

Linux reset子系统有什么功能
描述
Linux reset子系统
reset子系统非常简单,与clock子系统非常类似,但在驱动实现上,reset驱动更简单。
因为clock驱动主要是时钟的实现,涉及到固定时钟、分频、门控等一些时钟的分级关系,需要弄清楚时钟树里每个时钟的关系。
而reset驱动有点相当于clock驱动的门控,它只有复位和解复位两个功能。
类似于clock子系统,reset子系统也分为了consumer和provider,结构体关系如下:
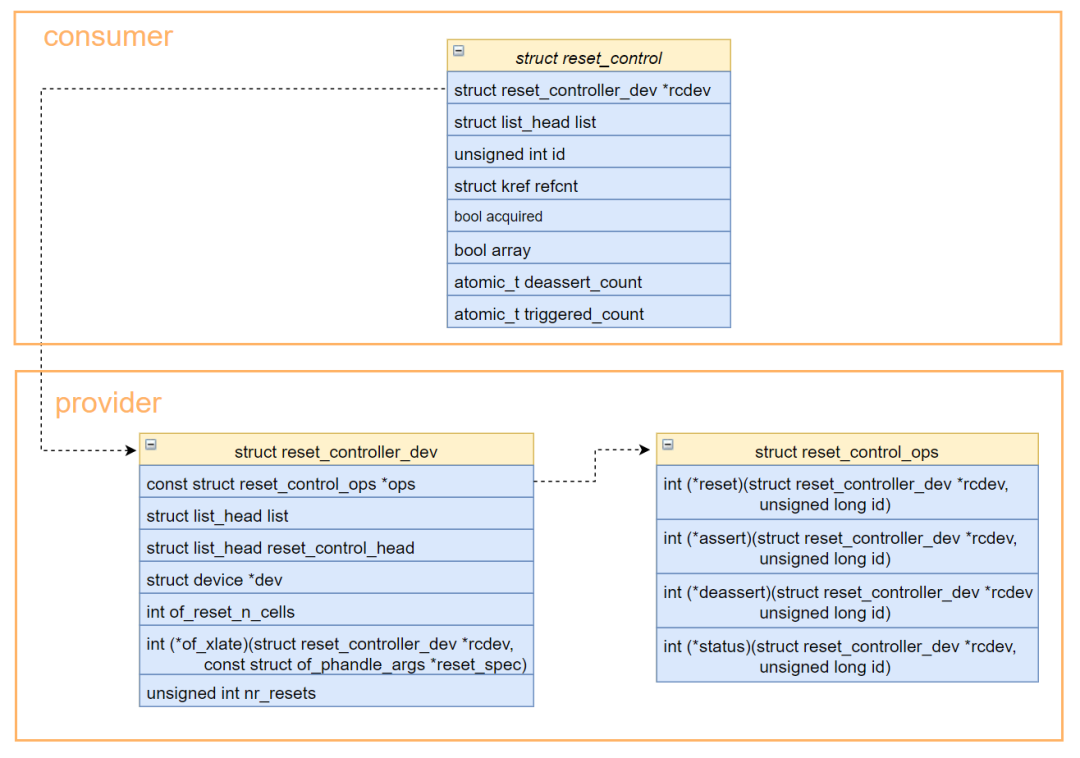
consumer :
reset API接口的使用者,内核提供了统一的reset接口:
devm_reset_control_get(struct device *dev, const char *id)//获取reset句柄
reset_control_deassert(struct reset_control *rstc)//解复位
reset_control_assert(struct reset_control *rstc)//复位
reset_control_reset(struct reset_control *rstc)//先复位,延迟一会,然后解复位
struct reset_control结构体表示一个reset句柄,驱动中使用reset API,需要先获取reset句柄
provider :
reset提供者,即reset驱动。struct reset_controller_dev结构体代表一个reset控制器,内部包含了reset操作函数集合struct reset_control_ops,注册reset驱动时,需要分配一个struct reset_controller_dev结构体,然后填充成员,最后将该结构体注册。
struct reset_controller_dev{
const struct reset_control_ops *ops;//复位控制操作函数
struct list_head list;//全局链表,复位控制器注册后挂载到全局链表
struct list_head reset_control_head;//各个模块复位的链表头
struct device *dev;
int of_reset_n_cells;//dts中引用时,需要几个参数
//通过dts引用的参数,解析复位控制器中相应的参数
int (*of_xlate)(struct reset_controller_dev *rcdev, const struct of_phandle_args *reset_spec);
unsigned int nr_resets;//复位设备个数
}
struct reset_control_ops{
int (*reset)(struct reset_controller_dev *rcdev, unsigned long id);//复位+解复位
int (*assert)(struct reset_controller_dev *rcdev, unsigned long id);//复位
int (*deassert)(struct reset_controller_dev *rcdev, unsigned long id);//解复位
int (*status)(struct reset_controller_dev *rcdev, unsigned long id);//复位状态查询
}
声明:本文内容及配图由入驻作者撰写或者入驻合作网站授权转载。文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表电子发烧友网立场。文章及其配图仅供工程师学习之用,如有内容侵权或者其他违规问题,请联系本站处理。
举报投诉
-
Linux网络子系统的实现2023-11-11 2853
-
Linux内核reset驱动实例2023-09-27 1622
-
Linux LED子系统详解2023-06-10 2256
-
Linux reset子系统及驱动实例2023-05-31 1783
-
linux-usb子系统的核心描述2023-01-14 3736
-
Windows 子系统助力 Linux 2.02023-01-04 1369
-
Linux下输入子系统上报触摸屏坐标2022-09-25 3600
-
在Linux子系统中使用adb功能有哪几种方式呢2022-04-19 3874
-
如何使用Linux内核中的input子系统2020-12-29 1988
-
Windows 10操作系统会有专门的Linux子系统2020-03-14 3494
-
详细了解Linux设备模型中的input子系统2019-05-12 1296
-
Linux内核输入子系统的驱动研究2017-10-31 980
-
基于Linux内核输入子系统的驱动研究2012-09-12 742
全部0条评论

快来发表一下你的评论吧 !

