

MyBatis Plus如何简化开发
描述
本篇文章,我们通过 MyBatis Plus 来对一张表进行 CRUD 操作,来看看是如何简化我们开发的。
1、创建测试表
创建 USER 表:
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `user`;
CREATE TABLE `user` (
`ID` int(11) NOT NULL,
`USER_NAME` varchar(32) COLLATE utf8mb4_bin DEFAULT NULL,
`USER_AGE` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`ID`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_bin;
向 USER 表中插入两条数据:
INSERT INTO `user` VALUES ('1', 'IT可乐', '18');
INSERT INTO `user` VALUES ('2', 'YSOcean', '22');
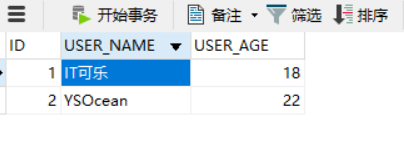
打开表,发现有两条数据了:
2、创建 Spring Boot 工程
通过 IDEA 创建 Spring Boot 工程,如果不连接 https://start.spring.io/ 网址,可以将网址变成 https://start.aliyun.com/ ,如下所示:

3、导入依赖
< dependency >
< groupId >com.baomidou< /groupId >
< artifactId >mybatis-plus-boot-starter< /artifactId >
< version >3.4.3.2< /version >
< /dependency >
< dependency >
< groupId >mysql< /groupId >
< artifactId >mysql-connector-java< /artifactId >
< scope >runtime< /scope >
< /dependency >
首先mybatis-plus 我们导入最新版 3.4.3.2。另外,由于我数据采用的是 MySql,所以这里导入了 Mysql 的连接依赖。
另外,为了简化JavaBean 类的书写,我这里额外导入一个 lombok 插件依赖。
< dependency >
< groupId >org.projectlombok< /groupId >
< artifactId >lombok< /artifactId >
< optional >true< /optional >
< /dependency >
通过这个依赖的相关注解,我们可以不用书写繁琐的 get/set 方法。
4、编写数据库配置文件
在 springboot 项目的 resource 目录下,新建 application.yml 文件,添加如下内容:
server:
port: 8082
spring:
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatisplus?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8
username: root
password: root
# >= 6.x: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
# <= 5.x: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
注意 :url里面填写的 mybatisplus 是我的数据库名称,注意修改,username和password分别填写自己的数据库连接名称和密码。
5、编写代码
①、实体类User.java
@Getter
@Setter
public class User {
private Long id;
private String userName;
private String userAge;
}
②、创建UserMapper 接口
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.mapper.BaseMapper;
import com.ys.mybatisplusstudy.entry.User;
public interface UserMapper extends BaseMapper< User > {
}
③、启动类增加@MapperScan注解
@SpringBootApplication
@MapperScan("com.ys.mybatisplusstudy.mapper")
public class MybatisplusstudyApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(MybatisplusstudyApplication.class, args);
}
}
如果不想在启动类加 @MapperScan 注解,也可在每个 Mapper 接口上增加 @Mapper 注解。
所有配置上面都已完成,是不是很简单,接下来我们对这张表进行CRUD 测试。
6、CRUD 测试
我们在编写 UserMapper 接口时,其继承了一个 BaseMapper 接口:
public interface UserMapper extends BaseMapper< User > {
}
我们进入到 BaseMapper 内部,发现其结构如下:
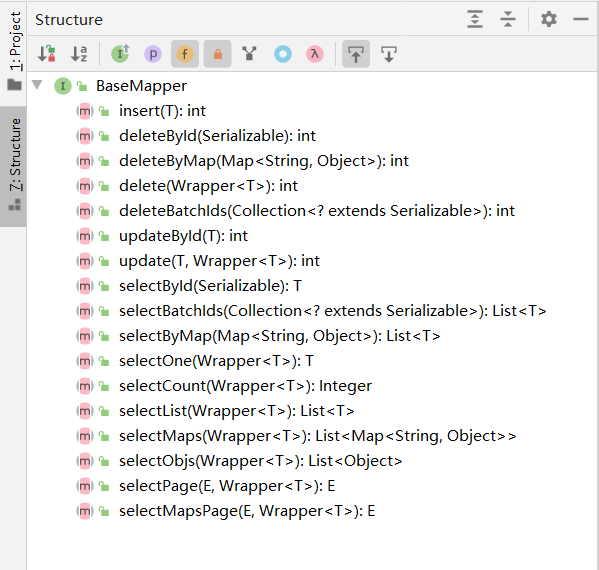
这些方法便是我们常用的增删改查了,下面我们分别演示几个常用的。
①、insert:新增一条记录
@SpringBootTest
class MybatisplusstudyApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
/**
* 新增一条记录
*/
@Test
public void testInsert(){
User user = new User();
user.setId(3L);
user.setUserName("test insert");
user.setUserAge("1");
int insert = userMapper.insert(user);
System.out.println("影响记录数:"+insert);
}
}
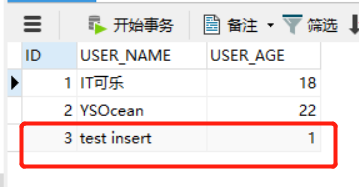
执行完毕后,我们查看数据库:
②、delete:删除记录
/**
* 根据id删除一条记录
*/
@Test
public void testDeleteById(){
int num = userMapper.deleteById(3L);
System.out.println("删除的记录数为:"+num);
QueryWrapper wrapper = new QueryWrapper();
wrapper.eq("id",3L);
userMapper.delete(wrapper);
}
/**
* 构造相关条件删除记录
*/
@Test
public void testDelete(){
QueryWrapper wrapper = new QueryWrapper();
wrapper.eq("USER_NAME","test insert");
int num = userMapper.delete(wrapper);
System.out.println("删除的记录数为:"+num);
}
③、update:修改记录
/**
* 根据id修改
*/
@Test
public void testudpateById(){
User user = new User();
user.setId(3L);
user.setUserName("test update");
int num = userMapper.updateById(user);
System.out.println("修改的记录数为:"+num);
}
④、select:查询记录
/**
* 查询User表所有记录
*/
@Test
public void testSelectAll(){
List< User > users = userMapper.selectList(null);
users.forEach(x- > System.out.println(x.getId()+"-"+x.getUserName()+"-"+x.getUserAge()));
}
/**
* 查询指定记录
*/
@Test
public void testSelectWrapper(){
QueryWrapper wrapper = new QueryWrapper();
wrapper.eq("user_name","IT可乐");
List< User > users = userMapper.selectList(wrapper);
users.forEach(x- > System.out.println(x.getId()+"-"+x.getUserName()+"-"+x.getUserAge()));
}
发现没有,做增删改查是如此的丝滑流畅,都不用写SQL语句了。
当然,这都只是单表的简单玩法,后面我们会介绍高阶玩法。
7、打印SQL语句
这里补充一个小知识点,通过如下配置,我们可以查看执行的 SQL 语句日志。
在 applicatio.yml 文件中,进行如下配置:
# 配置slq打印日志
mybatis-plus:
configuration:
log-impl: org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl
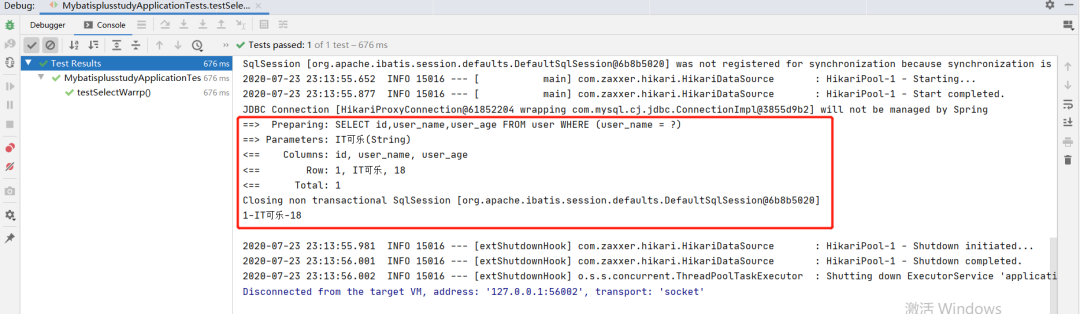
执行效果如下:
当然,这种配置只是把 SQL 日志打印到控制台便于我们调试,后面会介绍更加强大的 SQL 分析工具。
-
mybatis和mybatisplus的区别2023-12-03 3634
-
mybatis plus的常规用法2023-09-25 1489
-
如何调优MyBatis 25倍性能2023-05-30 1305
-
介绍一款基于Mybatis-Plus的代码自助生成器2023-05-23 1949
-
MyBatis-Plus为什么不支持联表2023-02-28 3771
-
Fluent Mybatis、原生Mybatis和Mybatis Plus对比2022-09-15 1952
-
MyBatis-Plus的使用与测试2022-08-22 2012
-
Mybatis-Plus Mybatis增强工具包2022-06-13 668
-
LDO简化开关电源的设计2021-10-29 2007
-
一篇让你熟练掌握 MyBatis-Plus!2021-06-01 3121
-
如何使用Myeclipse进行java可视化开发2019-01-10 1152
-
如何简化开关电源设计2017-01-14 635
全部0条评论

快来发表一下你的评论吧 !

