

ROS部署PaddlePaddle的CV模型
描述
本篇博客应该是全网第一篇将ROS和PaddlePaddle做结合,并且手把手教基于python3部署的文章,目的是为了把ROS和Paddle Inference打通,方便大家基于飞桨做ROS+CV方面的任务!本文只是Demo,大家跑通该Demo后即可将自己的模型替换,实现你自己的创意~
快速体验
paddle_inference_ros_demo
paddle_inference_ros_demo功能包是基于paddle_inference_ros开发的,帮助开发者快速体验paddle_inference在ROS环境下的推理部署效果的功能包。可以直接进入该项目链接进行查看和快速体验。
项目地址:
https://gitee.com/irvingao/paddle_inference_ros_demo
1.环境准备
(1)硬件平台
Jetson nano(Jetson系列开发板配置和以下都相同)
Jetson系列基础环境配置:
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_45779334/article/details/108611797
(2)软件环境
-
Ubuntu18.04
-
python3.6.9
-
ROS Melodic
-
PaddlePaddle-gpu 2.1.1
PaddlePaddle:跑通Paddle inference Demo:
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_45779334/article/details/118611953
待Paddle inference GPU预测正常之后再将其迁移进ROS中。
2.编译python3的cv_bridge
在ROS中想使用原生python3的Paddle Inference,最重要的就是需要重新编译基于python3的cv_bridge,只有我们在编译完成python3后,才能基于python3实现Paddle Inference目标检测、分类、分割等相关节点。
所以编译基于python3的cv_bridge便是最基础和最重要的一步,该博客详细介绍了完整的编译过程,按步骤进行操作即可成功。
ROS——基于Ubuntu18.04和ROS Melodic编译python3的cv_bridge:
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_45779334/article/details/119641789
3.创建python3Paddle inference ROS节点
这里将以机器人开发中最常用的目标检测为例,进行部署演示,大家可以自行修改代码,完成分类、分割等任务的ROS节点。
(1)初始化paddle_ros_ws工作空间
mkdir -p paddle_ros_ws/src && cd paddle_ros_ws/src
catkin_init_workspace
(2)创建功能包
catkin_create_pkg py3_camera rospy rosmsg roscpp
catkin_create_pkg py3_infer rospy rosmsg roscpp
(3)编写python图像发布和paddle inference预测节点
①摄像头发布节点
cd py3_camera && mkdir scripts
cd scripts && touch camera.py
chmod +x camera.py
cd ../..
camera.py
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# coding:utf-8
import cv2
import numpy as np
import rospy
from std_msgs.msg import Header
from sensor_msgs.msg import Image
from cv_bridge import CvBridge , CvBridgeError
import time
if __name__=="__main__":
import sys
print(sys.version) # 查看python版本
capture = cv2.VideoCapture(0) # 定义摄像头
rospy.init_node('camera_node', anonymous=True) #定义节点
image_pub=rospy.Publisher('/image_view/image_raw', Image, queue_size = 1) #定义话题
while not rospy.is_shutdown(): # Ctrl C正常退出,如果异常退出会报错device busy!
start = time.time()
ret, frame = capture.read()
if ret: # 如果有画面再执行
frame = cv2.flip(frame,1) #水平镜像操作
ros_frame = Image()
header = Header(stamp = rospy.Time.now())
header.frame_id = "Camera"
ros_frame.header=header
ros_frame.width = 640
ros_frame.height = 480
ros_frame.encoding = "bgr8"
ros_frame.step = 1920
ros_frame.data = np.array(frame).tostring() #图片格式转换
image_pub.publish(ros_frame) #发布消息
end = time.time()
print("cost time:", end-start ) # 看一下每一帧的执行时间,从而确定合适的rate
rate = rospy.Rate(25) # 10hz
capture.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
print("quit successfully!")
②paddle inference目标检测节点
cd py3_infer && mkdir scripts
cd scripts && touch pp_infer.py
chmod +x pp_infer.py
pp_infer.py
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# coding:utf-8
import cv2
import numpy as np
import rospy
from sensor_msgs.msg import Image
from cv_bridge import CvBridge, CvBridgeError
from paddle.inference import Config
from paddle.inference import PrecisionType
from paddle.inference import create_predictor
import yaml
import time
# ————————————————图像预处理函数————————————————
def resize(img, target_size):
"""resize to target size"""
if not isinstance(img, np.ndarray):
raise TypeError('image type is not numpy.')
im_shape = img.shape
im_size_min = np.min(im_shape[0:2])
im_size_max = np.max(im_shape[0:2])
im_scale_x = float(target_size) / float(im_shape[1])
im_scale_y = float(target_size) / float(im_shape[0])
img = cv2.resize(img, None, None, fx=im_scale_x, fy=im_scale_y)
return img
def normalize(img, mean, std):
img = img / 255.0
mean = np.array(mean)[np.newaxis, np.newaxis, :]
std = np.array(std)[np.newaxis, np.newaxis, :]
img -= mean
img /= std
return img
def preprocess(img, img_size):
mean = [0.485, 0.456, 0.406]
std = [0.229, 0.224, 0.225]
img = resize(img, img_size)
resize_img = img
img = img[:, :, ::-1].astype('float32')
img = normalize(img, mean, std)
img = img.transpose((2, 0, 1))
return img[np.newaxis, :], resize_img
# ——————————————————————模型配置、预测相关函数——————————————————————————
def predict_config(model_file, params_file):
'''
函数功能:初始化预测模型predictor
函数输入:模型结构文件,模型参数文件
函数输出:预测器predictor
'''
# 根据预测部署的实际情况,设置Config
config = Config()
# 读取模型文件
config.set_prog_file(model_file)
config.set_params_file(params_file)
# Config默认是使用CPU预测,若要使用GPU预测,需要手动开启,设置运行的GPU卡号和分配的初始显存。
config.enable_use_gpu(400, 0)
# 可以设置开启IR优化、开启内存优化。
config.switch_ir_optim()
config.enable_memory_optim()
predictor = create_predictor(config)
return predictor
def predict(predictor, img):
'''
函数功能:初始化预测模型predictor
函数输入:模型结构文件,模型参数文件
函数输出:预测器predictor
'''
input_names = predictor.get_input_names()
for i, name in enumerate(input_names):
input_tensor = predictor.get_input_handle(name)
input_tensor.reshape(img[i].shape)
input_tensor.copy_from_cpu(img[i].copy())
# 执行Predictor
predictor.run()
# 获取输出
results = []
# 获取输出
output_names = predictor.get_output_names()
for i, name in enumerate(output_names):
output_tensor = predictor.get_output_handle(name)
output_data = output_tensor.copy_to_cpu()
results.append(output_data)
return results
# ——————————————————————后处理函数——————————————————————————
def draw_bbox_image(frame, result, label_list, threshold=0.5):
for res in result:
cat_id, score, bbox = res[0], res[1], res[2:]
if score < threshold:
continue
xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax = bbox
cv2.rectangle(frame, (int(xmin), int(ymin)), (int(xmax), int(ymax)), (255,0,255), 2)
label_id = label_list[int(cat_id)]
print('label is {}, bbox is {}'.format(label_id, bbox))
try:
# #cv2.putText(图像, 文字, (x, y), 字体, 大小, (b, g, r), 宽度)
cv2.putText(frame, label_id, (int(xmin), int(ymin-2)), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, (255,0,0), 2)
cv2.putText(frame, str(round(score,2)), (int(xmin-35), int(ymin-2)), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, (0,255,0), 2)
except KeyError:
pass
def callback(data):
global bridge, predictor, im_size, im_shape, scale_factor, label_list
cv_img = bridge.imgmsg_to_cv2(data, "bgr8")
img_data, cv_img = preprocess(cv_img, im_size)
# 预测
result = predict(predictor, [im_shape, img_data, scale_factor])
draw_bbox_image(cv_img, result[0], label_list, threshold=0.1)
cv2.imshow("cv_img", cv_img)
cv2.waitKey(1)
if __name__ == '__main__':
import sys
print(sys.version) # 查看python版本
# 初始化节点
rospy.init_node('ppinfer_node', anonymous=True)
bridge = CvBridge()
# 模型文件路径(最好写绝对路径)
model_dir = '/home/nano/workspace/paddle_ros_ws/src/py3_infer/scripts/yolov3_r50vd_dcn_270e_coco/'
# 从infer_cfg.yml中读出label
infer_cfg = open(model_dir + 'infer_cfg.yml')
data = infer_cfg.read()
yaml_reader = yaml.load(data)
label_list = yaml_reader['label_list']
print(label_list)
# 配置模型参数
model_file = model_dir + "model.pdmodel"
params_file = model_dir + "model.pdiparams"
# 图像尺寸相关参数初始化
try:
img = bridge.imgmsg_to_cv2(data, "bgr8")
except AttributeError:
img = np.zeros((224,224,3), np.uint8)
im_size = 224
scale_factor = np.array([im_size * 1. / img.shape[0], im_size * 1. / img.shape[1]]).reshape((1, 2)).astype(np.float32)
im_shape = np.array([im_size, im_size]).reshape((1, 2)).astype(np.float32)
# 初始化预测模型
predictor = predict_config(model_file, params_file)
rospy.Subscriber('/image_view/image_raw', Image, callback)
rospy.spin()
准备模型文件
wget https://paddle-inference-dist.bj.bcebos.com/Paddle-Inference-Demo/yolov3_r50vd_dcn_270e_coco.tgz &&tar xzf yolov3_r50vd_dcn_270e_coco.tgz
4.在ROS中运行Paddle Inference节点
(1)编译
cd ../../..
catkin_make -DPYTHON_EXECUTABLE=/usr/bin/python3
(2)将工作空间添加进环境变量
sudo vim ~/.bashrc
source /home/nano/workspace/paddle_ros_ws/devel/setup.bash
(3)运行节点
roscore
rosrun py3_camera camera.py
rosrun py3_infer pp_infer.py
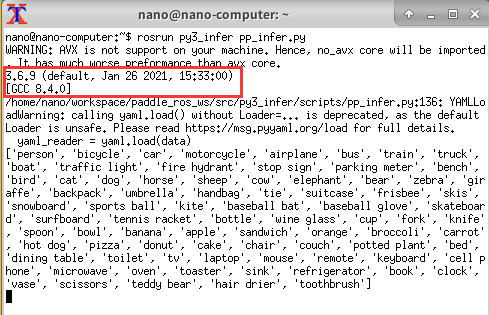
rosrun rqt_iamge_view rqt_iamge_view
(4)运行成功示意图
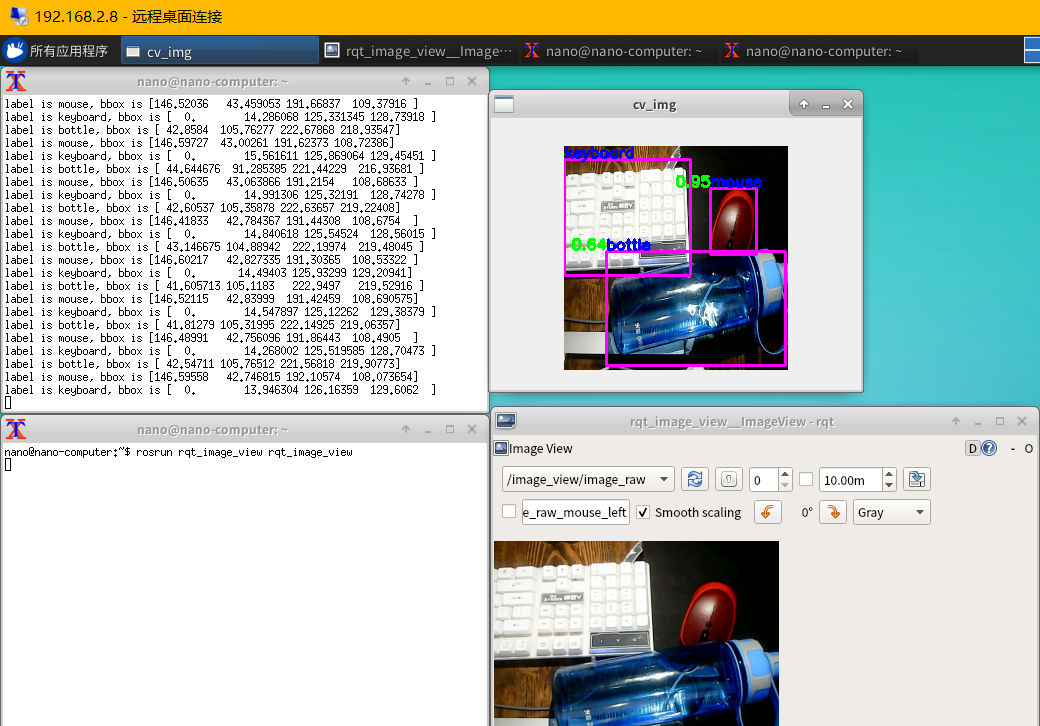
-
K230D部署模型失败的原因?2025-03-11 515
-
【「# ROS 2智能机器人开发实践」阅读体验】视觉实现的基础算法的应用2025-05-03 3262
-
PaddlePaddle Fluid版本的PaddlePaddle如何保存模型2019-04-15 2515
-
PaddlePaddle Fluid版PaddlePaddle加载图像数据出错解决方案2019-04-18 1383
-
PaddlePaddle使用预测模型预测图片报错及解决方法2019-05-31 2341
-
介绍在STM32cubeIDE上部署AI模型的系列教程2021-12-14 3206
-
RV1126 PaddlePaddle编译环境的搭建2022-06-06 4652
-
如何用Arm虚拟硬件在Arm Cortex-M上部署PaddlePaddle2022-09-02 3068
-
部署基于嵌入的机器学习模型2022-11-02 3495
-
基于深度学习模型的点云目标检测及ROS实现2018-11-05 18772
-
使用OpenVINO™ 部署PaddleSeg模型库中的DeepLabV3+模型2021-11-22 10972
-
实现ARM+ROS(机器人操作系统)之运行ROS!2022-10-10 2000
-
机器人的ROS模型建立2023-11-28 1360
-
如何使用Docker部署大模型2025-05-24 876
全部0条评论

快来发表一下你的评论吧 !

