

线程间通信的几种方式
描述
1 使用synchronized,wait,notify,notifyAll
使用synchronized 等方法来控制共享变量,完成交替打印。
思路:
- 在同步方法中先判断信号量,如果不是当前需要的信号使用wait()阻塞线程。
- 完成打印之后切换信号变量。再唤醒所有线程。
public class ThreadSignaling2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
NorthPrint print = new NorthPrint(new NorthSignal());
ThreadA threadA = new ThreadA(print);
ThreadB threadB = new ThreadB(print);
threadA.start();
threadB.start();
}
public static class ThreadA extends Thread {
private NorthPrint print;
public ThreadA(NorthPrint print) {
this.print = print;
}
@Override
public void run() {
print.printNumber();
}
}
public static class ThreadB extends Thread {
private NorthPrint print;
public ThreadB(NorthPrint print) {
this.print = print;
}
@Override
public void run() {
print.printChar();
}
}
}
public class NorthSignal {
protected boolean hasDataToProcess = false;
public synchronized boolean hasDataToProcess(){
return this.hasDataToProcess;
}
public synchronized void setHasDataToProcess(boolean hasData){
this.hasDataToProcess = hasData;
}
}
public class NorthPrint {
private NorthSignal signal;
public NorthPrint(NorthSignal signal) {
this.signal = signal;
}
public synchronized void printNumber() {
try {
for (int i = 1; i <= 26; ) {
if (signal.hasDataToProcess()) {
wait();
}else {
System.out.print(i * 2 - 1);
System.out.print(i * 2);
signal.setHasDataToProcess(true);
i++;
notifyAll();
}
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public synchronized void printChar() {
try {
for (int i = 'A'; i <= 'Z'; ) {
if (!signal.hasDataToProcess()) {
wait();
}else {
System.out.print((char)i);
signal.setHasDataToProcess(false);
i++;
notifyAll();
}
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
2 Lock,Condition
通过使用Lock,Condition的signal() 和 await()来进行换新阻塞交替打印。
public class ThreadSignalingReentrant {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
Condition condition1 = lock.newCondition();
Condition condition2 = lock.newCondition();
new Thread(() - > {
try{
lock.lock();
int i = 1;
while (i <= 26) {
System.out.print(i * 2 - 1);
System.out.print(i * 2);
i++;
condition2.signal();
condition1.await();
}
condition2.signal();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}).start();
new Thread(() - > {
try{
lock.lock();
char i = 'A';
while (i <= 'Z') {
System.out.print(i);
i++;
condition1.signal();
condition2.await();
}
condition1.signal();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}).start();
}
}
3 LockSupport
LockSupport 用来创建锁和其他同步类的基本线程阻塞。当调用LockSupport.park时,表示当前线程将会等待,直至获得许可,当调用LockSupport.unpark时,必须把等待获得许可的线程作为参数进行传递,好让此线程继续运行。
其中:
- park函数,阻塞线程,并且该线程在下列情况发生之前都会被阻塞: ① 调用unpark函数,释放该线程的许可。② 该线程被中断。③ 设置的时间到了。并且,当time为绝对时间时,isAbsolute为true,否则,isAbsolute为false。当time为0时,表示无限等待,直到unpark发生。
- unpark函数,释放线程的许可,即激活调用park后阻塞的线程。这个函数不是安全的,调用这个函数时要确保线程依旧存活。
public class ThreadSignalingLockSupport {
private static Thread threadA = null;
private static Thread threadB = null;
public static void main(String[] args) {
threadA = new Thread(() - > {
int i = 1;
while (i <= 26) {
System.out.print(i * 2 - 1);
System.out.print(i * 2);
i++;
LockSupport.unpark(threadB);
LockSupport.park();
}
});
threadB = new Thread(() - > {
char i = 'A';
while (i <= 'Z') {
LockSupport.park();
System.out.print(i);
i++;
LockSupport.unpark(threadA);
}
});
threadA.start();
threadB.start();
}
}
4 volatile
根据volatile修饰的对象在JVM内存中的可见性,完成交替打印
public class ThreadSignalingVolatile {
enum ThreadRunFlag{PRINT_NUM, PRINT_CHAR}
private volatile static ThreadRunFlag threadRunFlag = ThreadRunFlag.PRINT_NUM;
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread(() - > {
int i = 1;
while (i <= 26) {
while(threadRunFlag == ThreadRunFlag.PRINT_CHAR){}
System.out.print(i * 2 - 1);
System.out.print(i * 2);
i++;
threadRunFlag = ThreadRunFlag.PRINT_CHAR;
}
}).start();
new Thread(()- >{
char i = 'A';
while (i <= 'Z'){
while (threadRunFlag == ThreadRunFlag.PRINT_NUM){}
System.out.print(i);
i++;
threadRunFlag = ThreadRunFlag.PRINT_NUM;
}
}).start();
}
}
5 AtomicInteger
同样利用了AtomicInteger的并发特性,来完成交替打印。
public class AtomicIntegerSignal {
private static AtomicInteger threadSignal = new AtomicInteger(1);
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread(() - > {
int i = 1;
while (i <= 26) {
while(threadSignal.get() == 2){}
System.out.print(i * 2 - 1);
System.out.print(i * 2);
i++;
threadSignal.set(2);
}
}).start();
new Thread(()- >{
char i = 'A';
while (i <= 'Z'){
while (threadSignal.get() == 1){}
System.out.print(i);
i++;
threadSignal.set(1);
}
}).start();
}
}
6 利用 Piped Stream
使用Stream中的Piped Stream分别控制输出,但是其运行速度极慢。
public class ThreadSignalPipedStream {
private final PipedInputStream inputStream1;
private final PipedOutputStream outputStream1;
private final PipedInputStream inputStream2;
private final PipedOutputStream outputStream2;
private final byte[] MSG;
public ThreadSignalPipedStream() {
inputStream1 = new PipedInputStream();
outputStream1 = new PipedOutputStream();
inputStream2 = new PipedInputStream();
outputStream2 = new PipedOutputStream();
MSG = "Go".getBytes();
try {
inputStream1.connect(outputStream2);
inputStream2.connect(outputStream1);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadSignalPipedStream signal = new ThreadSignalPipedStream();
signal.threadA().start();
signal.threadB().start();
}
public Thread threadA (){
final String[] inputArr = new String[2];
return new Thread() {
String[] arr = inputArr;
PipedInputStream in1 = inputStream1;
PipedOutputStream out1 = outputStream1;
@Override
public void run() {
int i = 1;
while (i <= 26) {
try {
System.out.print(i * 2 - 1);
System.out.print(i * 2);
out1.write(MSG);
byte[] inArr = new byte[2];
in1.read(inArr);
while(!"Go".equals(new String(inArr))){ }
i++;
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
};
}
public Thread threadB (){
final String[] inputArr = new String[2];
return new Thread() {
private String[] arr = inputArr;
private PipedInputStream in2 = inputStream2;
private PipedOutputStream out2 = outputStream2;
@Override
public void run() {
char i = 'A';
while (i <= 'Z'){
try {
byte[] inArr = new byte[2];
in2.read(inArr);
while(!"Go".equals(new String(inArr))){ }
System.out.print(i);
i++;
out2.write(MSG);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
};
}
}
7 利用BlockingQueue
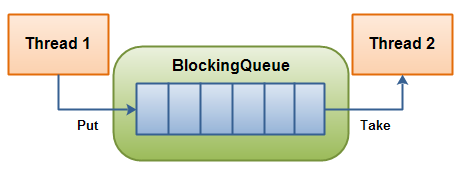
BlockingQueue 通常用于一个线程生产对象,另外一个线程消费这些对象的场景。
img
一个线程负责往里面放,另一个线程从里面取一个BlockingQueue。
线程可以持续将新对象插入到队列之中,直到队列达到可容纳的临界点。当队列到达临界点之后,线程生产者会在插入对象是进入阻塞状态,直到有另外一个线程从队列中拿走一个对象。消费线程会不停的从队列中拿出对象。如果消费线程从一个空的队列中获取对象的话,那么消费线程会处阻塞状态,直到一个生产线程把对象丢进队列。
BlockingQueue常用方法如下:
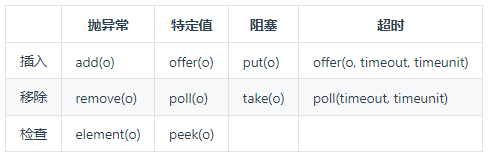
image-20210906230302480
那么我们使用一个LinkedBlockingQueue来完成开始出现的题目
方法中我们使用offer,peek,poll这几个方法来完成。
public class ThreadSignalBlockingQueue {
private static LinkedBlockingQueue< String > queue = new LinkedBlockingQueue< >();
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
new Thread(() - > {
int i = 1;
while (i <= 26) {
System.out.print(i * 2 - 1);
System.out.print(i * 2);
i++;
queue.offer("printChar");
while(!"printNumber".equals(queue.peek())){}
queue.poll();
}
}).start();
new Thread(()- >{
char i = 'A';
while (i <= 'Z'){
while(!"printChar".equals(queue.peek())){}
queue.poll();
System.out.print(i);
i++;
queue.offer("printNumber");
}
}).start();
}
}
我们也可以使用两个LinkedBlockinQueue来完成,分别使用带阻塞的put,take来完成。代码如下
public class ThreadSignalBlockingQueue2 {
private static LinkedBlockingQueue< String > queue1 = new LinkedBlockingQueue< >();
private static LinkedBlockingQueue< String > queue2 = new LinkedBlockingQueue< >();
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
new Thread(() - > {
int i = 1;
while (i <= 26) {
System.out.print(i * 2 - 1);
System.out.print(i * 2);
i++;
try {
queue2.put("printChar");
queue1.take();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}).start();
new Thread(()- >{
char i = 'A';
while (i <= 'Z'){
try {
queue2.take();
System.out.print(i);
i++;
queue1.put("printNumber");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}).start();
}
}
8 使用CyclicBarrier
CyclicBarrier的字面意思就是可循环使用的屏障,它可以让一组线程到达一个阻塞点(屏障)时被阻塞。直到最后一个线程到达阻塞点后,屏障才会开门,然后所有被拦截的线程就可以继续运行。
CyclicBarrier中有一个barrierCommand,主要就是在所有线程到达阻塞点之后执行的一个线程。可以使用构造方法来 CyclicBarrier(int parties, Runnable barrierAction)进行构建。
关于使用CyclicBarrier进行交替打印,先来说一下思路。
- 利用await()方法使得每循环一次都阻塞线程。
- 将每次循环输出的值放到一个共享的同步list里面。
- 然后再使用barrierAction到达阻塞点之后进行输出。由于list里面的值先后顺序有变化,所有先排序然后再打印。
下面我们看一下实操代码:
public class ThreadSignalCyclicBarrier {
private static List< String > list = Collections.synchronizedList(new ArrayList< >());
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
CyclicBarrier barrier = new CyclicBarrier(2,barrierRun());
new Thread(() - > {
int i = 1;
while (i <= 26) {
list.add(String.valueOf(i * 2 - 1));
list.add(String.valueOf(i * 2));
i++;
try {
barrier.await();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}).start();
new Thread(()- >{
char i = 'A';
while (i <= 'Z'){
try {
list.add(String.valueOf(i));
i++;
barrier.await();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}).start();
}
public static Runnable barrierRun(){
return new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
Collections.sort(list);
list.forEach(str- >System.out.print(str));
list.clear();
}
};
}
}
-
java实现多线程的几种方式2024-03-14 1779
-
线程池的创建方式有几种2023-12-04 1573
-
RTT多线程间通信机制有哪几种及推荐?2023-04-07 2317
-
RT-Thread文档_线程间通信2023-02-22 587
-
哪些方式可以实现Linux系统下的进程间通信2021-12-24 1280
-
IOT-OS之RT-Thread--- 线程间同步与线程间通信2021-07-02 1921
-
线程的同步方式有哪几种?2021-05-26 1289
-
使用MQTT作为进程间通信的方式2020-10-22 6964
-
了解Linux多线程及线程间同步2019-04-23 950
-
浅析嵌入式Linux中进程间的几种通信方式2018-08-20 6815
-
进程间与线程间的通信方式2018-04-09 9356
-
线程和进程的区别和联系,线程和进程通信方式2017-12-08 12796
-
c线程间通信2016-08-09 667
-
QNX消息传递及其在线程间通信的应用2009-08-11 747
全部0条评论

快来发表一下你的评论吧 !

