通过@Cached,@CacheUpdate,@CacheInvalidate注解
@RestController
@RequestMapping("user")
public class UserController {
@GetMapping("getRemote")
@Cached(name="userCache:", key = "#id", expire = 3600, timeUnit = TimeUnit.SECONDS, cacheType = CacheType.REMOTE)
public User getRemote(Long id){
// 直接新建用户,模拟从数据库获取数据
User user = new User();
user.setId(id);
user.setName("用户remote"+id);
user.setAge(23);
user.setSex(1);
System.out.println("第一次获取数据,未走缓存:"+id);
return user;
}
@GetMapping("getLocal")
@Cached(name="userCache:", key = "#id", expire = 3600, timeUnit = TimeUnit.SECONDS, cacheType = CacheType.LOCAL)
public User getLocal(Long id){
// 直接新建用户,模拟从数据库获取数据
User user = new User();
user.setId(id);
user.setName("用户local"+id);
user.setAge(23);
user.setSex(1);
System.out.println("第一次获取数据,未走缓存:"+id);
return user;
}
@GetMapping("getBoth")
@Cached(name="userCache:", key = "#id", expire = 3600, timeUnit = TimeUnit.SECONDS, cacheType = CacheType.BOTH)
public User getBoth(Long id){
// 直接新建用户,模拟从数据库获取数据
User user = new User();
user.setId(id);
user.setName("用户both"+id);
user.setAge(23);
user.setSex(1);
System.out.println("第一次获取数据,未走缓存:"+id);
return user;
}
@PostMapping("updateUser")
@CacheUpdate(name = "userCache:", key = "#user.id", value = "#user")
public Boolean updateUser(@RequestBody User user){
// TODO 更新数据库
return true;
}
@PostMapping("deleteUser")
@CacheInvalidate(name = "userCache:", key = "#id")
public Boolean deleteUser(Long id){
// TODO 从数据库删除
return true;
}
}
这里要注意实体类User一定要实现序列化,即声明Serializable
@Data
public class User implements Serializable {
private Long id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
private Integer sex;
}
方式二 API模式:通过@CreateCache,注:在jetcache 2.7 版本CreateCache注解已废弃,不推荐使用
@RestController
@RequestMapping("user2")
public class User2Controller {
@CreateCache(name= "userCache:", expire = 3600, timeUnit = TimeUnit.SECONDS, cacheType = CacheType.BOTH)
private Cache userCache;
@GetMapping("get")
public User get(Long id){
if(userCache.get(id) != null){
return (User) userCache.get(id);
}
User user = new User();
user.setId(id);
user.setName("用户both"+id);
user.setAge(23);
user.setSex(1);
userCache.put(id, user);
System.out.println("第一次获取数据,未走缓存:"+id);
return user;
}
@PostMapping("updateUser")
public Boolean updateUser(@RequestBody User user){
// TODO 更新数据库
userCache.put(user.getId(), user);
return true;
}
@PostMapping("deleteUser")
public Boolean deleteUser(Long id){
// TODO 从数据库删除
userCache.remove(id);
return true;
}
}
方式三 高级API模式:通过CacheManager,2.7 版本才可使用
(1)添加依赖
com.alibaba fastjson 2.0.25
(2)书写配置类
@Configuration
public class JetcacheConfig {
@Autowired
private CacheManager cacheManager;
private Cache userCache;
@PostConstruct
public void init(){
QuickConfig qc = QuickConfig.newBuilder("userCache:")
.expire(Duration.ofSeconds(3600))
.cacheType(CacheType.BOTH)
// 本地缓存更新后,将在所有的节点中删除缓存,以保持强一致性
.syncLocal(false)
.build();
userCache = cacheManager.getOrCreateCache(qc);
}
@Bean
public Cache getUserCache(){
return userCache;
}
}
(3)调用代码
@RestController
@RequestMapping("user3")
public class User3Controller {
@Autowired
JetcacheConfig jetcacheConfig;
@Autowired
private Cache userCache;
@GetMapping("get")
public User get(Long id){
if(userCache.get(id) != null){
return (User) userCache.get(id);
}
User user = new User();
user.setId(id);
user.setName("用户both"+id);
user.setAge(23);
user.setSex(1);
userCache.put(id, user);
System.out.println("第一次获取数据,未走缓存:"+id);
return user;
}
@PostMapping("updateUser")
public Boolean updateUser(@RequestBody User user){
// TODO 更新数据库
userCache.put(user.getId(), user);
return true;
}
@PostMapping("deleteUser")
public Boolean deleteUser(Long id){
// TODO 从数据库删除
userCache.remove(id);
return true;
}
}
多级缓存的形式,会先从本地缓存获取数据,本地获取不到会从远程缓存获取
5、启动redis,启动演示项目
注意,如果启动出现NoClassDefFoundError: redis/clients/util/Pool或NoClassDefFoundError: redis/clients/jedis/UnifiedJedis报错,说明springboot与jetcache版本不一致,对应关系可参考上述第一步中的说明 同时如果使用的是jetcache2.7.x版本,因为该版本中有jedis包的依赖,需要额外添加如下依赖,或者将jetcache版本将至2.6.5以下
redis.clients jedis 4.3.1
3. 测试
3.1 方式一测试
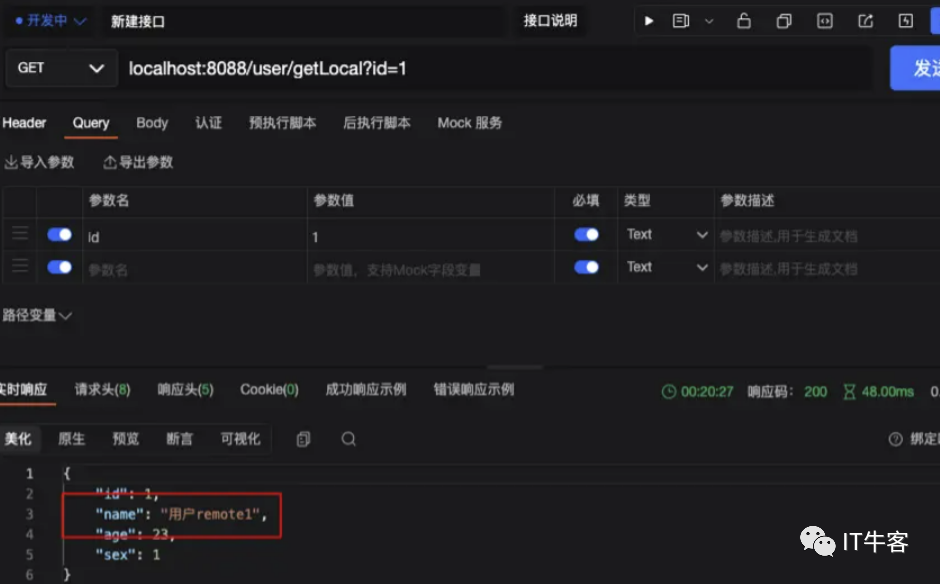
1、访问localhost:8088/user/getRemote?id=1
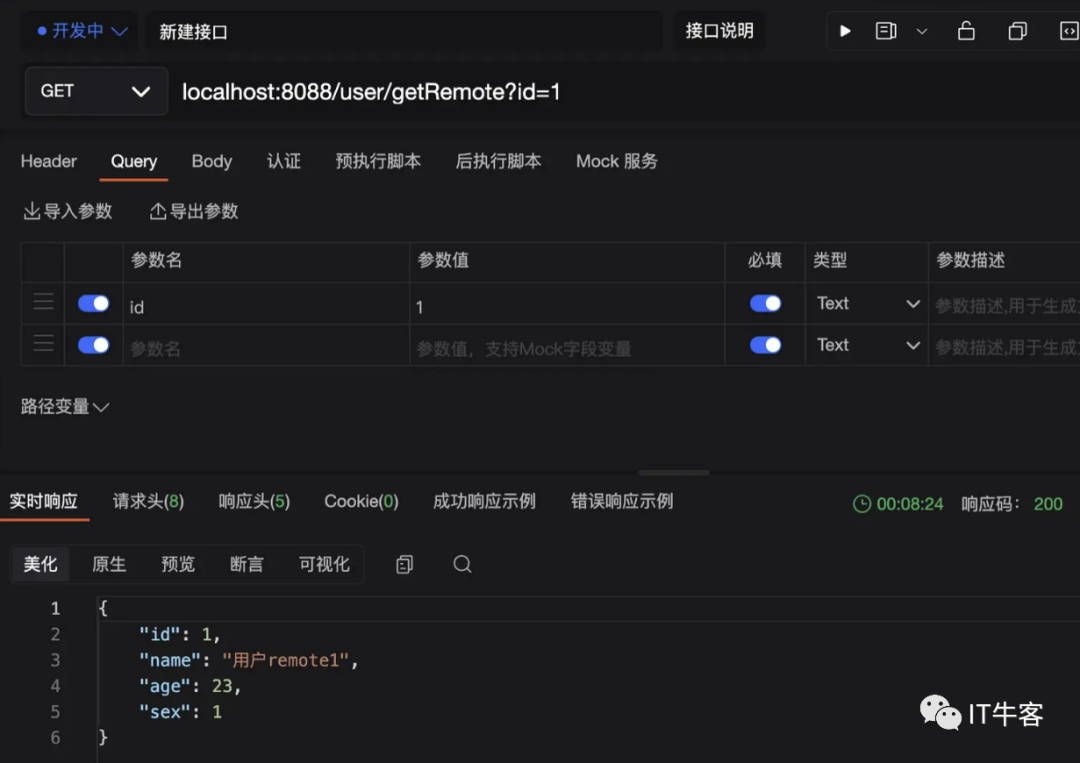
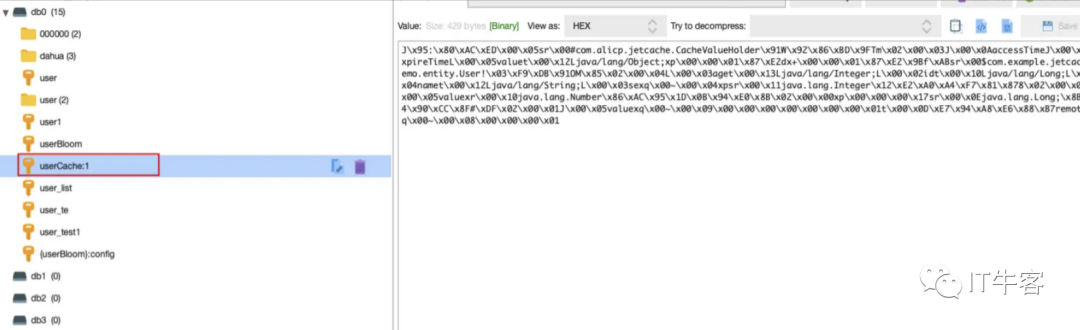
因为配置的是远程缓存,在redis中也能看到对应的key
2、访问localhost:8088/user/getLocal?id=1,这个方法是从本地缓存获取的,现在只有远程缓存上有数据,我们调用发现缓存数据还是拿到了,这说明当我们在配置文件中配置了本地缓存和远程缓存后,方式一中本地缓存和远程缓存会自动相互调用
比如本地缓存有这个key,redis中没有,通过远程缓存方式访问时,会先从redis获取,如果没有会自动获取本地缓存,但是数据还是存储在本地缓存,并不会同步到redis上,这样更加灵活的实现了多级缓存架构
3.2 方式二测试
1、再测试下CreateCache的形式:localhost:8088/user2/get?id=4
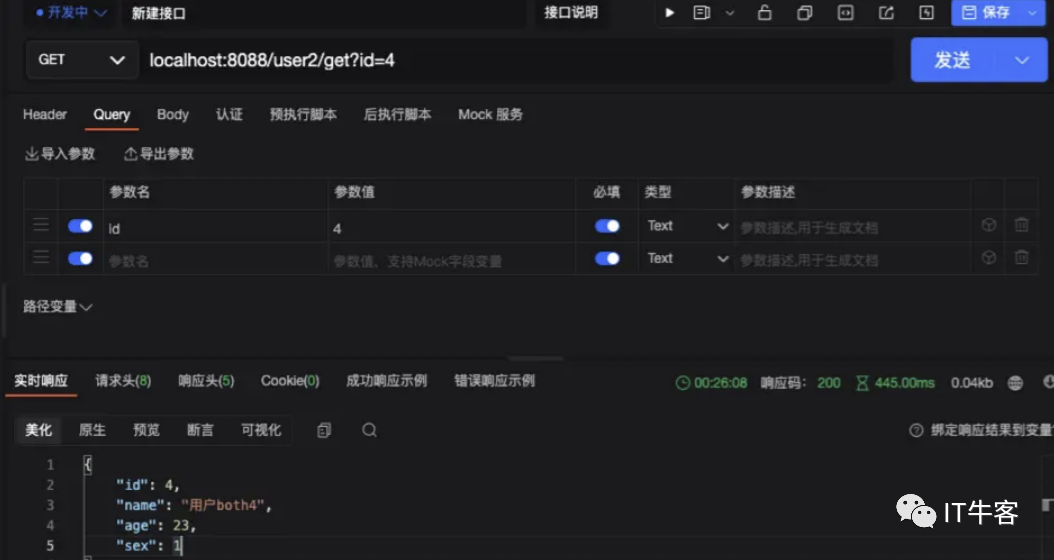
正常获取了,并且redis中也有了对应的值
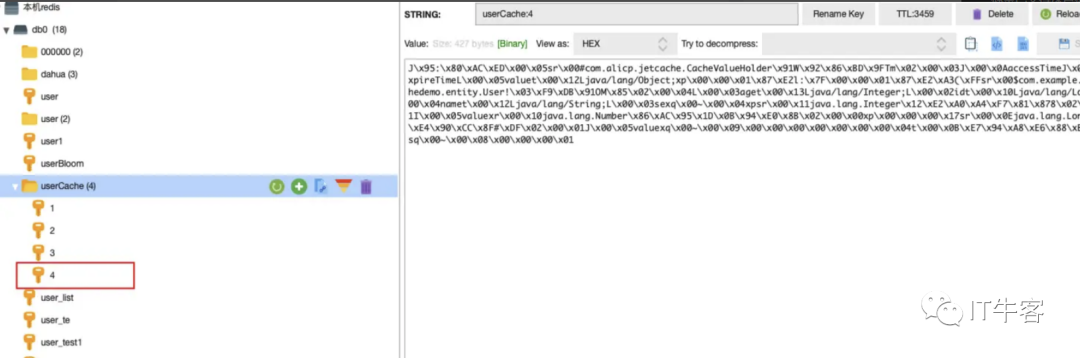
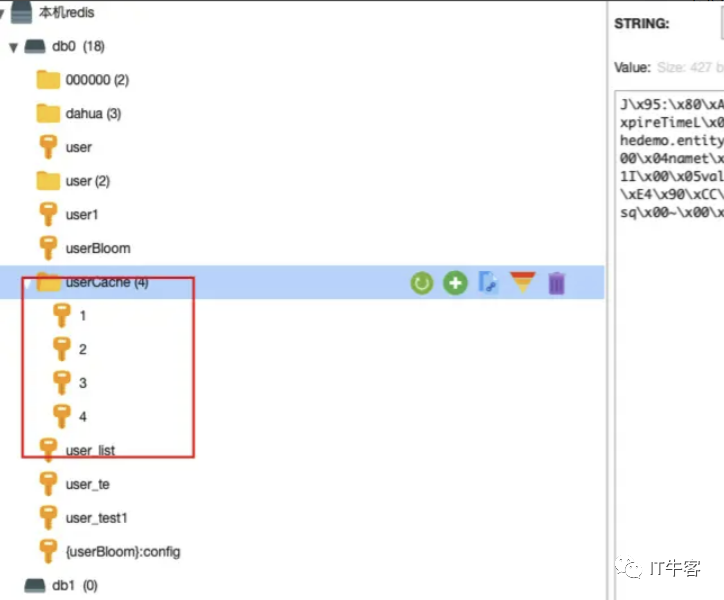
而当我们把缓存方式更改为LOCAL后,再访问localhost:8088/user2/get?id=5
@CreateCache(name= "userCache:", expire = 3600, timeUnit = TimeUnit.SECONDS, cacheType = CacheType.LOCAL)
会发现redis中就没有对应缓存了,只在本地缓存存在,说明我们指定本地缓存的形式成功了
3.3 方式三测试
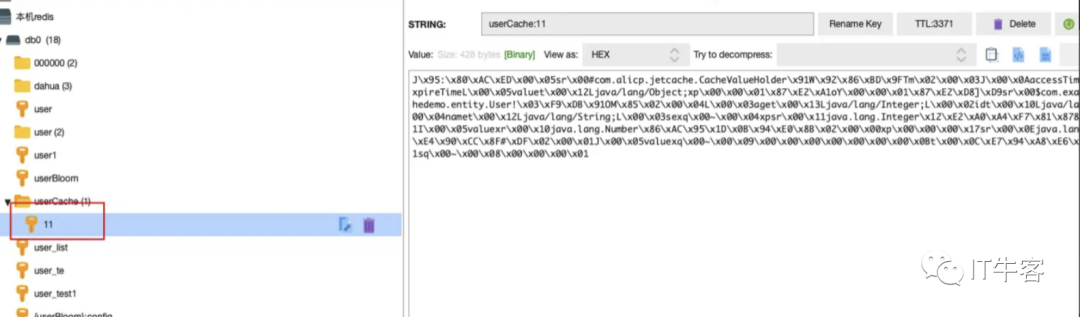
1、调用localhost:8088/user3/get?id=11
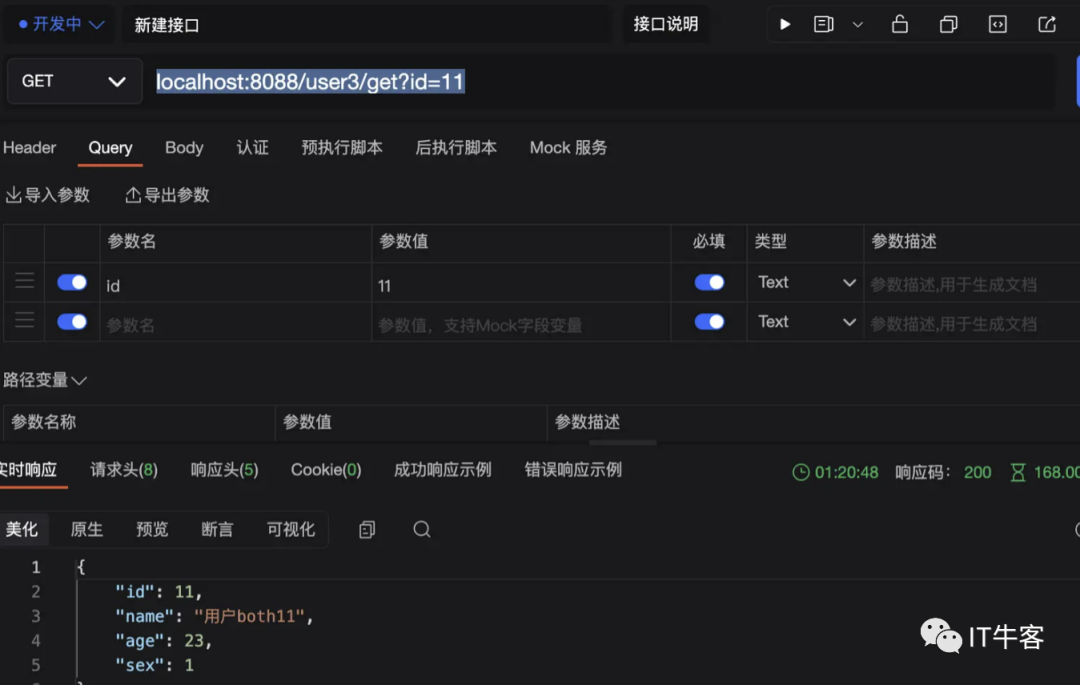
redis中缓存设置成功!
4. 常见报错
1、 ClassNotFoundException: com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON 解决:添加依赖
com.alibaba fastjson 2.0.25
2、NoClassDefFoundError: redis/clients/jedis/UnifiedJedis 解决: 添加依赖
redis.clients jedis 4.3.1
或者将jetcache版本降低至2.6.5以下
演示源码
https://gitee.com/wuhanxue/wu_study/tree/master/demo/jetcache-demo
审核编辑:汤梓红
-
java框架学习-Webwork2开发2008-09-29 3768
-
【南京】诚聘JAVA开发工程师2017-07-05 1767
-
英创主板JAVA应用开发简介2017-10-20 2454
-
java开源工具包-Jodd框架2018-03-19 2677
-
阿里巴巴开源的通用缓存访问框架JetCache介绍2018-04-24 4065
-
基于AOP的智能Web缓存框架2009-04-11 760
-
Java 使用Redis缓存工具的详细解说2018-02-09 8221
-
Java Web的开发前奏详细资料免费下载2019-02-21 1168
-
你想选择哪一种Java框架2019-08-09 1500
-
基于Java的接口快速开发框架2021-09-10 4380
-
基于Java的接口快速开发框架——magic-api2023-07-19 2307
-
Ehcache!这才是Java本地缓存之王!2023-07-29 2870
-
基于springboot和vue框架的Java2023-12-03 1778
-
SSM框架在Java开发中的应用 如何使用SSM进行web开发2024-12-16 2211
-
Perforce JRebel 简介:即时加载代码变更,加速Java应用开发2025-08-14 523
全部0条评论

快来发表一下你的评论吧 !

