

如何搭建 Swagger API文档平台
描述
相信大家平时开发的过程中,都会使用到 API文档工具吧?大家都在使用什么呀?Java docs,I/O Docs, apiary.io, Docco, Dexy, Doxygen, TurnAPI,Swagger。今天我就来教大家如何使用 Swagger 搭建 API 文档,并且配置权限使用。毕竟开发文档还是内容使用的为好,万一上线到生产环境,没有关swagger 又没有设置权限,那可不GG啦。
好,我们这就上手搞起来。
我们将使用 Springfox 对 Swagger 2 规范的实现,并通过 JWT 的方式来设置权限。
配置SwaggerUI
第一步:向Spring Boot项目添加Maven依赖项
打开 pom.xml 文件,添加 springfox-boot-starter 到 maven 依赖中。
< dependency >
< groupId >io.springfox< /groupId >
< artifactId >springfox-boot-starter< /artifactId >
< version >3.0.0< /version >
< /dependency >
添加 springfox-boot-starter 依赖后,spring boot 能启动配置功能,配置好 swagger,所以我们不需要手动添加注解来启用 Swagger。
我们启动一下项目访问 Swagger 文档的 JSON API , 来看看 Springfox 是否正常运行。我们可以在浏览器中输入以下URL:
http://localhost:8080/v3/api-docs
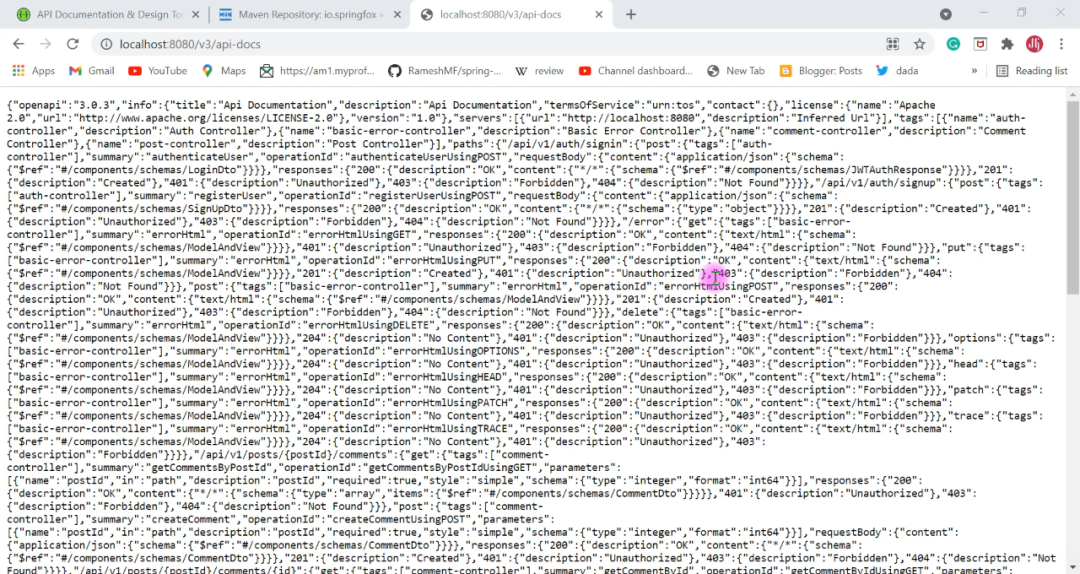
能够看到以上的类似结果,说明我们第一步已经成功了。
第二步:将 Swagger 2 集成到 Spring Boot 项目中去
我们创建一个 SwaggerConfig 类,并用 @Configuration 注解来注释。Swagger 的配置主要围绕着 Docket 对象来完成。我们可以在 SwaggerConfig 类中添加以下代码。
@Configuration
public class SwaggerConfiguration {
private ApiInfo apiInfo() {
return new ApiInfo("Blog REST APIs",
"REST APIs for Blog Application",
"1.0",
"Terms of service",
new Contact("xxx", "xxx", "xxx"),
"License of API",
"API license URL",
Collections.emptyList());
}
@Bean
public Docket api() {
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2)
.apiInfo(apiInfo())
.select()
.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.any())
.paths(PathSelectors.any())
.build();
}
}
在构造 Docket 对象之后,它的 select() 方法返回了 ApiSelectorBuilder 的一个实例,它提供了一种控制 Swagger 所暴露的端点的方法。
我们可以通过使用 RequestHandlerSelectors 和 PathSelectors 配置选择 RequestHandlers 的路径。如果两者两者使用 any() , 那就说明配置所有的 API 都能在 Swagger 上显示了。
第三步:访问 Swagger UI
Swagger UI 是一个内置的解决方案,使用户与 Swagger 生成的API文档的交互变得更加容易。我们在浏览器中输入下面URL即可查看:
http://localhost:8080/swagger-ui/
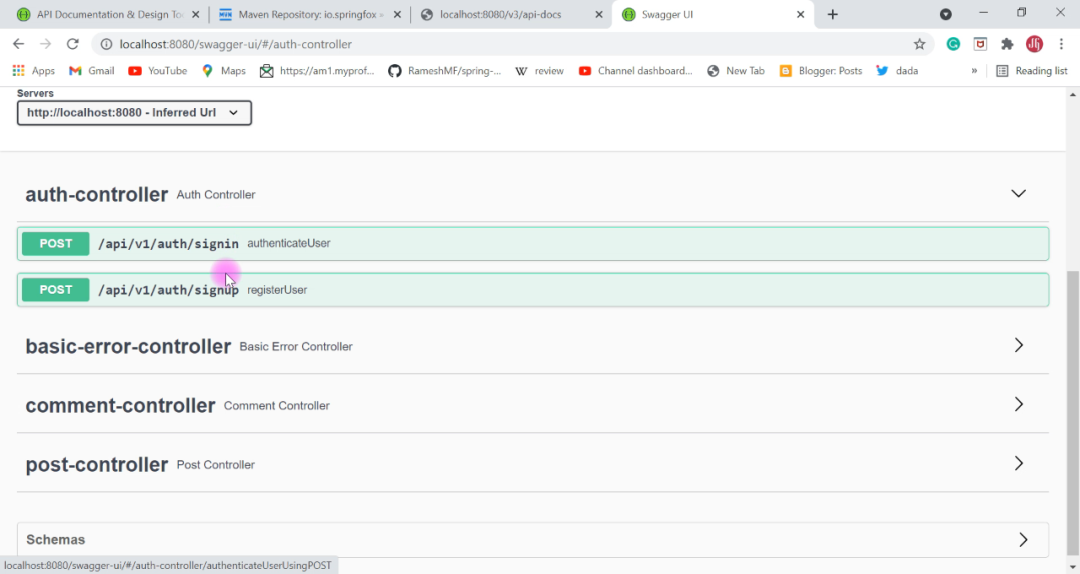
结果应该是这样的。
好,到这里 Swagger 的使用配置就算结束了。那接下来我们来看看怎么用JWT增加权限配置呢?
配置 JWT
JWT 是什么?相信大家都一定听过吧,它就是 JSON Web Token 的缩写。话不多说,直接上手代码配置起来。在 SwaggerConfig 里面新增代码。
我们先来配置 ApiKey 作为 JWT 的认证 header 信息:
public static final String AUTHORIZATION_HEADER = "Authorization";
private ApiKey apiKey(){
return new ApiKey("JWT", AUTHORIZATION_HEADER, "header");
}
下一步,我们配置 JWT 的 SecurityContext , 对 SecurityContext 配置全局的 AuthorizationScope :
private SecurityContext securityContext(){
return SecurityContext.builder().securityReferences(defaultAuth()).build();
}
private List< SecurityReference > defaultAuth(){
AuthorizationScope authorizationScope = new AuthorizationScope("global", "accessEverything");
AuthorizationScope[] authorizationScopes = new AuthorizationScope[1];
authorizationScopes[0] = authorizationScope;
return Arrays.asList(new SecurityReference("JWT", authorizationScopes));
}
然后我们配置 Docket 对象,对 Docket 对象设置 SecurityContext ,SecuritySchemes。
@Bean
public Docket api(){
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2)
.apiInfo(apiInfo())
.securityContexts(Arrays.asList(securityContext()))
.securitySchemes(Arrays.asList(apiKey()))
.select()
.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.any())
.paths(PathSelectors.any())
.build();
}
到这里,JWT 就配置完成了,感觉是不是挺简单的?好,我们再来运行一下,看看效果
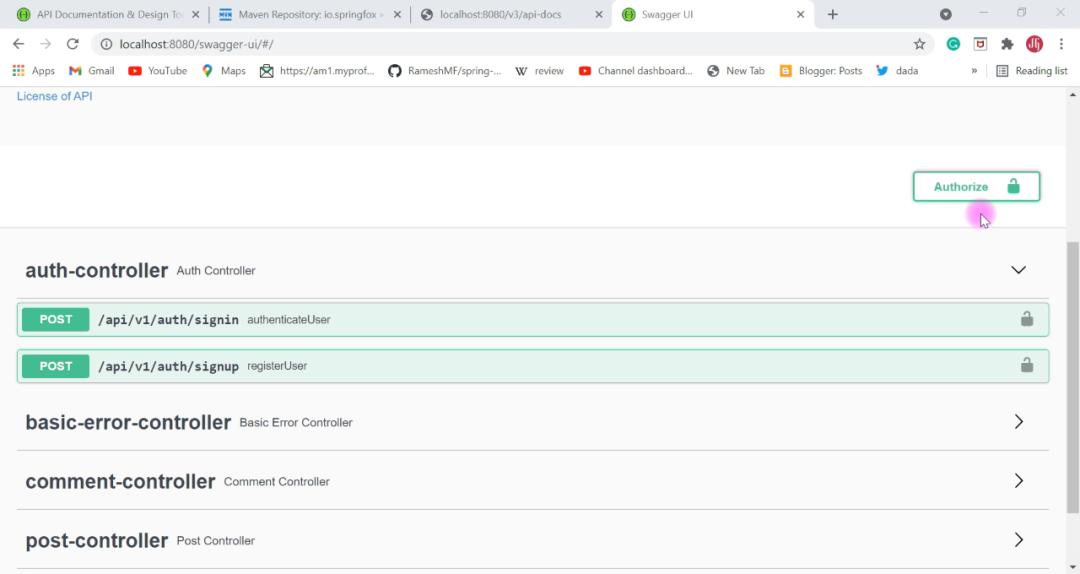
我们点击右上角的 Authorize 按钮,弹出一个输入 apiKey 的弹出层。
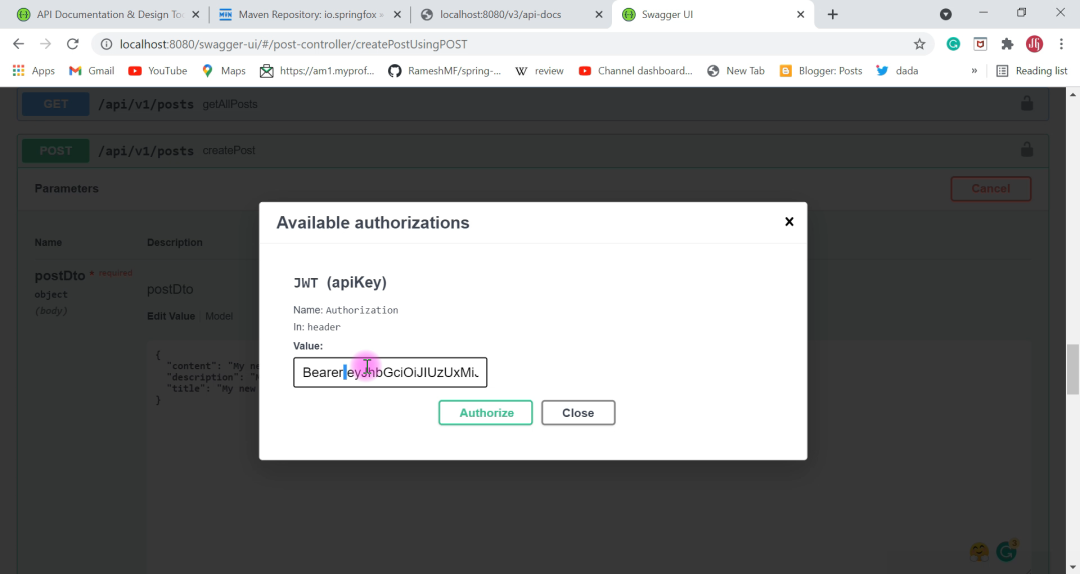
输入 api key 之后,点击 Authorize 认证通过,我们就又能调用 API 接口调试了。
用注解定制 Swagger API 文档
为了能够定制 Swagger 文档,swagger-core 提供了一套注解来声明和操作输出。
Swagger-core 注解:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| @Api | 标记为 Swagger 资源 |
| @ApiModel | 标记为 Swagger 模型 |
| @ApiModelProperty | 模型字段的属性说明 |
| @ApiOperation | http接口的说明 |
| @ApiParam | http 接口参数说明 |
更多详细的说明可以参考 GitHub 上的解释:https://github.com/swagger-api/swagger-core/wiki/annotations
现在我们就举个例子来解释怎么使用这些个注解, 首先来看 @Api 和 @ApiOperation 怎么使用:
@Api(value = "CRUD Rest APIs for Post resources")
@RestController
@RequestMapping()
public class PostController {
@ApiOperation(value = "Get All Posts REST API")
@GetMapping("/api/v1/posts")
public PostResponse getAllPosts(
@RequestParam(value = "pageNo", defaultValue = "0", required = false) int pageNo,
@RequestParam(value = "pageSize", defaultValue = "100", required = false) int pageSize
){
...
}
}
再来看看 @ApiModel 和 @ApiModelProperty 怎么使用:
@ApiModel(description = "Post model information")
@Data
public class PostDto {
@ApiModelProperty(value = "Blog post id")
private long id;
}
是不是感觉 so easy?
总结
通过这篇文章我们学习了如何通过 Springfox 来搭建 Swagger API 文档平台,然后也学会了如何设置 JWT 的方式做认证,保证 API 不会被别人能够恶意使用。
-
Wildberries API 全解析2025-12-04 275
-
淘宝平台获取商品视频 API 接口技术指南2025-11-07 319
-
闲鱼平台获取商品详情API接口2025-10-27 694
-
电商API集成入门:从零开始搭建高效接口2025-07-10 458
-
集成API设计+测试+文档管理,全新一站式解决方案SmartBear API Hub功能介绍2025-04-08 678
-
swagger和smart-doc的区别2023-09-30 926
-
红绿灯倒计时API开发文档2023-06-30 1157
-
ChatGPT API文档2023-06-06 569
-
缺少VGlite字体渲染api文档,求分享2023-04-24 768
-
深度“盘”一下Eolink这款免费API协作平台2022-12-15 1708
-
如何通过ApiFox来构建API场景测试2022-09-01 2260
-
Tasking平台搭建流程2018-12-14 4869
-
如何搭建API程序_框架api接口规范2018-01-04 12355
-
关于IAR搭建开发平台2014-07-03 2845
全部0条评论

快来发表一下你的评论吧 !

