

 鸿蒙OpenHarmony开发板解析:【Rust模块配置规则和指导】
鸿蒙OpenHarmony开发板解析:【Rust模块配置规则和指导】
电子说
描述
概述
Rust是一门静态强类型语言,具有更安全的内存管理、更好的运行性能、原生支持多线程开发等优势。Rust官方也使用Cargo工具来专门为Rust代码创建工程和构建编译。 OpenHarmony为了集成C/C++代码和提升编译速度,使用了GN + Ninja的编译构建系统。GN的构建语言简洁易读,Ninja的汇编级编译规则直接高效。 为了在OpenHarmony中集成Rust代码,并最大程度发挥Rust和OpenHarmony中原有C/C++代码的交互性,采用GN作为统一构建工具,即通过GN构建Rust源码文件(xxx.rs),并增加与C/C++互操作、编译时lint、测试、IDL转换、三方库集成、IDE等功能。同时扩展gn框架,支持接口自动化转换,最大程度简化开发。
基本概念
| 术语 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| Cargo | Cargo是Rust官方使用的构建工具,允许Rust项目声明其各种依赖项,并确保您始终获得可重复的构建。 |
| crate | crate是一个独立的可编译单元。 |
| Lint | Lint是指出常见编程错误、错误、样式错误和可疑结构的工具。可以对程序进行更加广泛的错误分析。 |
配置规则
OpenHarmony提供了用于Rust代码编译构建的各类型GN模板,可以用于编译Rust可执行文件,动态库和静态库等。各类型模板说明如下:
| GN模板 | 功能 | 输出 |
|---|---|---|
| ohos_rust_executable | rust可执行文件 | rust可执行文件,不带后缀 |
| ohos_rust_shared_liary | rust动态库 | rust dylib动态库,默认后缀.dylib.so |
| ohos_rust_static_liary | rust静态库 | rust rlib静态库,默认后缀.rlib |
| ohos_rust_proc_macro | rust proc_macro | rust proc_macro库, 默认后缀.so |
| ohos_rust_shared_ffi | rust FFI动态库 | rust cdylib动态库,给C/C++模块调用,默认后缀.so |
| ohos_rust_static_ffi | rust FFI静态库 | rust staticlib库,给C/C++模块调用,默认后缀.a |
| ohos_rust_cargo_crate | 三方包Cargo crate | rust三方crate,支持rlib、dylib、bin |
| ohos_rust_systemtest | rust系统测试用例 | rust可执行系统测试用例,不带后缀 |
| ohos_rust_unittest | rust单元测试用例 | rust可执行单元测试用例,不带后缀 |
| ohos_rust_fuzztest | rust Fuzz测试用例 | rust可执行Fuzz测试用例,不带后缀 |
配置指导
配置Rust模块与C/C++模块类似,参考[模块配置规则]。下面是使用不同模板的示例。
开发前请熟悉鸿蒙开发指导文档:[gitee.com/li-shizhen-skin/harmony-os/blob/master/README.md]
配置Rust静态库示例
该示例用于测试Rust可执行bin文件和静态库rlib文件的编译,以及可执行文件对静态库的依赖,使用模板ohos_rust_executable和ohos_rust_static_library。操作步骤如下:
- 创建build/rust/tests/test_rlib_crate/src/simple_printer.rs,如下所示:
//! simple_printer /// struct RustLogMessage pub struct RustLogMessage { /// i32: id pub id: i32, /// String: msg pub msg: String, } /// function rust_log_rlib pub fn rust_log_rlib(msg: RustLogMessage) { println!("id:{} message:{:?}", msg.id, msg.msg) } - 创建build/rust/tests/test_rlib_crate/src/main.rs,如下所示:
//! rlib_crate example for Rust. extern crate simple_printer_rlib; use simple_printer_rlib::rust_log_rlib; use simple_printer_rlib::RustLogMessage; fn main() { let msg: RustLogMessage = RustLogMessage { id: 0, msg: "string in rlib crate".to_string(), }; rust_log_rlib(msg); } - 配置gn脚本build/rust/tests/test_rlib_crate/BUILD.gn,如下所示:
import("//build/ohos.gni") ohos_rust_executable("test_rlib_crate") { sources = [ "src/main.rs" ] deps = [ ":simple_printer_rlib" ] } ohos_rust_static_library("simple_printer_rlib") { sources = [ "src/simple_printer.rs" ] crate_name = "simple_printer_rlib" crate_type = "rlib" features = [ "std" ] } - 执行编译得到的可执行文件,运行结果如下:

配置三方库示例
rust三方库的BUILD.gn文件可通过cargo2gn工具自动生成。参见:[Cargo2gn工具操作指导]
该示例用于测试包含预编译文件build.rs的三方静态库rlib文件的编译,使用了模板ohos_rust_executable和ohos_rust_cargo_crate。操作步骤如下:
- 创建build/rust/tests/test_rlib_cargo_crate/crate/src/lib.rs,如下所示:
include!(concat!(env!("OUT_DIR"), "/generated/generated.rs")); pub fn say_hello_from_crate() { assert_eq!(run_some_generated_code(), 45); #[cfg(is_new_rustc)] println!("Is new rustc"); #[cfg(is_old_rustc)] println!("Is old rustc"); #[cfg(is_ohos)] println!("Is ohos"); #[cfg(is_mac)] println!("Is darwin"); #[cfg(has_feature_a)] println!("Has feature_a"); #[cfg(not(has_feature_a))] panic!("Wasn't passed feature_a"); #[cfg(not(has_feature_b))] #[cfg(test_a_and_b)] panic!("feature_b wasn't passed"); #[cfg(has_feature_b)] #[cfg(not(test_a_and_b))] panic!("feature_b was passed"); } #[cfg(test)] mod tests { /// Test features are passed through from BUILD.gn correctly. This test is the target configuration. #[test] #[cfg(test_a_and_b)] fn test_features_passed_target1() { #[cfg(not(has_feature_a))] panic!("feature a was not passed"); #[cfg(not(has_feature_b))] panic!("feature b was not passed"); } #[test] fn test_generated_code_works() { assert_eq!(crate::run_some_generated_code(), 45); } } - 创建build/rust/tests/test_rlib_cargo_crate/crate/src/main.rs,如下所示:
pub fn main() { test_rlib_crate::say_hello_from_crate(); } - 创建build/rust/tests/test_rlib_cargo_crate/crate/build.rs,如下所示:
use std::env; use std::path::Path; use std::io::Write; use std::process::Command; use std::str::{self, FromStr}; fn main() { println!("cargo:rustc-cfg=build_script_ran"); let my_minor = match rustc_minor_version() { Some(my_minor) = > my_minor, None = > return, }; if my_minor >= 34 { println!("cargo:rustc-cfg=is_new_rustc"); } else { println!("cargo:rustc-cfg=is_old_rustc"); } let target = env::var("TARGET").unwrap(); if target.contains("ohos") { println!("cargo:rustc-cfg=is_ohos"); } if target.contains("darwin") { println!("cargo:rustc-cfg=is_mac"); } let feature_a = env::var_os("CARGO_FEATURE_MY_FEATURE_A").is_some(); if feature_a { println!("cargo:rustc-cfg=has_feature_a"); } let feature_b = env::var_os("CARGO_FEATURE_MY_FEATURE_B").is_some(); if feature_b { println!("cargo:rustc-cfg=has_feature_b"); } // Some tests as to whether we're properly emulating various cargo features. assert!(Path::new("build.rs").exists()); assert!(Path::new(&env::var_os("CARGO_MANIFEST_DIR").unwrap()).join("build.rs").exists()); assert!(Path::new(&env::var_os("OUT_DIR").unwrap()).exists()); // Confirm the following env var is set env::var_os("CARGO_CFG_TARGET_ARCH").unwrap(); generate_some_code().unwrap(); } fn generate_some_code() - > std::io::Result< () > { let test_output_dir = Path::new(&env::var_os("OUT_DIR").unwrap()).join("generated"); let _ = std::fs::create_dir_all(&test_output_dir); // Test that environment variables from .gn files are passed to build scripts let preferred_number = env::var("ENV_VAR_FOR_BUILD_SCRIPT").unwrap(); let mut file = std::fs::File::create(test_output_dir.join("generated.rs"))?; write!(file, "fn run_some_generated_code() - > u32 {{ {} }}", preferred_number)?; Ok(()) } fn rustc_minor_version() - > Option< u32 > { let rustc_bin = match env::var_os("RUSTC") { Some(rustc_bin) = > rustc_bin, None = > return None, }; let output = match Command::new(rustc_bin).arg("--version").output() { Ok(output) = > output, Err(_) = > return None, }; let rustc_version = match str::from_utf8(&output.stdout) { Ok(rustc_version) = > rustc_version, Err(_) = > return None, }; let mut pieces = rustc_version.split('.'); if pieces.next() != Some("rustc 1") { return None; } let next_var = match pieces.next() { Some(next_var) = > next_var, None = > return None, }; u32::from_str(next_var).ok() } - 配置gn脚本build/rust/tests/test_rlib_cargo_crate/BUILD.gn,如下所示:
import("//build/templates/rust/ohos_cargo_crate.gni") ohos_cargo_crate("target") { crate_name = "test_rlib_crate" crate_root = "crate/src/lib.rs" sources = [ "crate/src/lib.rs" ] #To generate the build_script binary build_root = "crate/build.rs" build_sources = [ "crate/build.rs" ] build_script_outputs = [ "generated/generated.rs" ] features = [ "my-feature_a", "my-feature_b", "std", ] rustflags = [ "--cfg", "test_a_and_b", ] rustenv = [ "ENV_VAR_FOR_BUILD_SCRIPT=45" ] } # Exists to test the case that a single crate has both a library and a binary ohos_cargo_crate("test_rlib_crate_associated_bin") { crate_root = "crate/src/main.rs" crate_type = "bin" sources = [ "crate/src/main.rs" ] #To generate the build_script binary build_root = "crate/build.rs" build_sources = [ "crate/build.rs" ] features = [ "my-feature_a", "my-feature_b", "std", ] rustenv = [ "ENV_VAR_FOR_BUILD_SCRIPT=45" ] deps = [ ":target" ] } - 执行编译得到的可执行文件,运行结果如下:
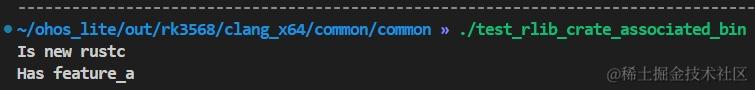
其他源码实例
在build/rust/tests目录下有Rust各类型模块的配置实例可供参考:
| 用例目录 | 测试功能 |
|---|---|
| build/rust/tests/test_bin_crate | 用ohos_rust_executable模板在host平台编译可执行文件,在target平台上运行可执行文件。 |
| build/rust/tests/test_static_link | 测试可执行文件对标准库的静态链接。 |
| build/rust/tests/test_dylib_crate | 测试对动态库的编译和动态链接功能 |
| build/rust/tests/test_rlib_crate | 测试对静态库的编译和静态链接功能 |
| build/rust/tests/test_proc_macro_crate | 测试对Rust过程宏的编译和链接功能。提供对不同类型的宏的测试用例。 |
| build/rust/tests/test_cdylib_crate | 测试将Rust代码编译成C/C++动态库。 |
| build/rust/tests/test_staticlib_crate | 测试将Rust代码编译成C/C++静态库。 |
| build/rust/tests/rust_test_ut | 测试Rust代码单元测试模板功能(ability)。 |
| build/rust/tests/rust_test_st | 测试Rust代码系统测试模板功能(ability)。 |
| build/rust/tests/test_bin_cargo_crate | 测试Rust三方可执行文件的编译和运行。三方源码中包含build.rs。 |
| build/rust/tests/test_rlib_cargo_crate | 测试Rust三方静态库的编译和静态链接。三方源码中包含build.rs。 |
| build/rust/tests/test_proc_macro_cargo_crate | 测试Rust三方过程宏的编译和链接。三方源码中包含build.rs。 |
| build/rust/tests/rust_test_fuzzb | 测试Rust代码Fuzz测试模板功能。 |
参考
特性点实例
Rust源码依赖调用C/C++库
OpenHarmony上C/C++模块动态库默认用.z.so后缀,但是Rust的编译命令通过-l链接时,默认只会链接.so后缀的动态库。因此如果要依赖一个C/C++动态库编译模块,需要在该动态库的GN构建文件中添加output_extension = "so"的声明,这样编译得到的动态库将会以".so"作为后缀,而不是".z.so"。 在Rust源码中如果直接链接动态库,后缀也需要使用".so",这时使用动态库的中间名,不需要添加lib前缀。例如Rust源码中链接libhilog.so:
#[link(name = "hilog")]
externs使用
某个模块如果依赖二进制的rlib库,可以使用externs属性:
executable("foo") {
sources = [ "main.rs" ]
externs = [{ # 编译时会转成`--extern bar=path/to/bar.rlib`
crate_name = "bar"
path = "path/to/bar.rlib"
}]
}
Lint规则
OpenHarmony框架支持rustc lints和clippy lints两种Lint,每种Lint划为三个等级的标准:"openharmony"、"vendor"和"none",严格程度按照"openharmony" -> "vendor" -> "none"逐级递减。 配置Rust模块时可以通过rustc_lints和clippy_lints来指定使用Lint的等级。 模块中没有配置rustc_lints或者clippy_lints时会根据模块所在路径来匹配lints等级。不同路径下的Rust代码的语法规范会有不同程度地约束,因此用户在OpenHarmony配置Rust代码编译模块时还应关注模块所在路径。
rustc lints和clippy lints的各等级标志
| lints类型 | 模块属性 | lints等级 | lints等级标志 | lints内容 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| rustc_lints | rustc_lints | openharmony | RustOhosLints | "-A deprecated", "-D missing-docs", "-D warnigngs" |
| rustc_lints | rustc_lints | vendor | RustcVendorLints | "-A deprecated", "-D warnigs" |
| rustc_lints | rustc_lints | none | allowAllLints | "-cap-lints allow" |
| clippy lints | clippy lints | openharmony | ClippyOhosLints | "-A clippy::type-complexity", "-A clippy::unnecessary-wraps", "-A clippy::unusual-byte-groupings", "-A clippy::upper-case-acronyms" |
| clippy lints | clippy lints | vendor | ClippyVendorLints | "-A clippy::complexity", "-A Clippy::perf", "-A clippy::style" |
| clippy lints | clippy lints | none | allowAllLints | "--cap-lints allow" |
代码路径与lints等级的对应关系
| 路径 | Lints等级 |
|---|---|
| thirdparty | none |
| prebuilts | none |
| vendor | vendor |
| device | vendor |
| others | openharmony |
审核编辑 黄宇
- 相关推荐
- 热点推荐
- 开发板
- Rust
- 鸿蒙
- OpenHarmony
-
鸿蒙OpenHarmony开发板:【产品配置规则】2024-05-09 2069
-
鸿蒙OpenHarmony开发板解析:【 模块配置规则】2024-05-10 2164
-
鸿蒙OpenHarmony南向/北向快速开发教程-迅为RK3568开发板2024-07-23 2344
-
openharmony开发版 openharmony开发板2021-06-24 4284
-
[鸿蒙]OpenHarmony4.0的Rust开发2024-02-26 1927
-
瑞芯微RK3566鸿蒙开发板OpenHarmony标准系统应用兼容性测试指导2024-09-10 2041
-
如何在开源鸿蒙OpenHarmony开启SELinux模式?RK3566鸿蒙开发板演示2024-11-18 1339
-
OpenHarmony属性信息怎么修改?触觉智能RK3566鸿蒙开发板来演示2024-11-27 1114
-
OpenHarmony怎么修改DPI密度值?触觉智能RK3566鸿蒙开发板演示2024-12-24 1138
-
OpenHarmony源码编译后烧录镜像教程,RK3566鸿蒙开发板演示2024-12-30 1601
-
【北京迅为】itop-3568 开发板openharmony鸿蒙烧写及测试-第1章 体验OpenHarmony—烧写镜像2025-03-04 930
-
【北京迅为】iTOP-RK3568开发板鸿蒙OpenHarmony系统南向驱动开发实操-HDF驱动配置UART2025-03-25 1397
-
鸿蒙北向开发OpenHarmony5.0 DevEco Studio开发工具安装与配置2025-03-28 1421
-
贝启BQ3568HM 开发板被选用为 OpenHarmony 明星开发板2025-05-25 1270
-
触觉智能Purple Pi OH开发板率先适配OpenHarmony6.0 Release,鸿蒙明星开发板2025-10-29 530
全部0条评论

快来发表一下你的评论吧 !



