

Spring AOP如何破解java应用
描述
前面我们看过javaassit是如何破解java应用,核心都是AOP相关的知识,今天我们看下Spring AOP是怎么回事!
Spring-AOP
spring 5.x版本
AOP面向切面编程,通过预编译方式和运行期间动态代理实现程序功能的统一维护的一种技术。AOP是OOP的延续,从另一视角扩展了对面向对象编程的形式。利用AOP可以对业务逻辑的各个部分进行隔离,从而使得业务逻辑各部分之间的耦合度降低,提高程序的可重用性,同时提高了开发的效率。
Spring AOP与IOC作为整个Spring框架最为核心的两个部分,其意义不言而喻。在Spring中,我们都是面向Bean的装配与管理,一个Bean是一个对象,也可以是一个代理。
概念
Aspect(切面):Aspect声明类似于Java中的类声明,在Aspect中会包含着一些Pointcut以及相应的 Advice。
JointPoint(连接点):表示在程序中明确定义的点,典型的包括方法调用,对类成员的访问以及异常处理程序块的执行等等,它自身还可以嵌套其它joint point。
Pointcut(切点):按规则匹配的JointPoint,这些JointPoint或是通过逻辑关系组合起来,或是通过通配、正则表达式等方式集中起来,它定义了相应的Advice执行的具体地方。
Advice(通知):Advice定义了在Pointcut里面定义的程序点具体要做的操作,它通过before、after和around来区别是在每个JointPoint之前、之后还是代替执行的代码。
Target(目标对象):将Advice织入到目标对象.。
Weaving(织入):将Aspect和其他对象连接起来, 并创建增强(代理)对象的过程
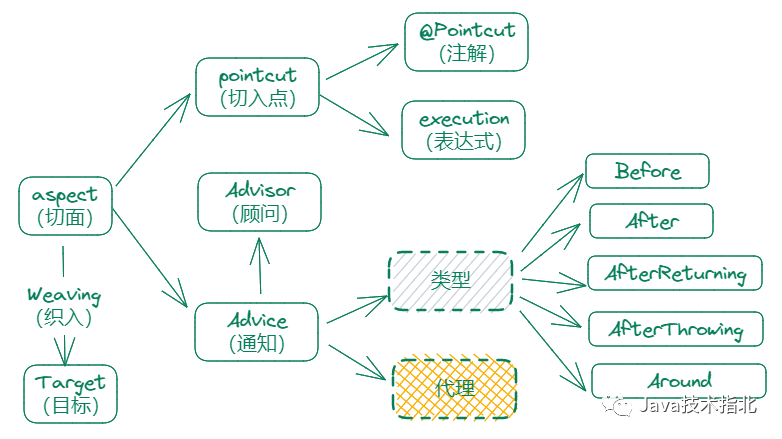
下面从几个方面了解Spring中如何使用AOP,你会发现,所有的配置都是围绕着这些概念。Spring提供了AOP代理的上下文环境,而对目标对象的加强(Aspect、Advisor)都是由开发者自己完成。
Spring-aop.xml
- 基于aspect配置AOP,一个Aspect包含Pointcut与Advice:
< beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd" >
< !-- 业务类 -- >
< bean id="queryService" class="com.sucl.blog.springaop.service.QueryService"/ >
< !-- 定义Aspect,aop:method 的来源 -- >
< bean id="logAspect" class="com.sucl.blog.springaop.aspect.LogAspect"/ >
< !-- 基于Aspect-- >
< aop:config >
< aop:aspect ref="logAspect" >
< aop:pointcut id="pointcut" expression="execution(* com.sucl.blog.springaop.service..*(..))"/ >
< aop:before method="before" pointcut-ref="pointcut"/ >
< aop:after-returning method="afterReturning" pointcut-ref="pointcut" returning="result"/ >
< aop:after-throwing method="afterThrowing" pointcut-ref="pointcut" throwing="e"/ >
< aop:after method="after" pointcut-ref="pointcut"/ >
< aop:around method="around" pointcut-ref="pointcut"/ >
< /aop:aspect >
< /aop:config >
< /beans >
- 基于advice配置AOP,这种方式更方便Advice的复用
< beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd" >
< bean id="queryService" class="com.sucl.blog.springaop.service.QueryService"/ >
< bean id="logAdvice" class="com.sucl.blog.springaop.advice.LogAdvice"/ >
< !-- 基于Advisor -- >
< aop:config >
< aop:pointcut id="pointcut" expression="execution(* com.sucl.blog.springaop.service..*(..))"/ >
< aop:advisor advice-ref="logAdvice" pointcut-ref="pointcut"/ >
< /aop:config >
< /beans >
@Aspect注解
基于注解@Aspect定义切面来增强目标对象,与上面的XML第一种配置对应,记得使用@EnableAspectJAutoProxy注解开启
@Slf4j
@Aspect
public class LogAspect {
@Pointcut("execution(* com.sucl.blog.springaop.service..*(..))")
public void pointcut(){}
/**
* 方法执行前执行
* @param joinPoint
* @param arg1
*/
@Before(value = "pointcut()")
public void before(JoinPoint joinPoint){
log.info(" > > > 执行 before");
}
/**
* 方法出现异常时执行
* @param joinPoint
*/
@AfterThrowing(value = "pointcut()", throwing = "e")
public void afterThrowing(JoinPoint joinPoint, Exception e){
log.info(" > > > 执行 afterThrowing: {}", e.getMessage());
}
/**
* 方法返回后执行,异常时不执行
* @param joinPoint
*/
@AfterReturning(value = "pointcut()", returning = "result")
public void afterReturning(JoinPoint joinPoint, Object result){
log.info(" > > > 执行 afterReturning: {}" ,result);
}
/**
* 方法执行完执行,不管是否发生异常
* @param joinPoint
*/
@After(value = "pointcut()")
public void after(JoinPoint joinPoint){
log.info(" > > > 执行 after");
}
/**
* 在after与 around 前后执行
* @param pjp
* @param jp
*/
@Around(value = "pointcut()")
public void around(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp){
try {
log.info(" > > > 执行 around starting");
pjp.proceed();
log.info(" > > > 执行 around finished");
} catch (Throwable e) {
log.info(" > > > 执行 around 异常:{}", e.getMessage());
}
}
}
AOP代理执行顺序
spring 5.2.7之后的执行顺序:

Pointcut表达式(AspectJ)
execution:用于匹配方法执行的连接点
within:用于匹配指定类型内的方法执行
this:用于匹配当前AOP代理对象类型的执行方法;注意是AOP代理对象的类型匹配,这样就可能包括引入接口也类型匹配
target:用于匹配当前目标对象类型的执行方法;注意是目标对象的类型匹配,这样就不包括引入接口也类型匹配
args:用于匹配当前执行的方法传入的参数为指定类型的执行方法
@within:用于匹配所以持有指定注解类型内的方法
@target:用于匹配当前目标对象类型的执行方法,其中目标对象持有指定的注解
@args:用于匹配当前执行的方法传入的参数持有指定注解的执行
@annotation:用于匹配当前执行方法持有指定注解的方法
bean:Spring AOP扩展的,AspectJ没有对于指示符,用于匹配特定名称的Bean对象的执行方法
基于@Configuration
通过ProxyFactoryBean我们可以生成基于目标对象的代理。通过下面几行代码,加上自定义的切面实现(MethodInterceptor、Advice等接口的实现),就可以实现上面的before、after、around等通知切面。
@Configuration
public class ProxyConfiguration {
@Bean
public ProxyFactoryBean printServiceProxy() {
ProxyFactoryBean proxyFactoryBean = new ProxyFactoryBean();
proxyFactoryBean.setTarget(new PrintService());
proxyFactoryBean.setProxyTargetClass(true);
addInterceptors(proxyFactoryBean);
return proxyFactoryBean;
}
/**
* 定义方法拦截器:(支持通配符)
* org.springframework.aop.Advisor
* org.aopalliance.intercept.Interceptor
*
* MethodBeforeAdvice
* AfterReturningAdvice
* ThrowsAdvice
*
* org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInterceptor
* org.aopalliance.aop.Advice
*
* @param proxyFactoryBean
*/
private void addInterceptors(ProxyFactoryBean proxyFactoryBean) {
proxyFactoryBean.setInterceptorNames("logAdvice");
}
@Bean
public LogAdvice logAdvice() {
return new LogAdvice();
}
}
@Slf4j
public class LogAdvice implements MethodInterceptor {
@Override
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable {
try {
log.info(" > > > before");
Object result = invocation.proceed();
log.info(" > > > afterReturning : {}", result);
return result;
} catch (Throwable e) {
log.info(" > > > afterThrowing : {}", e.getMessage());
throw e;
} finally {
log.info(" > > > after");
}
}
}
实现原理
这里说到的是上面第二种通过@Aspect的形式实现AOP功能,这种模式更适合业务模块中对特定模块内的方法进行业务代理。我们需要依赖注解 EnableAspectJAutoProxy , 下面来看看具体如何实现?
- 在EnableAspectJAutoProxy中可以看到@Import(AspectJAutoProxyRegistrar.class),如果你之前看过之前的spring boot start你就知道,这里是基于ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar在Spring容器中注册BeanDefinition。
- 可以看到AspectJAutoProxyRegistrar#registerBeanDefinitions第一行,AopConfigUtils.registerAspectJAnnotationAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary(registry), 主要是注册了BeanPostProcessor(AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator)。
- 我们知道在Spring Bean生命中期中,Bean执行初始化前后会执行容器中的nPostProcessor,Spring AOP即通过AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator这个BeanPostProcessor完成Bean的代理工作。
- 其父类AbstractAutoProxyCreator中,postProcessAfterInitialization -> wrapIfNecessary -> createProxy -> ProxyFactory -> getProxy 到这里,Bean的代理对象也就生成了, 当然省略了各种判断以及加工过程。
代理方式
- Cglib和JDK Proxy
Spring AOP主要是通过这两个代理框架来实现代理的。一般情况下,基于接口代理时使用JDK动态代理,否则使用Cglib.- Java动态代理只能够对接口进行代理,不能对普通的类进行代理(因为所有生成的代理类的父类为Proxy,Java类继承机制不允许多重继承)。而CGLIB能够代理普通类
- Java动态代理使用Java原生的反射API进行操作,在生成类上比较高效;CGLIB使用ASM框架直接对字节码进行操作,在类的执行过程中比较高效
- AspectJ
AspectJ是一个功能强大的面相切面编程框架,是对Java面向对象的扩展,支持编译时、编译后、加载时为目标对象(不仅仅是类方法)织入代理。在Spring AOP中引入了aspectjweaver.jar,仅仅使用了其注解。
下面是网上Spring AOP与AspectJ的比对
| Spring AOP | AspectJ |
|---|---|
| 用纯Java实现 | 使用Java编程语言的扩展实现 |
| 无需单独的编译过程 | 除非设置了LTW,否则需要AspectJ编译器(ajc) |
| 仅需运行时编织 | 运行时编织不可用。支持编译时,后编译和加载时编织 |
| 不足–仅支持方法级编织 | 更强大–可以编织字段,方法,构造函数,静态初始值设定项,最终类/方法等 |
| 只能在Spring容器管理的bean上实现 | 可以在所有领域对象上实施 |
| 仅支持方法执行切入点 | 支持所有切入点 |
| 代理是针对目标对象创建的,并且方面已应用于这些代理 | 在应用程序执行之前(运行时之前)将方面直接编织到代码中 |
| 比AspectJ慢得多 | 更好的性能 |
| 易于学习和应用 | 比Spring AOP复杂得多 |
结束语
Spring AOP是整个Spring框架的核心,里面涉及到的内容不是很多,但是都比较有深度,在spring诸多模块中,比如事务、缓存、鉴权等等方面都有使用到。由于springboot的出现,xml的配置形式使用 得比较少了,但是这种配置的形式更直白地体现了AOP需要的配置以及各个组件的依赖关系。而基于@Aspect的形式代理业务模块中的方法更简单直观,而基于ProxyFactoryBean、ProxyFactory的方式,在编写类似 cache的模块会更加的灵活。
-
AOP要怎么使用2023-10-09 1325
-
AOP知识详解2023-09-25 1705
-
聊聊在使用Spring AOP时一个非常常见的概念AspectJ2023-08-30 1001
-
解读Spring源码中的IOC和AOP部分2023-06-06 1249
-
Spring认证是什么?2022-07-04 1781
-
「Spring认证」Spring IoC 容器2022-06-28 1155
-
「Spring认证」Spring Hello World 项目示例2021-08-17 2238
-
Spring认证_什么是Spring GraphQL2021-08-06 1168
-
Spring笔记分享2020-11-04 1801
-
Spring工作原理2019-07-10 2638
-
java动态代理机制详解的类和接口描述2017-09-28 688
-
java的动态代理机制和作用2017-09-27 760
-
java spring教程2008-09-11 4771
全部0条评论

快来发表一下你的评论吧 !

