

电源管理入门:Thermal热管理
电子说
描述
热管理(Thermal Management)是什么?
热管理指的是在电子设备或系统中通过各种方式控制其温度来保证其正常工作或延长寿命的过程。其中包括散热设计、温度监测、温度控制等方面。热管理的重要性越来越凸显,尤其在高性能计算、人工智能等领域的应用中更为重要。
管理之前要有策略,之后要有控制操作。
热设计(Thermal Design)是指在产品设计阶段为了满足特定工作负载和环境条件等要求,采用合适的散热方案和材料等措施,以达到良好的热管理效果。其主要目的是确保产品在正常工作条件下温度不超过设计范围,避免由于过热导致的性能下降、系统崩溃、寿命缩短等问题。
热控(Thermal Control)是指在实际使用中采用各种措施控制电子设备或系统的温度,以确保其工作在安全、稳定的温度范围内。主要包括基于温度感应器的风扇旋转控制、电压和频率的调整、动态散热管理等技术。
热管理、热设计、热控三者密不可分,热设计是热管理的前置条件,而热控则是热管理的具体实现。同时,三者也相互影响,优良的热设计可以降低需要的热控次数,有效延长产品寿命。热控根据具体实际情况,需要根据实际情况进行决策和优化,以达到最佳热管理效果。
1. Linux中Thermal框架
在 Linux 内核中,Thermal 特指一套关于温控机制的驱动框架,其目的是为了防止 SoC 等硬件芯片因过热而造成系统不稳定,甚至缩减芯片寿命。
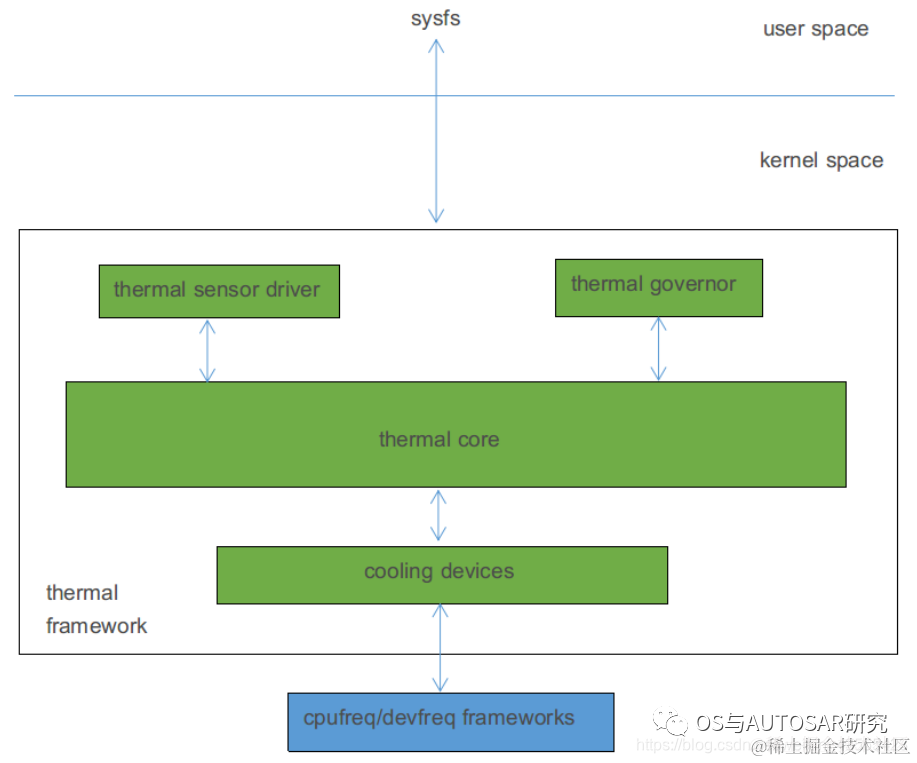
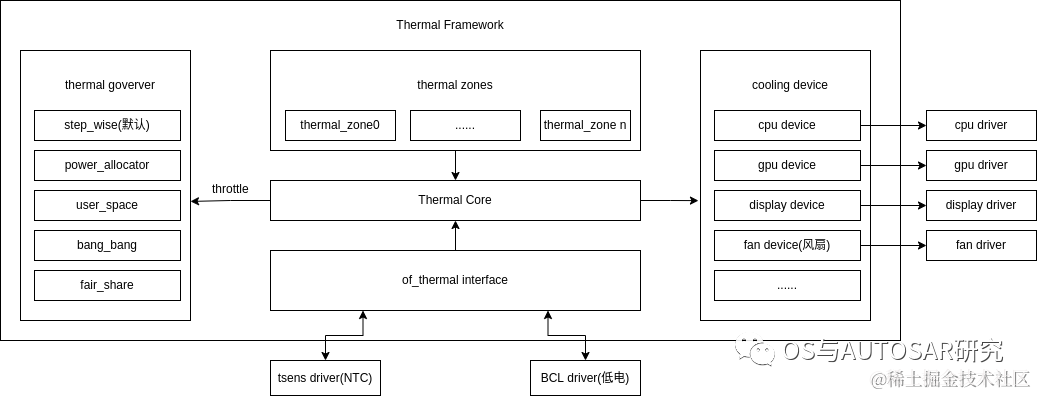
Thermal sensor driver,SoC 内部 CPU 和 GPU 的旁边通常会有用于获取它们温度的传感器,比如 tsadc(Temperature Sensor ADC)。关于传感器的更多细节我们在 sensor driver 章节再进行深入探讨。获取温度的设备:在 Thermal 框架中被抽象为 Thermal Zone Device;
Thermal cooling device,降温设备,比如风扇。这里有点特殊的是,CPU 和 GPU 不仅是发热设备(即需要实施温控策略的设备),也可以是降温设备,当我们降低 CPU/GPU 的运行频率的时候,它们就在充当降温设备。降低产热量即是在降温。
Thermal governer,温控策略,Linux 内核中的温控策略要比空调控制精细得多,而且也提供了多种策略。
Thermal core,组织并管理上面三个组件,并通过 sysfs 和用户空间交互。
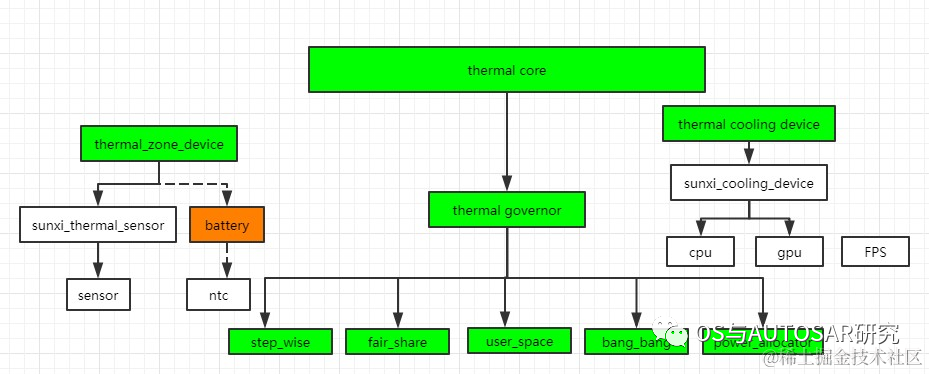
代码举例:
Thermal sensor driver 代码: drivers/thermal/rockchip_thermal.c /* tsadc驱动 */ Thermal cooling device 相关代码: drivers/thermal/devfreq_cooling.c drivers/thermal/cpu_cooling.c Thermal governor 相关代码: drivers/thermal/power_allocator.c /* power allocator 温控策略 */ drivers/thermal/step_wise.c /* step wise 温控策略 */ drivers/thermal/fair_share.c /* fair share 温控策略 */ drivers/thermal/user_space.c /* userspace 温控策略 */ Thermal core 相关代码: drivers/thermal/thermal_core.c drivers/thermal/of_thermal.c
相关的节点:/sys/class/thermal
例如使用step_wise温控策略: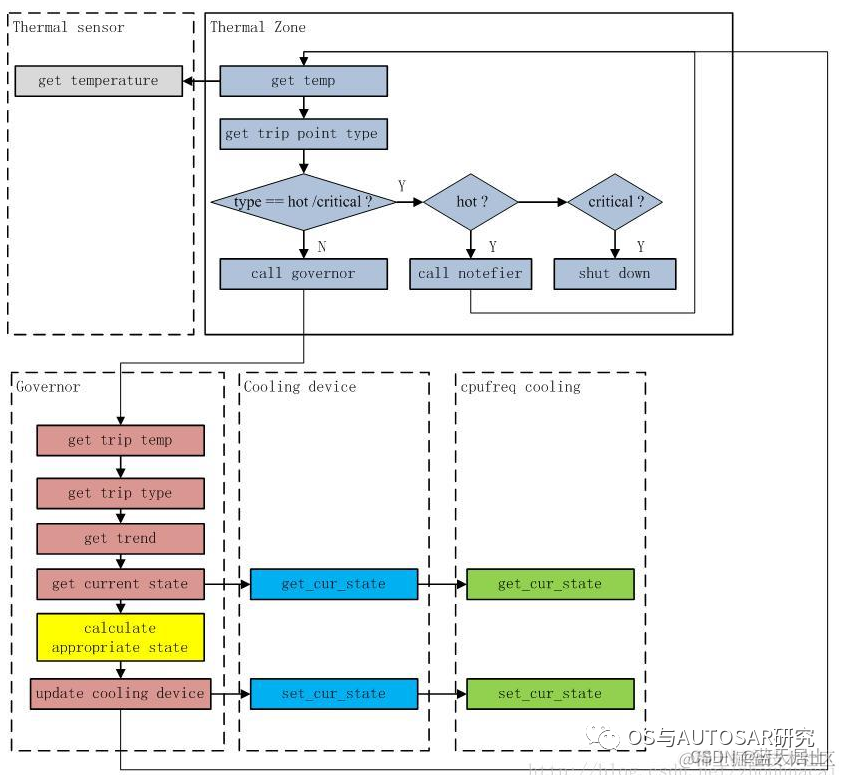
2. sensor driver相关
这部分一般需要自己开发,例如rockchip平台上
struct rockchip_thermal_sensor {
struct rockchip_thermal_data *thermal;
struct thermal_zone_device *tzd;
int id;
};
struct rockchip_thermal_sensor:RK 平台上该结构体代表了一个 tsadc;
struct rockchip_thermal_data:见下面的介绍;
struct thermal_zone_device:一个 tsadc 会和一个 thermal zone 绑定;
int id:该 tsadc 的编号,一般来说 RK 的 SoC 内部有两个 tsadc;
struct rockchip_thermal_data:sensor driver 的私有数据,详见注释。RK 的 sensor driver 为了兼容他们家很多 SoC 的 tsadc,把差异性的东西抽出来。比如那些函数指针,由于寄存器地址的不一样函数体的具体内容也会不一样,如 RK3399 和 PX30 之间。再比如由于 SoC 制程不一样,默认的关机温度也可能不一样。
3. governor
struct thermal_governor:用来描述一个 governor(即温控策略) 信息。
内核目前有五种 governor:
1、power_allocator:引⼊ PID(⽐例-积分-微分)控制,根据当前温度,动态给各 cooling device 分配 power,并将 power 转换为频率,从而达到根据温度限制频率的效果。
2、step_wise:根据当前温度,cooling device 逐级降频。
3、fair share:频率档位⽐较多的 cooling device 优先降频。
4、bang bang:两点温度调节,可用于 cooling device 有风扇的场景。
5、userspace:用户空间控制。
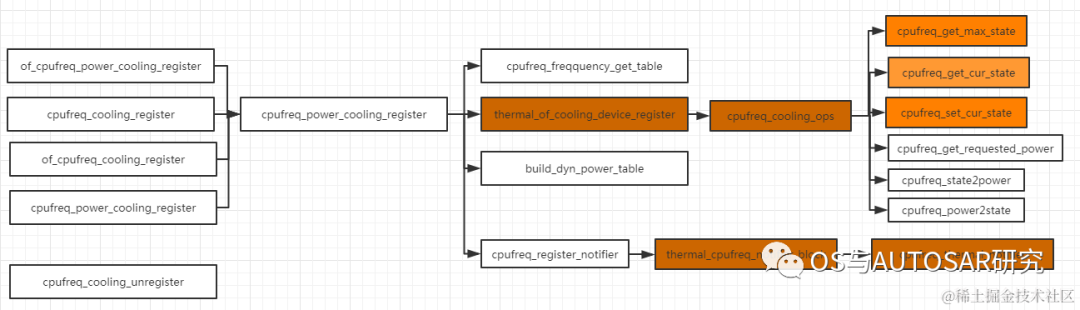
4. cooling device
嵌入式设备通过改变频率电压,来达到改变功耗的目的,cooling_device提供了获取当前设备的温控状态以及设置等接口;
struct thermal_cooling_device {
int id;
char type[THERMAL_NAME_LENGTH];
struct device device;
struct device_node *np;
void *devdata;
const struct thermal_cooling_device_ops *ops;
bool updated; /* true if the cooling device does not need update */
struct mutex lock; /* protect thermal_instances list */
struct list_head thermal_instances;
struct list_head node;
};
struct thermal_cooling_device_ops {
int (*get_max_state) (struct thermal_cooling_device *, unsigned long *);
int (*get_cur_state) (struct thermal_cooling_device *, unsigned long *);
int (*set_cur_state) (struct thermal_cooling_device *, unsigned long);
int (*get_requested_power) (struct thermal_cooling_device *,
struct thermal_zone_device *, u32 *);
int (*state2power) (struct thermal_cooling_device *,
struct thermal_zone_device *, unsigned long, u32 *);
int (*power2state) (struct thermal_cooling_device *,
struct thermal_zone_device *, u32, unsigned long *);
struct thermal_cooling_device:用来描述一个 cooling device(即降温设备) 信息,并将函数操作集抽取出来。DTS中配置:
bind1{
contribution = <0>;
trip = <&cpu_trip1>;
cooling-device
= <&cpu_budget_cooling 2 2>;
};
cpu_budget_cooling:cpu_budget_cool{
compatible = "allwinner,budget_cooling";
device_type = "cpu_budget_cooling";
#cooling-cells = <2>;
status = "okay";
state_cnt = <7>;
cluster_num = <1>;
state0 = <1800000 4>;
state1 = <1512000 4>;

5. thermal zone
获取温度的设备:在 Thermal 框架中被抽象为 Thermal Zone Device;
struct thermal_zone_device {
int id;
char type[THERMAL_NAME_LENGTH];
struct device device;
struct thermal_attr *trip_temp_attrs;
struct thermal_attr *trip_type_attrs;
struct thermal_attr *trip_hyst_attrs;
void *devdata;
int trips;
unsigned long trips_disabled;/* bitmap for disabled trips */
int passive_delay;
int polling_delay;
int temperature;
int last_temperature;
int emul_temperature;
int passive;
unsigned int forced_passive;
atomic_t need_update;
struct thermal_zone_device_ops *ops;
struct thermal_zone_params *tzp;
struct thermal_governor *governor;
void *governor_data;
struct list_head thermal_instances;
struct idr idr;
struct mutex lock;
struct list_head node;
struct delayed_work poll_queue;
};
struct thermal_zone_device_ops {
int (*bind) (struct thermal_zone_device *,
struct thermal_cooling_device *);
int (*unbind) (struct thermal_zone_device *,
struct thermal_cooling_device *);
int (*get_temp) (struct thermal_zone_device *, int *);
int (*get_mode) (struct thermal_zone_device *,
enum thermal_device_mode *);
int (*set_mode) (struct thermal_zone_device *,
enum thermal_device_mode);
int (*get_trip_type) (struct thermal_zone_device *, int,
enum thermal_trip_type *);
int (*get_trip_temp) (struct thermal_zone_device *, int, int *);
int (*set_trip_temp) (struct thermal_zone_device *, int, int);// 设置温度窗口
int (*get_trip_hyst) (struct thermal_zone_device *, int, int *);
int (*set_trip_hyst) (struct thermal_zone_device *, int, int);
int (*get_crit_temp) (struct thermal_zone_device *, int *);
int (*set_emul_temp) (struct thermal_zone_device *, int);
int (*get_trend) (struct thermal_zone_device *, int,
enum thermal_trend *);
int (*notify) (struct thermal_zone_device *, int,
enum thermal_trip_type);
struct thermal_zone_device:一个 thermal zone 是根据 dts 里的配置一步步解析并构建的,包含了很多信息,比如服务于该 thermal zone 的 tsadc,服务于该 thermal zone 的降温设备,该 thermal zone 所用的 governor,以及 thermal 机制工作时所需的一些参数,等等。
通常,RK 平台上 thermal zone 的 dts 配置格式如下。其它平台应该和这个大同小异,因为都要基于 thermal core 来配置。
thermal_zones: thermal-zones {
/* 一个节点对应一个thermal zone,并包含温控策略相关参数 */
soc_thermal: soc-thermal {
/* 温度高于trip-point-0指定的值,每隔20ms获取一次温度 */
polling-delay-passive = <20>; /* milliseconds */
/* 温度低于trip-point-0指定的值,每隔1000ms获取一次温度 */
polling-delay = <1000>; /* milliseconds */
/* 温度等于trip-point-1指定的值时,系统分配给cooling device的能量 */
sustainable-power = <1000>; /* milliwatts */
/* 当前thermal zone通过tsadc0获取温度 */
thermal-sensors = <&tsadc 0>;
/* trips包含不同温度阈值,不同的温控策略,配置不一定相同 */
trips {
/*
* 温控阈值,超过该值温控策略开始工作作,但不一定马上限制频率,
* power小到一定程度才开始限制频率
*/
threshold: trip-point-0 {
/* 超过70摄氏度,温控策略开始工作,并且70度也是tsadc触发中断的一个阈值 */
temperature = <70000>; /* millicelsius */
/* 温度低于temperature-hysteresis时触发中断,当前未实现,但框架要求必须填 */
hysteresis = <2000>; /* millicelsius */
type = "passive"; /* 表示超过该温度值时,使用polling-delay-passive */
};
/* 温控目标温度,期望通过降频使得芯片不超过该值 */
target: trip-point-1 {
/* 期望通过降频使得芯片不超过85摄氏度,并且85度也是tsadc触发中断的一个阈值 */
temperature = <85000>; /* millicelsius */
/* 温度低于temperature-hysteresis时触发中断,当前未实现,但框架要求必须填 */
hysteresis = <2000>; /* millicelsius */
type = "passive"; /* 表示超过该温度值时,使用polling-delay-passive */
};
/* 过温保护阈值,如果降频后温度仍然上升,那么超过该值后,让系统重启 */
soc_crit: soc-crit {
/* 超过115摄氏度重启,并且115度也是tsadc触发中断的一个阈值 */
temperature = <115000>; /* millicelsius */
/* 温度低于temperature-hysteresis时触发中断,当前未实现,但框架要求必须填 */
hysteresis = <2000>; /* millicelsius */
type = "critical"; /* 表示超过该温度值时,重启 */
};
};
/* cooling device配置节点,每个子节点代表一个cooling device */
cooling-maps {
map0 {
/*
* 表示在target trip下,该cooling device才起作用,
* 对于power allocater策略必须填target
*/
trip = <&target>;
/* A53做为cooloing device, THERMAL_NO_LIMIT不起作用,但必须填 */
cooling-device = <&cpu_l0 THERMAL_NO_LIMIT THERMAL_NO_LIMIT>;
/* 计算功耗时乘以4096/1024倍,用于调整降频顺序和尺度 */
contribution = <4096>;
};
map1 {
/*
* 表示在target trip下,该cooling device才起作用,
* 对于power allocater策略必须填target
*/
trip = <&target>;
/* A72做为cooloing device, THERMAL_NO_LIMIT不起作用,但必须填 */
cooling-device = <&cpu_b0 THERMAL_NO_LIMIT THERMAL_NO_LIMIT>;
/* 计算功耗时乘以1024/1024倍,用于调整降频顺序和尺度 */
contribution = <1024>;
};
map2 {
/*
* 表示在target trip下,该cooling device才起作用,
* 对于power allocater策略必须填target
*/
trip = <&target>;
/* GPU做为cooloing device, THERMAL_NO_LIMIT不起作用,但必须填 */
cooling-device = <&gpu THERMAL_NO_LIMIT THERMAL_NO_LIMIT>;
/* 计算功耗时乘以4096/1024倍,用于调整降频顺序和尺度 */
contribution = <4096>;
};
};
};
/* 一个节点对应一个thermal zone,并包含温控策略相关参数,当前thermal zone只用于获取温度 */
gpu_thermal: gpu-thermal {
/* 包含温控策略配置的情况下才起作用,框架要求必须填 */
polling-delay-passive = <100>; /* milliseconds */
/* 每隔1000ms获取一次温度 */
polling-delay = <1000>; /* milliseconds */
/* 当前thermal zone通过tsadc1获取温度 */
thermal-sensors = <&tsadc 1>;
};
};
在probe中完成注册:
sensor->tz = thermal_zone_of_sensor_register(&pdev->dev,
id, sensor, &combine_ops);
温度获取流程:
sunxi_combine_get_temp //sunxi_ths_combine.c
-->ret = controller->ops->get_temp(controller,sensor_id, &temp);
sunxi_ths_get_temp // sunxi_ths_core.c
-->t = ths_driver_get_temp(ths_data, id);
ths_driver_reg_to_temp(reg_data, id, ths_data->ths_driver_version, ths_data->ths_coefficent->calcular_para); //sunxi_ths_driver.c
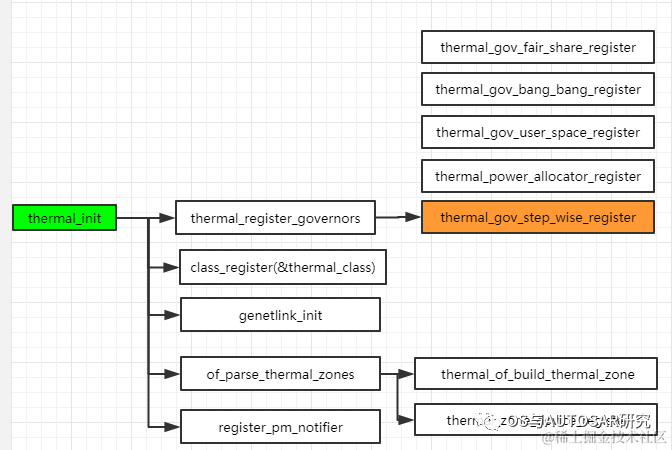
6. thermal core
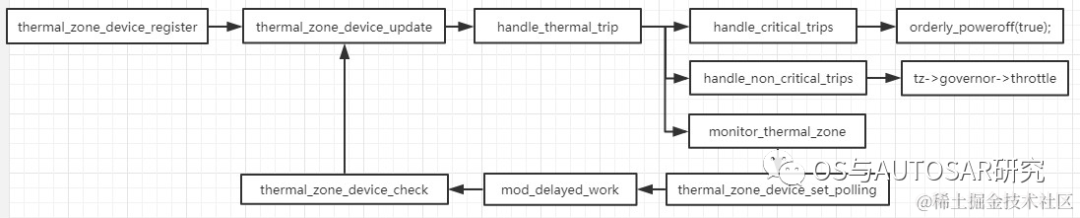
在thermar core作为中枢注册governor,注册Thermal类,并且基于Device Tree注册Thermal Zone;提供Thermal zone注册函数,Cooling Device注册函数,提供将Cooling设备绑定到Zone的函数,一个Thermal Zone可以有多个Cooling设备;同时还提供一个核心函数Thermal_zone_deviceupdate作为Thermal中断处理函数和轮询函数,轮询时间会根据不同Trip Delay调节
thermal轮询流程:
在thermal core中通过不断的轮询来检测温度变化,如果温度没有达到crital则调用governor的throttle,通过governor的throttle决定下一次轮询的时间;如果温度为crital则走关机流程;
7. SoC硬件中设计
一般传感器使用PVT模块实现,PVTC中会包含多个temperature sensors、Voltage Monitor、Process Detectors PVT包含以下几种传感器:
Thermal Sensing(TS):热传感,精度高,集成方便。支持功率优化和可靠性
Distributed Thermal Sensing(DTS):分布式热传感。支持thermal mapping,高度精细的布放,低延时
Supply Monitoring(VM):供电监控,测量多个域的电源电压、验证配电网络、实施静态和动态IR压降分析
Process Monitoring(PD):工艺监控,在大规模量产或者单个芯片生命周期,了解硅片速度变化(slow,fast,typical)。提供功率优化和老化监控
另外一种方式是使用单独的thermal sensor,通过I2C slave接入MCU核心。CPU核心可以通过I2C读取稳定,可以防止内部PVT损坏的影响。
后记:
电源管理相关的知识看似不多,但是详细研究起来,根本研究不完。有时候要做一个件事情,不一定要追求完美,要确定好要做到的程度,比如公司里面调试某个功能,那么就必须研究透彻,但是相关的知识点自学,不需要实际动手调试,那就要了解框架即可,我们不可能什么活都干一遍,但是很多活不干一遍是不能体会其精髓的。确定好度很重要,防止陷入进去,同时防止走马观花没有任何效果的形式主义。
电源管理系列刚开始都是作者参与调试的代码,后来的就是扩展学习了,虽然不进行代码调试,但是也力求把框架搞明白,做个记录。以后或许那天要调试了再拿出来可以看看。
-
鸿蒙开发设备管理:ohos.thermal 热管理2024-07-05 1119
-
电源管理入门-芯片设计中的电源管理介绍2023-12-06 5399
-
电源管理入门:驱动Runtime PM管理2023-11-29 5275
-
热管理系统建模案例:各个回路的搭建2023-04-13 3735
-
热管理系统建模案例:模型工具、热管理系统2023-04-04 3730
-
电动汽车热管理系统和性能2021-04-23 3886
-
微型热管理和电源管理怎么解决散热设计的难题?2020-03-10 3004
-
PCB材料对热管理有什么影响?2019-08-29 2832
-
微波射频设计的热管理有什么影响?2019-08-28 2680
-
功率MOSFET的高效热管理2019-02-03 2204
-
热管理设计资源2016-05-24 695
-
【dln团队】DR-热管理2014-12-30 3109
-
Mouser与Nextreme合作开发用于发电的电源热管理及能源采集方案2011-11-17 1026
全部0条评论

快来发表一下你的评论吧 !

