

基于OpenHarmony音符检测实现原理
电子说
描述
一、音符检测的基本原理
本文基于 OpenHarmony 开源系统提供了一种音符检测的原理方法,结合多首音乐,运用了 python 和 C++ 两种编程环境实现了预期的检出效果。旨在为振动马达(vibrator)提供音乐节奏感的触觉效果,代码所在目录 .basesensorssensorvibration_convert。
先从 python 实现说起,Librosa 关于音符检测主要用到了两个函数,一个是 onset_strength(),负责生成包含音符产生的频率突变的包络线,如蓝色线条所示。另一个是 onset_detect(),主要运用峰点检测找到每个音符的位置,如黄色线条所示。
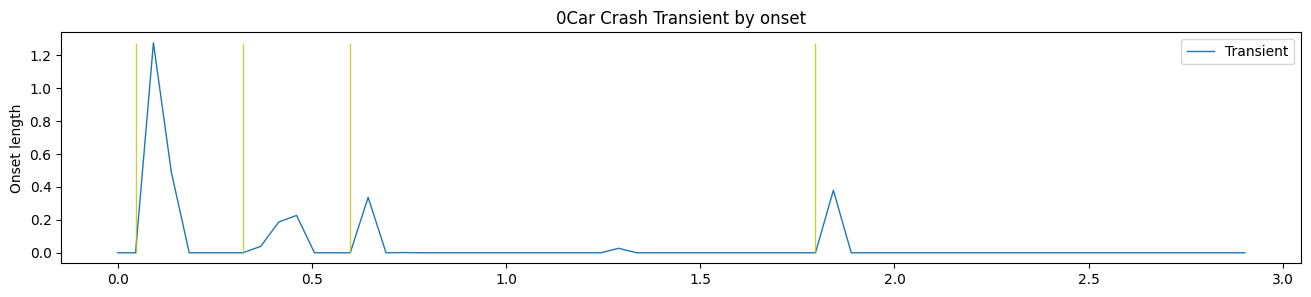
图 1 音符检测包络图
包含有用的频率突变的包络线是音符检测的核心所在。傅里叶变换能够得到全部信号采样的频谱图,即每个频率的能量贡献,如图 2 所示。但是每个时刻频谱图却得不到,于是将全部采样分割成若干固定长度的窗口,每个窗口应用傅里叶变化,从而得到这一窗口的频率分布,水平轴为时间,纵轴为频率,颜色代表能量大小如图 3 所示。
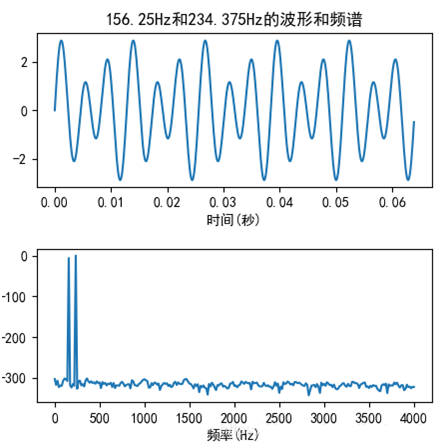
图 2 整体频率分布图
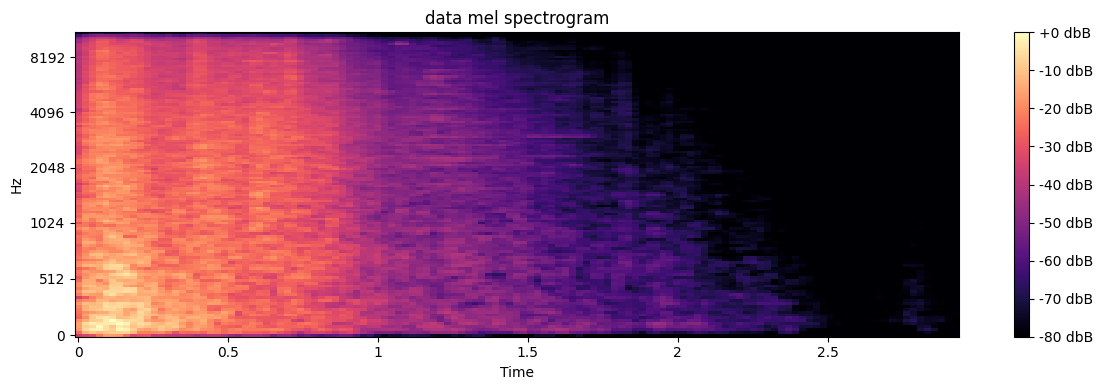
图 3 时频图
每种乐器在音符产生时,前后时间片段的频率将会发生明显变化,如图 4 所示。于是将时频图相邻列做差分,将明显看到变化的频率。为了便于分析,只取正值,具有相同的效果,所以负值填零。一个时刻变化的频率有多个,如何取舍,有三种方法,平均数、中位数和联合,目前常用到的是中位数和平均数。至此,将得到任意时刻发生明显频率变化的单一能量,如图 1 蓝色线条所示。
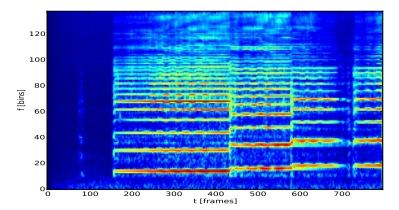
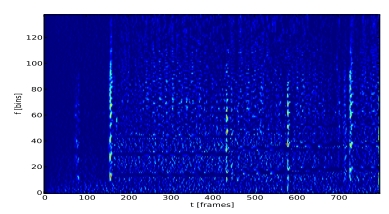
图 4 时频图相邻列差分前后变化
二、音符检测的准确性
目前采用频谱光通量(相邻列差分)方法检测是业界公认且较为准确的方法,音符检出率仅为 70% 多。不准确的原因可能有乐器多且差异较大,信号衰减对性能的影响,颤音影响,峰点检测时不同参数的影响,这些主要是针对音乐的研究。
三、音符检测的程序流程
3.1 程序实现
音符检测功能核心就是频谱图和梅尔滤波器,频谱图的核心就是短时傅里叶变换,C++ 代码片段如下,参考链接 https://github.com/kooBH/STFT/blob/main/cpp/STFT.h
void STFT::stft(short*in,int length,double**out){ int i,j; /*** Shfit & Copy***/ for (j = 0; j < channels; j++) { for (i = 0; i < ol; i++) { buf[j][i] = buf[j][i + shift_size]; } } // EOF if(length!=shift_size*channels){ length = length/channels; for (i = 0; i < length; i++) { for (j = 0; j < channels; j++) buf[j][i + ol] = (double)(in[i * channels+ j]); } for (i = length; i < shift_size; i++) { for (j = 0; j < channels; j++) buf[j][i + ol] = 0; } //continue }else{ for (i = 0; i < shift_size; i++) { for (j = 0; j < channels; j++){ buf[j][i + ol] = (double)(in[i * channels+ j]); } } } /*** Copy input - > hann_input buffer ***/ for (i = 0; i < channels; i++) memcpy(out[i], buf[i], sizeof(double) * frame_size); // scaling for precision if(opt_scale) for (i = 0; i < channels; i++) for (j = 0; j < frame_size; j++) out[i][j] /= MATLAB_scale; /*** Window ***/ hw- >Process(out, channels); /*** FFT ***/ fft- >FFT(out); } void STFT::stft(short*in,int length,double**out){ int i,j; /*** Shfit & Copy***/ for (j = 0; j < channels; j++) { for (i = 0; i < ol; i++) { buf[j][i] = buf[j][i + shift_size]; } } // EOF if(length!=shift_size*channels){ length = length/channels; for (i = 0; i < length; i++) { for (j = 0; j < channels; j++) buf[j][i + ol] = (double)(in[i * channels+ j]); } for (i = length; i < shift_size; i++) { for (j = 0; j < channels; j++) buf[j][i + ol] = 0; } //continue }else{ for (i = 0; i < shift_size; i++) { for (j = 0; j < channels; j++){ buf[j][i + ol] = (double)(in[i * channels+ j]); } } } /*** Copy input - > hann_input buffer ***/ for (i = 0; i < channels; i++) memcpy(out[i], buf[i], sizeof(double) * frame_size); // scaling for precision if(opt_scale) for (i = 0; i < channels; i++) for (j = 0; j < frame_size; j++) out[i][j] /= MATLAB_scale; /*** Window ***/ hw- >Process(out, channels); /*** FFT ***/ fft- >FFT(out); }
Mel 滤波器构造代码如下:
if fmax is None: fmax = float(sr) / 2 # Initialize the weights n_mels = int(n_mels) weights = np.zeros((n_mels, int(1 + n_fft // 2)), dtype=dtype) # Center freqs of each FFT bin fftfreqs = fft_frequencies(sr=sr, n_fft=n_fft) # 'Center freqs' of mel bands - uniformly spaced between limits mel_f = mel_frequencies(n_mels + 2, fmin=fmin, fmax=fmax, htk=htk) fdiff = np.diff(mel_f) ramps = np.subtract.outer(mel_f, fftfreqs) for i in range(n_mels): # lower and upper slopes for all bins lower = -ramps[i] / fdiff[i] upper = ramps[i + 2] / fdiff[i + 1] # .. then intersect them with each other and zero weights[i] = np.maximum(0, np.minimum(lower, upper)) if norm == "slaney": # Slaney-style mel is scaled to be approx constant energy per channel enorm = 2.0 / (mel_f[2 : n_mels + 2] - mel_f[:n_mels]) weights *= enorm[:, np.newaxis] else: weights = util.normalize(weights, norm=norm, axis=-1) # Only check weights if f_mel[0] is positive if not np.all((mel_f[:-2] == 0) | (weights.max(axis=1) > 0)): # This means we have an empty channel somewhere warnings.warn( "Empty filters detected in mel frequency basis. " "Some channels will produce empty responses. " "Try increasing your sampling rate (and fmax) or " "reducing n_mels.", stacklevel=2, ) return weights
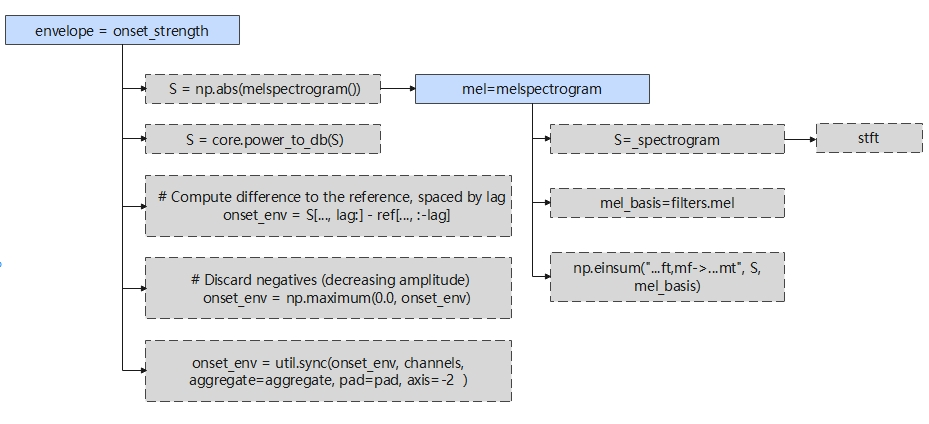
3.2 功能流程图
为了能让大家更好的学习鸿蒙 (OpenHarmony) 开发技术,这边特意整理了《鸿蒙 (OpenHarmony)开发学习手册》,希望对大家有所帮助:
《鸿蒙(Harmony OS)开发学习手册》
入门必看:https://docs.qq.com/doc/DUk51cHZJaUpmSlhH
1.应用开发导读(ArKTS)
2.……
HarmonyOS概念:https://docs.qq.com/doc/DUk51cHZJaUpmSlhH
1.系统定义
2.技术框架
3.技术特性
4.系统安全

快速入门:https://docs.qq.com/doc/DUk51cHZJaUpmSlhH
1.基本概念
2.构建第一个ArkTS应用
3.……
开发基础知识:https://docs.qq.com/doc/DUk51cHZJaUpmSlhH
1.应用基础知识
2.配置文件
3.应用数据管理
4.应用安全管理
5.应用隐私保护
6.三方应用调用管控机制
7.资源分类与访问
8.学习ArkTS
9…

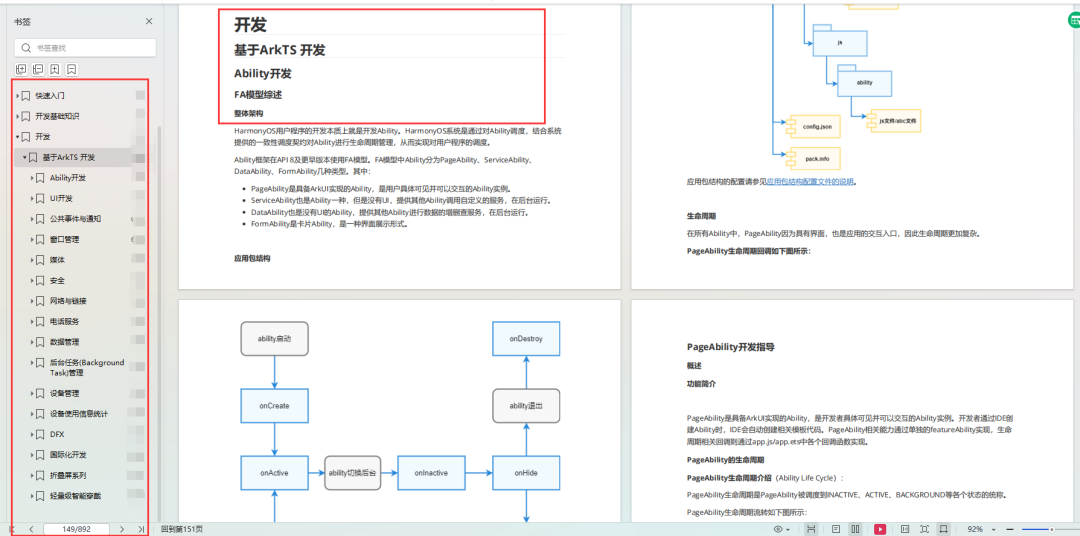
基于ArkTS 开发:https://docs.qq.com/doc/DUk51cHZJaUpmSlhH
1.Ability开发
2.UI开发
3.公共事件与通知
4.窗口管理
5.媒体
6.安全
7.网络与链接
8.电话服务
9.数据管理
10.后台任务(Background Task)管理
11.设备管理
12.设备使用信息统计
13.DFX
14.国际化开发
15.折叠屏系列
16………
审核编辑 黄宇
- 相关推荐
- 热点推荐
- 鸿蒙
- HarmonyOS
- OpenHarmony
-
水音符的基本原理是什么呢?2013-05-21 2380
-
制作一个音乐音符发生器的设计资料分享2022-01-14 1102
-
基于OpenHarmony的智能金属探测器2022-07-05 2595
-
音符乐器频率范围表2008-01-19 15876
-
555音符门铃电路2008-05-25 1059
-
十音符连续演奏电路图2009-05-23 543
-
基于Matlab的数字音符实时显示研究2016-01-04 600
-
使用iCoupler®数字隔离器的NAppkin音符分段功率2021-06-11 690
-
基于openharmony适配移植的手势检测器框架2022-04-08 520
-
基于OpenHarmony如何设计一款煤气检测装置2022-08-22 1028
-
如何在OpenHarmony开源代码基础上实现数字管家开发宿舍全屋智能2022-08-26 2710
-
关于OpenHarmony Jchardet组件介绍2022-10-12 1771
-
玩嗨OpenHarmony:基于OpenHarmony的道路维护方案2022-11-02 2087
-
【开源项目】OpenHarmony挑战赛-家庭医生终端系统-血压/心率/血氧检测2022-09-21 3466
-
Arduino音乐:音符和和弦检测器2023-06-26 831
全部0条评论

快来发表一下你的评论吧 !

