

R-Rhealstone框架使用教程
电子说
描述
本篇文章描述基于Rhealstone的系统实时性的测量基准的框架--R-Rhealstone框架。
在嵌入式软件设计和集成中,实时多任务操作系统的性能分析是至关重要的,它需要保证应用的时间限制得到满足,即是运行时间不能超过应用的时间限制。为了选择满足用于特定应用的嵌入式系统的一个适当的操作系统,我们需要对操作系统服务进行分析。这些操作系统服务是由形成性能指标的参数确定的,既定的性能指标包括上下文切换时间、任务抢占时间、中断延迟时间、信号量混洗时间、死锁解除时间、信息传输延迟。
关于实时操作系统对性能指标进行分析,是为了选择满足用于特定应用的嵌入式系统的最优的操作系统。
Rhealstone
Rhealstone是系统实时性的测量基准之一,Rhealstone性能基准程序是实时系统的六个关键操作的时间量进行操作,这六个关键操作是:上下文切换时间、任务抢占时间、中断延迟时间、信号量混洗时间、死锁解除时间、信息传输延迟。这六项操作作为Rhealstone的六个组件,每个组件被单独测量。然后将经验结果合并为单一的测量值,即是Rhealstone值。
测量Rhealstone值方式:
| 序号 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| 方式 1 | 通用Rhealstone |
| 方式 2 | 每个组件应用于具体应用程序的特定Rhealstone |
Rhealstone性能基准程的缺点:
| 序号 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| 缺点 1 | 测量的是平均时间,而不是最坏值 |
| 缺点 2 | 后的结论是加权平均值,没有给出确定权值的依据 |
R-Rhealstone框架
设计R-Rhealstone框架的目的:为了能让对比的系统实时性的测量的一致性,必须保证同一个环境,解除差异性带来测量干扰,所以R-Rhealstone框架提供了操作系统适配层,统一适配不同操作系统的各个接口,目的可以达到上层调用层次一致。
上下文切换时间
描述:
上下文切换时间也称任务切换时间(task switching time),定义为系统在两个独立的、处于就绪态并且具有相同优先级的任务之间切换所需要的时间。它包括三个部分,即保存当前任务上下文的时间、调度程序选中新任务的时间和恢复新任务上下文的时间。切换所需的时间主要取决于保存任务上下文所用的数据结构以及操作系统采用的调度算法的效率。产生任务切换的原因可以是资源可得,信号量的获取等。任务切换是任一多任务系统中基本效率的测量点,它是同步的,非抢占的,实时控制软件实现了一种基于同等优先级任务的时间片轮转算法。影响任务切换的因素有:主机CPU的结构,指令集以及CPU特性。
任务切换过程增加了应用程序的额外负荷。CPU的内部寄存器越多,额外负荷就越重。任务切换所需要的时间取决于CPU有多少寄存器要入栈。实时内核的性能不应该以每秒钟能做多少次任务切换来评价,RTOS中通常是1微秒左右。
流程:
原理:创建两个同等优先级的任务,两个任务相互切换多次,最后求平均值。
注意:①需要减去多次切换的循环时间(loop_overhead);②需要减去主动让CPU执行时间(dir_overhead)
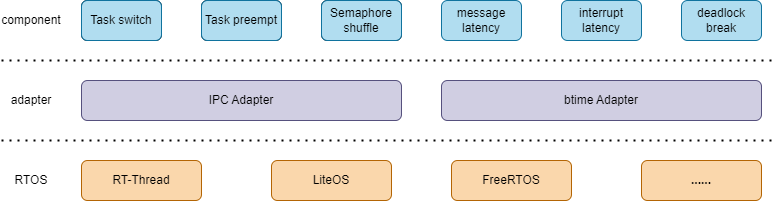
时间计算公式:
total_time:多次上下文切换总时间
loop_overhead:多次切换的循环时间
iterations:切换的次数
dir_overhead:调用让出CPU接口的时间

代码:
#include "rst.h"
#include "rst_ipc.h"
#include "rst_btime.h"
static float loop_overhead = 0.0;
static float dir_overhead = 0.0;
static float telapsed = 0.0;
static uint32_t count1, count2;
static rst_task_id rst_task1 = NULL;
static rst_task_id rst_task2 = NULL;
static rst_task_attr rst_task1_attr = {
.name = "task1",
#if RST_BIG_NUM_HIGH_PRIORITY
.priority = RST_TASK_HIGHEST_PRIORITY - 1,
#else
.priority = RST_TASK_HIGHEST_PRIORITY + 1,
#endif
.stack_size = RST_TASK_STACK_SIZE,
};
static rst_task_attr rst_task2_attr = {
.name = "task2",
#if RST_BIG_NUM_HIGH_PRIORITY
.priority = RST_TASK_HIGHEST_PRIORITY - 1,
#else
.priority = RST_TASK_HIGHEST_PRIORITY + 1,
#endif
.stack_size = RST_TASK_STACK_SIZE,
};
static void rst_task2_func(void *arg);
static void rst_task1_func(void *arg)
{
rst_task_create(&rst_task2, rst_task2_func, NULL, &rst_task2_attr);
if(rst_task2 == NULL)
{
RST_LOGE("RST: task2 create failed");
rst_task_delete(NULL);
return;
}
/* Yield processor so second task can startup and run */
rst_task_yield();
for(count1 = 0; count1 < RST_BENCHMARKS_COUNT; count1++)
{
rst_task_yield();
}
rst_task_delete(NULL);
}
static void rst_task2_func(void *arg)
{
/* All overhead accounted for now, we can begin benchmark */
rst_benchmark_time_init();
for(count2 = 0; count2 < RST_BENCHMARKS_COUNT; count2++)
{
rst_task_yield();
}
telapsed = rst_benchmark_time_read();
RST_PRINT_TIME(
"R-Rhealstone: task switch time",
telapsed, /* Total time of all benchmarks */
(RST_BENCHMARKS_COUNT * 2) - 1, /* ( BENCHMARKS * 2 ) - 1 total benchmarks */
loop_overhead, /* Overhead of loop */
dir_overhead /* Overhead of rst_task_yield directive */
);
rst_task_delete(NULL);
}
rst_status rst_task_switch_init(void)
{
/* find overhead of routine (no task switches) */
rst_benchmark_time_init();
for(count1 = 0; count1 < RST_BENCHMARKS_COUNT; count1 ++)
{
}
for(count1 = 0; count1 < RST_BENCHMARKS_COUNT; count1 ++)
{
}
loop_overhead = rst_benchmark_time_read();
/* find overhead of rtems_task_wake_after call (no task switches) */
rst_benchmark_time_init();
rst_task_yield();
dir_overhead = rst_benchmark_time_read();;
rst_task_create(&rst_task1, rst_task1_func, NULL, &rst_task1_attr);
if(rst_task1 == NULL)
{
RST_LOGE("RST: task1 create failed");
return RST_ERROR;
}
return RST_OK;
}
任务抢占时间
描述:
抢占时间即系统将控制权从低优先级的任务转移到高优先级任务所花费的时间。为了对任务进行抢占,系统必须首先识别引起高优先级任务就绪的事件,比较两个任务的优先级,最后进行任务的切换,所以抢占时间中包括了任务切换时间。
它和任务切换有些类似,但是抢占时间通常花费时间更长。这是因为执行中首先要确认唤醒事件,并评估正在运行的任务和请求运行的任务的优先级高低,然后才决定是否切换任务。实质上,所有的多处理任务可以在执行期间动态分配优先级,所以,抢占时间也是衡量实时性能的重要指标。
流程:
原理:创建两个任务,任务1优先级比任务2优先级低,两个任务进行抢占多次,最后求平均值。
注意:①需要减去多次任务抢占的循环时间(loop_overhead);②需要减去挂起任务所需要的时间(dir_overhead)
时间计算公式:
total_time:多次任务抢占总时间
loop_overhead:多次任务抢占的循环时间
iterations:任务抢占的次数
switch_overhead:挂起任务所需要的时间
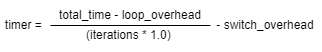
代码:
#include "rst.h"
#include "rst_ipc.h"
#include "rst_btime.h"
static float loop_overhead = 0.0;
static float switch_overhead = 0.0;
static float telapsed = 0.0;
static uint32_t count;
static rst_task_id rst_task1 = NULL;
static rst_task_id rst_task2 = NULL;
static rst_task_attr rst_task1_attr = {
.name = "task1",
#if RST_BIG_NUM_HIGH_PRIORITY
.priority = RST_TASK_HIGHEST_PRIORITY - 3,
#else
.priority = RST_TASK_HIGHEST_PRIORITY + 3,
#endif
.stack_size = RST_TASK_STACK_SIZE,
};
static rst_task_attr rst_task2_attr = {
.name = "task2",
#if RST_BIG_NUM_HIGH_PRIORITY
.priority = RST_TASK_HIGHEST_PRIORITY - 1,
#else
.priority = RST_TASK_HIGHEST_PRIORITY + 1,
#endif
.stack_size = RST_TASK_STACK_SIZE,
};
static void rst_task2_func(void *arg);
static void rst_task1_func(void *arg)
{
/* Start up task2, get preempted */
rst_task_create(&rst_task2, rst_task2_func, NULL, &rst_task2_attr);
if(rst_task2 == NULL)
{
RST_LOGE("RST: task2 create failed");
rst_task_delete(NULL);
return;
}
switch_overhead = rst_benchmark_time_read();
rst_benchmark_time_init();
/* Benchmark code */
for(count = 0; count < RST_BENCHMARKS_COUNT; count++)
{
rst_task_resume(rst_task2); /* Awaken task2, preemption occurs */
}
rst_task_delete(NULL);
}
static void rst_task2_func(void *arg)
{
/* Find overhead of task switch back to task1 (not a preemption) */
rst_benchmark_time_init();
rst_task_suspend(rst_task2);
/* Benchmark code */
for(; count < RST_BENCHMARKS_COUNT - 1;)
{
rst_task_suspend(rst_task2);
}
telapsed = rst_benchmark_time_read();
RST_PRINT_TIME(
"R-Rhealstone: task preempt time",
telapsed, /* Total time of all benchmarks */
RST_BENCHMARKS_COUNT - 1, /* BENCHMARKS - 1 total benchmarks */
loop_overhead, /* Overhead of loop */
switch_overhead /* Overhead of task switch back to task1 */
);
rst_task_delete(NULL);
}
rst_status rst_task_preempt_init(void)
{
/* Find loop overhead */
rst_benchmark_time_init();
for(count = 0; count < ((RST_BENCHMARKS_COUNT * 2) - 1); count++)
{
}
loop_overhead = rst_benchmark_time_read();
rst_task_create(&rst_task1, rst_task1_func, NULL, &rst_task1_attr);
if(rst_task1 == NULL)
{
RST_LOGE("RST: task1 create failed");
return RST_ERROR;
}
return RST_OK;
}
中断延迟时间
描述:
中断延迟时间是指从接收到中断信号到操作系统做出响应,并完成进入中断服务例程所需要的时间。多任务操作系统中,中断处理首先进入一个中断服务的总控程序,然后才进入驱动程序的ISR。
中断延迟时间=最大关中断时间+硬件开始处理中断到开始执行中断服务例程第一条指令之间的时间。
硬件开始处理中断到开始执行中断服务例程的第一条指令之间的时间由硬件决定,所以,中断延迟时间的长短主要取决于最大关中断的时间。硬实时操作系统的关中断时间通常是几微秒,而Linux最坏可达几毫秒。
流程:
原理:创建一个任务,任务执行主动触发中断,执行完中断服务程序返回,统计其时间。
注意:①需要减去读取时间接口的耗时时间(timer_overhead);
时间计算公式:
isr_enter_time:多次任务抢占总时间
iterations:任务抢占的次数
timer_overhead:读取时间接口的耗时时间
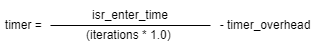
代码:
#include "rst.h"
#include "rst_ipc.h"
#include "rst_btime.h"
static float timer_overhead = 0.0;
static float isr_enter_time = 0.0;
static rst_task_id rst_task1 = NULL;
static rst_task_attr rst_task1_attr = {
.name = "task1",
#if RST_BIG_NUM_HIGH_PRIORITY
.priority = RST_TASK_LOWEST_PRIORITY + 1,
#else
.priority = RST_TASK_LOWEST_PRIORITY - 1,
#endif
.stack_size = RST_TASK_STACK_SIZE,
};
static void rst_isr_handler(void *param)
{
isr_enter_time = rst_benchmark_time_read();
}
static void rst_task1_func(void *arg)
{
rst_isr_install(RST_ISR_NUM, rst_isr_handler, NULL);
/* Benchmark code */
rst_benchmark_time_init();
/* goes to Isr_handler */
rst_isr_trigger(RST_ISR_NUM);
RST_PRINT_TIME(
"R-Rhealstone: interrupt latency time",
isr_enter_time,
1, /* Only Rhealstone that isn't an average */
timer_overhead,
0
);
rst_task_delete(NULL);
}
rst_status rst_interrupt_latency_init(void)
{
rst_task_create(&rst_task1, rst_task1_func, NULL, &rst_task1_attr);
if(rst_task1 == NULL)
{
RST_LOGE("RST: task1 create failed");
return RST_ERROR;
}
rst_benchmark_time_init();
rst_benchmark_time_read();
rst_benchmark_time_init();
timer_overhead = rst_benchmark_time_read();
return RST_OK;
}
信号量混洗时间
描述:
信号量混洗时间(semaphore shuffling time),是指从一个任务释放信号量到另一个等待该信号量的任务被激活的时间延迟。在RTOS中,通常有许多任务同时竞争某一共享资源,基于信号量的互斥访问保证了任一时刻只有一个任务能够访问公共资源。信号量混洗时间反映了与互斥有关的时间开销,因此也是衡量RTOS实时性能的一个重要指标。
流程:
原理:创建一个信号量和两个相同优先级的任务。代码需要执行两次,第一次信号量不介入调度,计算任务切换的时间,第二次多次循环,信号量接入调度,信号量在两个任务中ping-pong执行,计算总时间。
注意:①需要减去任务切换的时间(switch_overhead);
时间计算公式:
telapsed:多次信号量混洗总时间
iterations:信号量混洗的次数
switch_overhead:切换的时间

代码:
#include "rst.h"
#include "rst_ipc.h"
#include "rst_btime.h"
static float switch_overhead = 0.0;
static float telapsed = 0.0;
static uint32_t count = 0;
static uint32_t sem_exe = 1;
static rst_task_id rst_task1 = NULL;
static rst_task_id rst_task2 = NULL;
static rst_sem_id rst_sem = NULL;
static rst_task_attr rst_task1_attr = {
.name = "task1",
#if RST_BIG_NUM_HIGH_PRIORITY
.priority = RST_TASK_HIGHEST_PRIORITY - 1,
#else
.priority = RST_TASK_HIGHEST_PRIORITY + 1,
#endif
.stack_size = RST_TASK_STACK_SIZE,
};
static rst_task_attr rst_task2_attr = {
.name = "task2",
#if RST_BIG_NUM_HIGH_PRIORITY
.priority = RST_TASK_HIGHEST_PRIORITY - 1,
#else
.priority = RST_TASK_HIGHEST_PRIORITY + 1,
#endif
.stack_size = RST_TASK_STACK_SIZE,
};
static void rst_task2_func(void *arg);
static void rst_task1_func(void *arg)
{
/* Start up task2, yield so it can run */
rst_task_create(&rst_task2, rst_task2_func, NULL, &rst_task2_attr);
if(rst_task2 == NULL)
{
RST_LOGE("RST: task2 create failed");
rst_task_delete(NULL);
return;
}
rst_task_yield();
/* Benchmark code */
for ( ; count < RST_BENCHMARKS_COUNT; ) {
if ( sem_exe == 1 )
{
rst_sem_lock(rst_sem, (rst_time_t)RST_WAIT_FOREVER);
rst_task_yield();
rst_sem_unlock(rst_sem);
rst_task_yield();
}
}
rst_task_delete(NULL);
}
static void rst_task2_func(void *arg)
{
/* Benchmark code */
rst_benchmark_time_init();
for(count = 0; count < RST_BENCHMARKS_COUNT; count++)
{
if(sem_exe == 1)
{
rst_sem_lock(rst_sem, (rst_time_t)RST_WAIT_FOREVER);
rst_task_yield();
rst_sem_unlock(rst_sem);
rst_task_yield();
}
}
telapsed = rst_benchmark_time_read();
if(sem_exe == 0)
{
switch_overhead = telapsed;
}
else
{
RST_PRINT_TIME(
"R-Rhealstone: senaphore shuffle time",
telapsed, /* Total time of all benchmarks */
(RST_BENCHMARKS_COUNT * 2), /* Total number of times deadlock broken*/
switch_overhead, /* Overhead of loop and task switches */
0
);
}
rst_task_delete(NULL);
}
rst_status rst_semaphore_shuffle_init(void)
{
rst_sem = rst_sem_create(1);
if(rst_sem == NULL)
{
RST_LOGE("RST: sem create failed");
return RST_ERROR;
}
__RESTART:
sem_exe = !sem_exe;
/* Get time of benchmark with no semaphore shuffling */
rst_task_create(&rst_task1, rst_task1_func, NULL, &rst_task1_attr);
if(rst_task1 == NULL)
{
RST_LOGE("RST: task1 create failed");
rst_sem_delete(rst_sem);
return RST_ERROR;
}
/* Get time of benchmark with semaphore shuffling */
if(sem_exe == 0)
{
goto __RESTART;
}
return RST_OK;
}
死锁解除时间
描述:
死锁解除时间(deadlock breaking time),即系统解开处于死锁状态的多个任务所需花费的时间。死锁解除时间反映了RTOS解决死锁的算法的效率。
流程:
原理:创建一个信号量和三个任务,优先级排序:任务1 < 任务2 < 任务3。代码需要执行两次,第一次信号量不介入调度,计算任务3切换到任务2,任务2切换到任务1得时间(即从高优先级切换到低优先级得时间),第二次多次循环,信号量接入调度,任务3死锁,任务2唤醒任务1,任务1解除死锁,通过统计多次,求平均值。
注意:①需要减去任务切换的时间(switch_overhead);
时间计算公式:
telapsed:多次死锁解除总时间
iterations:死锁解除的次数
switch_overhead:任务切换的时间
lock_overhead:调用信号量持有接口所需要得时间
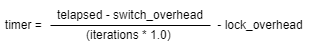
代码:
#include "rst.h"
#include "rst_ipc.h"
#include "rst_btime.h"
static float switch_overhead = 0.0;
static float lock_overhead = 0.0;
static float telapsed = 0.0;
static uint32_t count = 0;
static uint32_t sem_exe = 1;
static rst_task_id rst_task1 = NULL;
static rst_task_id rst_task2 = NULL;
static rst_task_id rst_task3 = NULL;
static rst_sem_id rst_sem = NULL;
static rst_task_attr rst_task1_attr = {
.name = "task1",
#if RST_BIG_NUM_HIGH_PRIORITY
.priority = RST_TASK_HIGHEST_PRIORITY - 1,
#else
.priority = RST_TASK_HIGHEST_PRIORITY + 1,
#endif
.stack_size = RST_TASK_STACK_SIZE,
};
static rst_task_attr rst_task2_attr = {
.name = "task2",
#if RST_BIG_NUM_HIGH_PRIORITY
.priority = RST_TASK_HIGHEST_PRIORITY - 3,
#else
.priority = RST_TASK_HIGHEST_PRIORITY + 3,
#endif
.stack_size = RST_TASK_STACK_SIZE,
};
static rst_task_attr rst_task3_attr = {
.name = "task3",
#if RST_BIG_NUM_HIGH_PRIORITY
.priority = RST_TASK_HIGHEST_PRIORITY - 5,
#else
.priority = RST_TASK_HIGHEST_PRIORITY + 5,
#endif
.stack_size = RST_TASK_STACK_SIZE,
};
static void rst_task1_func(void *arg)
{
/* All tasks have had time to start up once TA01 is running */
/* Benchmark code */
rst_benchmark_time_init();
for(count = 0; count < RST_BENCHMARKS_COUNT; count++)
{
if(sem_exe == 1)
{
/* Block on call */
rst_sem_lock(rst_sem, (rst_time_t)RST_WAIT_FOREVER);
/* Release semaphore immediately after obtaining it */
rst_sem_unlock(rst_sem);
}
/* Suspend self, go to task2 */
rst_task_suspend(rst_task1);
}
telapsed = rst_benchmark_time_read();
if(sem_exe == 0)
{
switch_overhead = telapsed;
}
else
{
RST_PRINT_TIME(
"R-Rhealstone: deadlock break time",
telapsed, /* Total time of all benchmarks */
RST_BENCHMARKS_COUNT, /* Total number of times deadlock broken*/
switch_overhead, /* Overhead of loop and task switches */
lock_overhead
);
}
rst_task_delete(NULL);
}
static void rst_task2_func(void *arg)
{
/* Start up task1, get preempted */
rst_task_create(&rst_task1, rst_task1_func, NULL, &rst_task1_attr);
if(rst_task1 == NULL)
{
RST_LOGE("RST: task1 create failed");
rst_task_delete(NULL);
return;
}
/* Benchmark code */
for( ; count < RST_BENCHMARKS_COUNT; )
{
/* Suspend self, go to task1 */
rst_task_suspend(rst_task2);
/* Wake up task1, get preempted */
rst_task_resume(rst_task1);
}
rst_task_delete(NULL);
}
static void rst_task3_func(void *arg)
{
if(sem_exe == 1)
{
/* Low priority task holds mutex */
rst_sem_lock(rst_sem, (rst_time_t)RST_WAIT_FOREVER);
}
/* Start up task2, get preempted */
rst_task_create(&rst_task2, rst_task2_func, NULL, &rst_task2_attr);
if(rst_task2 == NULL)
{
RST_LOGE("RST: task2 create failed");
rst_task_delete(NULL);
return;
}
for( ; count < RST_BENCHMARKS_COUNT; )
{
if(sem_exe == 1)
{
/* Preempted by task1 upon release */
rst_sem_unlock(rst_sem);
/* Prepare for next Benchmark */
rst_sem_lock(rst_sem, (rst_time_t)RST_WAIT_FOREVER);
}
/* Wake up task2, get preempted */
rst_task_resume(rst_task2);
}
rst_task_delete(NULL);
}
rst_status rst_deadlock_break_init(void)
{
rst_sem = rst_sem_create(1);
if(rst_sem == NULL)
{
RST_LOGE("RST: sem create failed");
return RST_ERROR;
}
/* find overhead of obtaining semaphore */
rst_benchmark_time_init();
rst_sem_lock(rst_sem, (rst_time_t)RST_WAIT_FOREVER);
lock_overhead = rst_benchmark_time_read();
rst_sem_unlock(rst_sem);
__RESTART:
sem_exe = !sem_exe;
/* Get time of benchmark with no semaphores involved, i.e. find overhead */
rst_task_create(&rst_task3, rst_task3_func, NULL, &rst_task3_attr);
if(rst_task3 == NULL)
{
RST_LOGE("RST: task3 create failed");
rst_sem_delete(rst_sem);
return RST_ERROR;
}
/* Get time of benchmark with semaphores */
if(sem_exe == 0)
{
goto __RESTART;
}
rst_sem_delete(rst_sem);
return RST_OK;
}
信息传输延迟
描述:
信息传输延迟(datagram throuShput time),指一个任务通过调用RTOS的消息队列,把数据传送到另一个任务去时,每秒可以传送的字节数。
流程:
原理:创建一个消息队列和两个任务,优先级排序:任务1 < 任务2。任务1负责发送数据,任务2负责接收数据,执行多次,求平均值
注意:①需要减去调用消息队列接收函数的时间(receive_overhead);
时间计算公式:
telapsed:多次信息传输总时间
iterations:死锁解除的次数
loop_overhead:多次循环的时间
receive_overhead:调用消息队列接收函数的时间

代码:
#include "rst.h"
#include "rst_ipc.h"
#include "rst_btime.h"
#define RST_QUEUE_BUFF_SIZE 4
static float loop_overhead = 0.0;
static float receive_overhead = 0.0;
static float telapsed = 0.0;
static uint32_t count;
static rst_task_id rst_task1 = NULL;
static rst_task_id rst_task2 = NULL;
static rst_queue_id rst_queue = NULL;
static int queue_buff[RST_QUEUE_BUFF_SIZE] = {0};
static rst_task_attr rst_task1_attr = {
.name = "task1",
#if RST_BIG_NUM_HIGH_PRIORITY
.priority = RST_TASK_HIGHEST_PRIORITY - 3,
#else
.priority = RST_TASK_HIGHEST_PRIORITY + 3,
#endif
.stack_size = RST_TASK_STACK_SIZE,
};
static rst_task_attr rst_task2_attr = {
.name = "task2",
#if RST_BIG_NUM_HIGH_PRIORITY
.priority = RST_TASK_HIGHEST_PRIORITY - 1,
#else
.priority = RST_TASK_HIGHEST_PRIORITY + 1,
#endif
.stack_size = RST_TASK_STACK_SIZE,
};
static void rst_task2_func(void *arg);
static void rst_task1_func(void *arg)
{
/* Put a message in the queue so recieve overhead can be found. */
rst_queue_send(rst_queue,
(const void *)queue_buff,
(uint32_t)sizeof(queue_buff),
(rst_time_t)RST_WAIT_FOREVER);
/* Start up second task, get preempted */
rst_task_create(&rst_task2, rst_task2_func, NULL, &rst_task2_attr);
if(rst_task2 == NULL)
{
RST_LOGE("RST: task2 create failed");
rst_task_delete(NULL);
return;
}
for(; count < RST_BENCHMARKS_COUNT; count++)
{
rst_queue_send(rst_queue,
(const void *)queue_buff,
(uint32_t)sizeof(queue_buff),
(rst_time_t)RST_WAIT_FOREVER);
}
rst_task_delete(NULL);
}
static void rst_task2_func(void *arg)
{
/* find recieve overhead - no preempt or task switch */
rst_benchmark_time_init();
rst_queue_recv(rst_queue, (void *)queue_buff,
(uint32_t)sizeof(queue_buff));
receive_overhead = rst_benchmark_time_read();
/* Benchmark code */
rst_benchmark_time_init();
for(count = 0; count < RST_BENCHMARKS_COUNT - 1; count++)
{
rst_queue_recv(rst_queue, (void *)queue_buff,
(uint32_t)sizeof(queue_buff));
}
telapsed = rst_benchmark_time_read();
RST_PRINT_TIME(
"R-Rhealstone: message latency time",
telapsed, /* Total time of all benchmarks */
RST_BENCHMARKS_COUNT - 1, /* BENCHMARKS - 1 total benchmarks */
loop_overhead, /* Overhead of loop */
receive_overhead /* Overhead of recieve call and task switch */
);
rst_task_delete(NULL);
}
rst_status rst_message_latency_init(void)
{
rst_queue = rst_queue_create(sizeof(queue_buff), 1);
if(rst_queue == NULL)
{
RST_LOGE("RST: queue create failed");
return RST_ERROR;
}
rst_benchmark_time_init();
for(count = 0; count < (RST_BENCHMARKS_COUNT - 1); count++)
{
}
loop_overhead = rst_benchmark_time_read();
rst_task_create(&rst_task1, rst_task1_func, NULL, &rst_task1_attr);
if(rst_task1 == NULL)
{
RST_LOGE("RST: task1 create failed");
rst_queue_delete(rst_queue);
return RST_ERROR;
}
return RST_OK;
}
RTOS对比结论
对比环境说明
| 项 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| 芯片 |
芯片型号:stm32f401 芯片架构:Cortex-M4 主频:84 MHz |
| 开发环境 | KEIL 5.x |
| 工具链 | ARMCC |
对比结果说明
| 对比项 | RT-Thread | LiteOS | FreeRTOS | TobudOS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 上下文切换 | 2.594596 us | 6.739740 us | 1.049049 us | 2.343343 |
| 任务抢占 | 7.360721 us | 7.603206 us | 2.715431 us | 4.523046 us |
| 中断延迟 | 2.000000 us | 1.000000 us | 1.000000 us | 1.000000 us |
| 信号量混洗 | 23.829000 us | 25.588000 us | 19.496000 us | 18.451000 us |
| 死锁解除 | 18.108000 us | 18.074000 us | 21.522000 us | 31.606000 us |
| 信息传输延迟 | 7.749499 us | 7.390782 us | 7.298597 us | 3.446894 us |
总结
作者测试过程采用定时器计数器是1us,精度上有所欠缺,策略结果大致对比
中断延时部分,RT-Thread的中断是有框架的,而LiteOS和FreeRTOS直接使用STM32的HAL库,时间差异在框架的耗时
FreeRTOS在本次的对比的优势比较明显,除了死锁解除稍微逊色一点,其他的持平或由于RT-Thread和LiteOS
LiteOS在本次对比表现最差,尤其是上下文切换的耗时是RT-Thread和FreeRTOS的2~3倍。
说明:该框架目前已经适配作为RT-Thread的软件包,可以通过软件包体验其功能
审核编辑:汤梓红
-
英特尔(R)动态平台和散热框架解决方案ESIF(8.1.10600.150)类型错误?2018-11-05 23511
-
LiteOS通信模组教程04-深度剖析LiteOS的AT框架2020-02-26 3918
-
JS应用开发框架组件2021-04-23 2098
-
什么是框架?为什么要有框架2021-11-09 1716
-
ARM时钟框架与编程实现概述2022-05-25 4309
-
基于SSH框架的图书管理应用框架研究张敏2017-03-17 734
-
微软发布开源框架驱动程序模块新框架2018-08-22 1500
-
漫谈MCU程序框架2021-10-28 572
-
用于实例分割的Mask R-CNN框架2022-04-13 3484
-
八种主流深度学习框架的介绍2022-04-26 9857
-
智能上位机框架2023-05-08 414
-
fastapi框架原理及应用2023-07-18 1426
-
深度学习框架是什么?深度学习框架有哪些?2023-08-17 3861
-
如何选择RTOS?使用R-Rhealstone框架评估2024-02-20 1848
-
铅框架 - Fusheng R970 RoHS/Halogen测试报告2024-01-31 305
全部0条评论

快来发表一下你的评论吧 !

