

鸿蒙开发之发动画篇
电子说
描述
动画的原理是在一个时间段内,多次改变UI外观,由于人眼会产生视觉暂留,所以最终看到的就是一个“连续”的动画。UI的一次改变称为一个动画帧,对应一次屏幕刷新,而决定动画流畅度的一个重要指标就是帧率FPS(Frame Per Second),即每秒的动画帧数,帧率越高则动画就会越流畅。
ArkUI中,产生动画的方式是改变属性值且指定动画参数。动画参数包含了如动画时长、变化规律(即曲线)等参数。当属性值发生变化后,按照动画参数,从原来的状态过渡到新的状态,即形成一个动画。
ArkUI提供的动画能力按照页面的分类方式,可分为页面内的动画和页面间的动画。如下图所示,页面内的动画指在一个页面内即可发生的动画,页面间的动画指两个页面跳转时才会发生的动画。
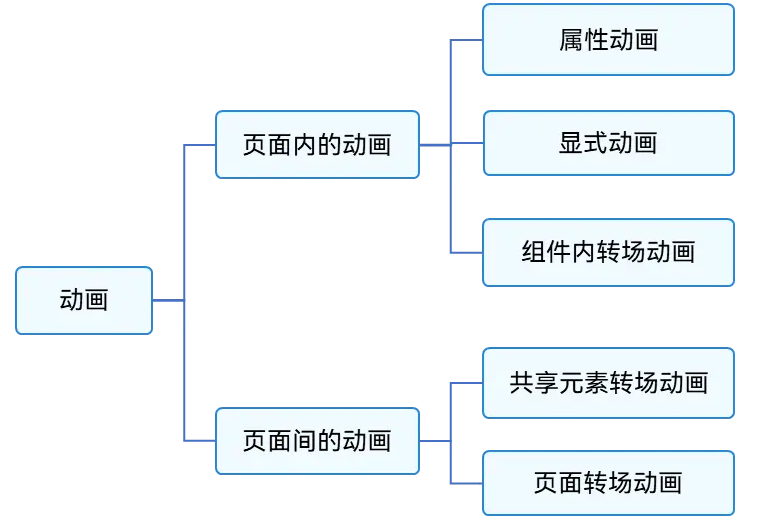
图1 按照页面分类的动画
如果按照基础能力分,可分为属性动画、显式动画、转场动画三部分。如下图所示。
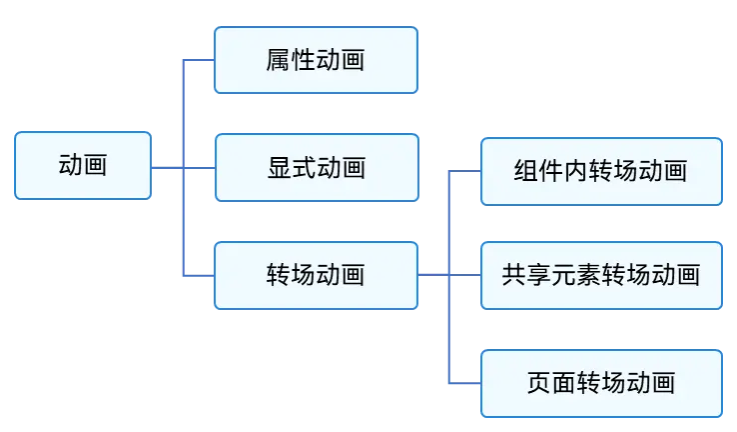
图2 按照基础能力分类的动画
使用显式动画产生布局更新动画
显式动画的接口为:
animateTo(value: AnimateParam, event: () = > void): void
第一个参数指定动画参数,第二个参数为动画的闭包函数。
以下是使用显式动画产生布局更新动画的示例。示例中,当Column组件的alignItems属性改变后,其子组件的布局位置结果发生变化。只要该属性是在animateTo的闭包函数中修改的,那么由其引起的所有变化都会按照animateTo的动画参数执行动画过渡到终点值。
@Entry
@Component
struct LayoutChange {
// 用于控制Column的alignItems属性
@State itemAlign: HorizontalAlign = HorizontalAlign.Start;
allAlign: HorizontalAlign[] = [HorizontalAlign.Start, HorizontalAlign.Center, HorizontalAlign.End];
alignIndex: number = 0;
build() {
Column() {
Column({ space: 10 }) {
Button("1").width(100).height(50)
Button("2").width(100).height(50)
Button("3").width(100).height(50)
}
.margin(20)
.alignItems(this.itemAlign)
.borderWidth(2)
.width("90%")
.height(200)
Button("click").onClick(() = > {
// 动画时长为1000ms,曲线为EaseInOut
animateTo({ duration: 1000, curve: Curve.EaseInOut }, () = > {
this.alignIndex = (this.alignIndex + 1) % this.allAlign.length;
// 在闭包函数中修改this.itemAlign参数,使Column容器内部孩子的布局方式变化,使用动画过渡到新位置
this.itemAlign = this.allAlign[this.alignIndex];
});
})
}
.width("100%")
.height("100%")
}
}
除直接改变布局方式外,也可直接修改组件的宽、高、位置。
@Entry
@Component
struct LayoutChange2 {
@State myWidth: number = 100;
@State myHeight: number = 50;
// 标志位,true和false分别对应一组myWidth、myHeight值
@State flag: boolean = false;
build() {
Column({ space: 10 }) {
Button("text")
.type(ButtonType.Normal)
.width(this.myWidth)
.height(this.myHeight)
.margin(20)
Button("area: click me")
.fontSize(12)
.margin(20)
.onClick(() = > {
animateTo({ duration: 1000, curve: Curve.Ease }, () = > {
// 动画闭包中根据标志位改变控制第一个Button宽高的状态变量,使第一个Button做宽高动画
if (this.flag) {
this.myWidth = 100;
this.myHeight = 50;
} else {
this.myWidth = 200;
this.myHeight = 100;
}
this.flag = !this.flag;
});
})
}
.width("100%")
.height("100%")
}
}
另一种方式是给第二个Button添加布局约束,如position的位置约束,使其位置不被第一个Button的宽高影响。核心代码如下:
Column({ space: 10 }) {
Button("text")
.type(ButtonType.Normal)
.width(this.myWidth)
.height(this.myHeight)
.margin(20)
Button("area: click me")
.fontSize(12)
// 配置position属性固定,使自己的布局位置不被第一个Button的宽高影响
.position({ x: "30%", y: 200 })
.onClick(() = > {
animateTo({ duration: 1000, curve: Curve.Ease }, () = > {
// 动画闭包中根据标志位改变控制第一个Button宽高的状态变量,使第一个Button做宽高动画
if (this.flag) {
this.myWidth = 100;
this.myHeight = 50;
} else {
this.myWidth = 200;
this.myHeight = 100;
}
this.flag = !this.flag;
});
})
}
.width("100%")
.height("100%")
使用属性动画产生布局更新动画
显式动画把要执行动画的属性的修改放在闭包函数中触发动画,而属性动画则无需使用闭包,把animation属性加在要做属性动画的组件的属性后即可。
属性动画的接口为:
animation(value: AnimateParam)
其入参为动画参数。想要组件随某个属性值的变化而产生动画,此属性需要加在animation属性之前。有的属性变化不希望通过animation产生属性动画,可以放在animation之后。上面显式动画的示例很容易改为用属性动画实现。例如:
@Entry
@Component
struct LayoutChange2 {
@State myWidth: number = 100;
@State myHeight: number = 50;
@State flag: boolean = false;
@State myColor: Color = Color.Blue;
build() {
Column({ space: 10 }) {
Button("text")
.type(ButtonType.Normal)
.width(this.myWidth)
.height(this.myHeight)
// animation只对其上面的type、width、height属性生效,时长为1000ms,曲线为Ease
.animation({ duration: 1000, curve: Curve.Ease })
// animation对下面的backgroundColor、margin属性不生效
.backgroundColor(this.myColor)
.margin(20)
Button("area: click me")
.fontSize(12)
.onClick(() = > {
// 改变属性值,配置了属性动画的属性会进行动画过渡
if (this.flag) {
this.myWidth = 100;
this.myHeight = 50;
this.myColor = Color.Blue;
} else {
this.myWidth = 200;
this.myHeight = 100;
this.myColor = Color.Pink;
}
this.flag = !this.flag;
})
}
}
}
上述示例中,第一个button上的animation属性,只对写在animation之前的type、width、height属性生效,而对写在animation之后的backgroundColor、margin属性无效。运行结果是width、height属性会按照animation的动画参数执行动画,而backgroundColor会直接跳变,不会产生动画
审核编辑 黄宇
- 相关推荐
- 热点推荐
- 鸿蒙
-
OpenHarmony实战开发-如何实现组件动画。2024-04-28 1352
-
鸿蒙NEXT南向开发案例:【智能台灯】2024-04-03 1936
-
使用 Taro 开发鸿蒙原生应用 —— 快速上手,鸿蒙应用开发指南2024-02-02 1903
-
ArkUI开发框架的动画能力2022-06-17 2168
-
Android中的alpha动画是这个AlphaAnimation, 鸿蒙的alpha动画是哪一个?2022-06-15 1972
-
供鸿蒙开发者使用的计数动画文本视图2022-04-02 1099
-
供鸿蒙应用开发者使用的计数动画文本视图2022-03-29 611
-
用鸿蒙开发AI应用(汇总)连载中2021-01-13 2983
-
《鸿蒙设备学习菜鸟指南》之 【五、搭建开发环境】2020-10-30 1618
-
android界面切换之动画效果全汇总2017-03-19 612
-
通俗易懂之电子称开发硬件篇2016-07-18 14024
-
MATLAB 程式设计入门篇之动画制作2012-02-29 46116
-
USB开发步骤之标准篇2009-05-06 1165
全部0条评论

快来发表一下你的评论吧 !

