

Linux设备模型流程分析和示例
描述
流程分析
kobject/kset的相关代码比较简单,毕竟它只是作为一个结构体嵌入其他high-level的结构中,充当纽带的作用。不过,我还是简单的上一张图吧:
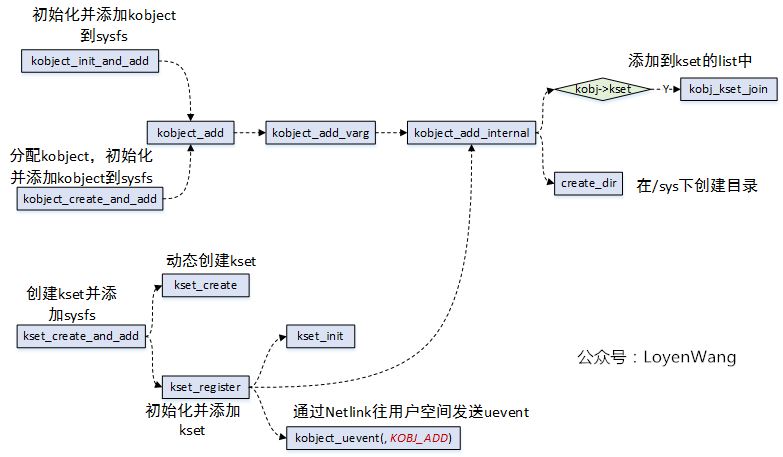
- 完成的工作基本就是分配结构体,初始化各个结构体字段,构建拓扑关系(主要是添加到kset的list中,parent的指向等)等,看懂了结构体的组织,这部分的代码理解起来就很轻松了;
示例
先上一个原理图:

代码
#include < linux/kernel.h >
#include < linux/module.h >
#include < linux/slab.h >
#include < linux/kobject.h >
//自定义一个结构,包含了struct kobject子结构
struct test_kobj {
int value;
struct kobject kobj;
};
//自定义个属性结构体,包含了struct attribute结构
struct test_kobj_attribute {
struct attribute attr;
ssize_t (*show)(struct test_kobj *obj, struct test_kobj_attribute *attr, char *buf);
ssize_t (*store)(struct test_kobj *obj, struct test_kobj_attribute *attr, const char *buf, size_t count);
};
//声明一个全局结构用于测试
struct test_kobj *obj;
//用于初始化sysfs_ops中的函数指针
static ssize_t test_kobj_attr_show(struct kobject *kobj, struct attribute *attr, char *buf)
{
struct test_kobj_attribute *test_kobj_attr;
ssize_t ret = -EIO;
test_kobj_attr = container_of(attr, struct test_kobj_attribute, attr);
//回调到具体的实现函数
if (test_kobj_attr- >show)
ret = test_kobj_attr- >show(container_of(kobj, struct test_kobj, kobj), test_kobj_attr, buf);
return ret;
}
//用于初始化sysfs_ops中的函数指针
static ssize_t test_kobj_attr_store(struct kobject *kobj, struct attribute *attr, const char *buf, size_t count)
{
struct test_kobj_attribute *test_kobj_attr;
ssize_t ret = -EIO;
test_kobj_attr = container_of(attr, struct test_kobj_attribute, attr);
//回调到具体的实现函数
if (test_kobj_attr- >store)
ret = test_kobj_attr- >store(container_of(kobj, struct test_kobj, kobj), test_kobj_attr, buf, count);
return ret;
}
//用于初始化kobj_ktype
const struct sysfs_ops test_kobj_sysfs_ops = {
.show = test_kobj_attr_show,
.store = test_kobj_attr_store,
};
//用于初始化kobj_ktype,最终用于释放kobject
void obj_release(struct kobject *kobj)
{
struct test_kobj *obj = container_of(kobj, struct test_kobj, kobj);
printk(KERN_INFO "test kobject release %sn", kobject_name(&obj- >kobj));
kfree(obj);
}
//定义kobj_ktype,用于指定kobject的类型,初始化的时候使用
static struct kobj_type test_kobj_ktype = {
.release = obj_release,
.sysfs_ops = &test_kobj_sysfs_ops,
};
//show函数的具体实现
ssize_t name_show(struct test_kobj *obj, struct test_kobj_attribute *attr, char *buffer)
{
return sprintf(buffer, "%sn", kobject_name(&obj- >kobj));
}
//show函数的具体实现
ssize_t value_show(struct test_kobj *obj, struct test_kobj_attribute *attr, char *buffer)
{
return sprintf(buffer, "%dn", obj- >value);
}
//store函数的具体实现
ssize_t value_store(struct test_kobj *obj, struct test_kobj_attribute *attr, const char *buffer, size_t size)
{
sscanf(buffer, "%d", &obj- >value);
return size;
}
//定义属性,最终注册进sysfs系统
struct test_kobj_attribute name_attribute = __ATTR(name, 0664, name_show, NULL);
struct test_kobj_attribute value_attribute = __ATTR(value, 0664, value_show, value_store);
struct attribute *test_kobj_attrs[] = {
&name_attribute.attr,
&value_attribute.attr,
NULL,
};
//定义组
struct attribute_group test_kobj_group = {
.name = "test_kobj_group",
.attrs = test_kobj_attrs,
};
//模块初始化函数
static int __init test_kobj_init(void)
{
int retval;
printk(KERN_INFO "test_kobj_initn");
obj = kmalloc(sizeof(struct test_kobj), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!obj) {
return -ENOMEM;
}
obj- >value = 1;
memset(&obj- >kobj, 0, sizeof(struct kobject));
//添加进sysfs系统
kobject_init_and_add(&obj- >kobj, &test_kobj_ktype, NULL, "test_kobj");
//在sys文件夹下创建文件
retval = sysfs_create_files(&obj- >kobj, (const struct attribute **)test_kobj_attrs);
if (retval) {
kobject_put(&obj- >kobj);
return retval;
}
//在sys文件夹下创建group
retval = sysfs_create_group(&obj- >kobj, &test_kobj_group);
if (retval) {
kobject_put(&obj- >kobj);
return retval;
}
return 0;
}
//模块清理函数
static void __exit test_kobj_exit(void)
{
printk(KERN_INFO "test_kobj_exitn");
kobject_del(&obj- >kobj);
kobject_put(&obj- >kobj);
return;
}
module_init(test_kobj_init);
module_exit(test_kobj_exit);
MODULE_AUTHOR("LoyenWang");
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
Makefile
ifneq ($(KERNELRELEASE),)
obj-m:=test_kobject.o
else
KERDIR := /lib/modules/$(shell uname -r)/build
PWD:=$(shell pwd)
all:
make -C $(KERDIR) M=$(PWD) modules
clean:
rm -f *.ko *.o *.symvers *.cmd *.cmd.o modules.* *.mod.c
endif
Makefile没有太多好说的,注意Tab的使用,否则容易出错;
测试结果

- 在/sys目录下创建了test_kobj文件夹,在该文件夹下除了
name和value外,还有一个test_kobj_group的子文件夹; - 可以通过
cat/echo的操作,来操作name和value,分别会调用到底层的xxx_show和xxx_store函数; - 对着代码看这个图,一目了然;
声明:本文内容及配图由入驻作者撰写或者入驻合作网站授权转载。文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表电子发烧友网立场。文章及其配图仅供工程师学习之用,如有内容侵权或者其他违规问题,请联系本站处理。
举报投诉
-
如何在代码V中使用示例模型2023-05-24 1421
-
Linux设备模型分析之(一):设备模型核心2022-10-28 455
-
Linux总线、设备、驱动模型的探究2022-02-14 707
-
Linux设备模型学习笔记(1)2021-12-22 498
-
Linux文件系统与IO流程和模型2020-06-13 1019
-
详解linux设备驱动模型架构2019-07-25 2574
-
Linux设备模型:Bus2019-05-10 1498
-
Linux设备模型之一:Kobject2019-05-06 3583
-
Linux设备驱动的模型摘抄2017-10-31 917
-
linux启动流程分析2012-08-04 3706
-
Linux设备驱动模型摘抄2012-03-19 549
全部0条评论

快来发表一下你的评论吧 !

