

一文看懂帧中继点到点与点到多点的区别
路由器
描述
帧中继简介
帧中继(FrameRelay)是一种用于连接计算机系统的面向分组的通信方法。它主要用在公共或专用网上的局域网互联以及广域网连接。大多数公共电信局都提供帧中继服务,把它作为建立高性能的虚拟广域连接的一种途径。帧中继是进入带宽范围从56Kbps到1.544Mbps的广域分组交换网的用户接口。
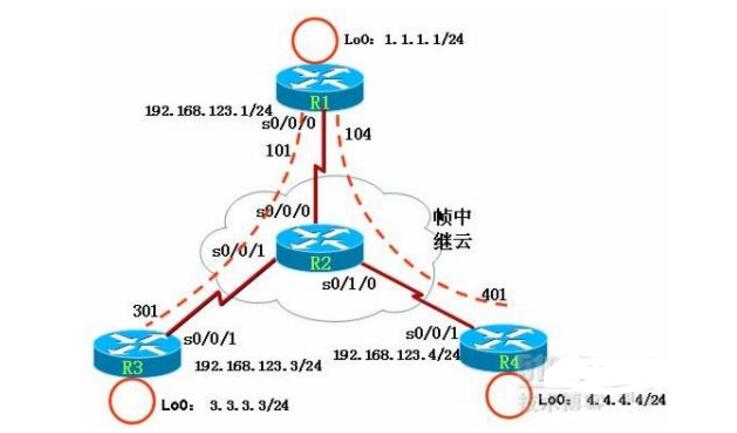
点到点子接口
子接口看作是专线
每一个点到点连接的子接口要求有自己的子网
适用于星型拓扑结构
试验拓扑说明:R1的物理接口不添加IP。R1的子接口S0/0.1的ip为192.168.1.1,
S0/0.2的ip为192.168.2.1。R2的ip为192.168.1.2。R3的ip为192.168.2.2网络
掩码都为255.255.255.0。
R1上S0/0.1的DLCI号为102,S0/0.2的DLCI号为103.
R2上S0/0的DLCI号为201
R3上S0/0的DLCI号为301
试验要求:在路由器间完成帧中继——点到点子接口的配置,并在路由器间配置
rip协议,最终使路由器间全网全通。
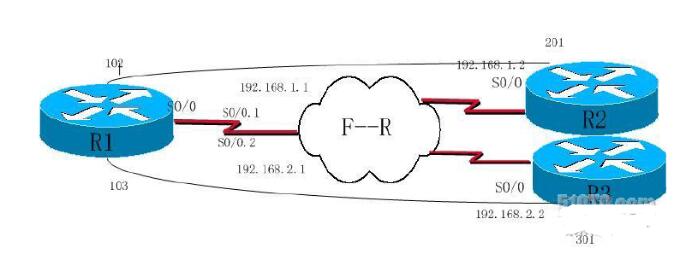
帧中继点到多点
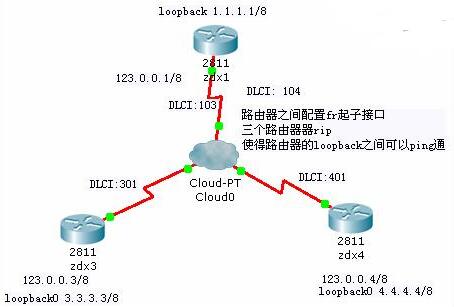
1、拓扑图
2、实验步骤
zdx1配置如下
Router(config)#hostnamezdx1
zdx1(config)#intloopback0起回环口
zdx1(config-if)#ipadd1.1.1.1255.0.0.0
zdx1(config-if)#ints0/0/0multipoint
zdx1(config-subif)#ipadd123.0.0.1255.0.0.0
zdx1(config-subif)#frame-relaymapip123.0.0.3103broadcast
zdx1(config-subif)#frame-relaymapip123.0.0.4104broadcast
zdx1(config-if)#encapsulationframe-relay起封装帧中继
zdx1(config-if)#noshut
zdx1(config)#routerrip
zdx1(config-router)#network1.0.0.0宣告网段
zdx1(config-router)#network123.0.0.0
zdx3配置如下
Router(config)#hostnamezdx2
Zdx3(config)#intloopback0
Zdx3(config-if)#ipadd3.3.3.3255.0.0.0
Zdx3(config-if)#ints0/0/0multipoint
Zdx3(config-if)#ipadd123.0.0.3255.0.0.0
Zdx3(config-if)#encapsulationframe-relay封装帧中继
Zdx3(config-if)#frame-relaymapip123.0.0.1301broadcast
Zdx3(config-if)#frame-relaymapip123.0.0.4304broadcast
Zdx3(config-if)#noshut
Zdx3(config-if)#exit
Zdx3(config)#routerrip
Zdx3(config-router)#network123.0.0.0
Zdx3(config-router)#network3.0.0.0
zdx4配置如下
Router(config)#hostnamezdx3
Zdx4(config)#intloopback0
Zdx4(config-if)#ipadd4.4.4.4255.0.0.0
Zdx4(config-if)#ints0/0/0multipoint
Zdx4(config-if)#ipadd123.0.0.4255.0.0.0
Zdx4(config-if)#encapsulationframe-relay
Zdx4(config-if)#frame-relaymapip123.0.0.1401broadcast
Zdx4(config-if)#frame-relaymapip123.0.0.3403broadcast
Zdx4(config-if)#noshut
Zdx4(config-if)#exit
Zdx4(config)#routerrip
Zdx4(config-router)#network123.0.0.0
Zdx4(config-router)#network4.0.0.0
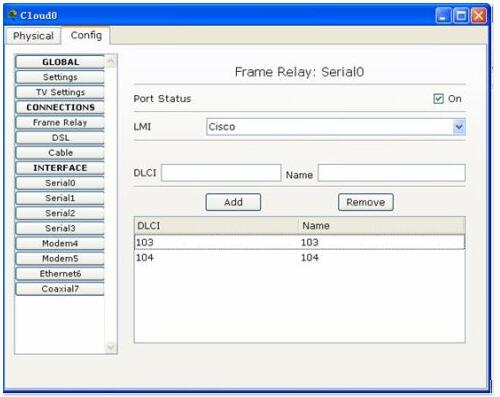
云中的配置:
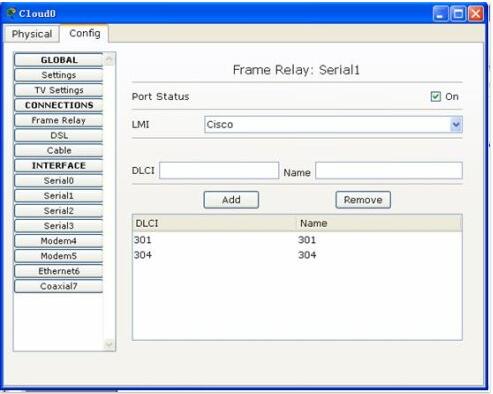
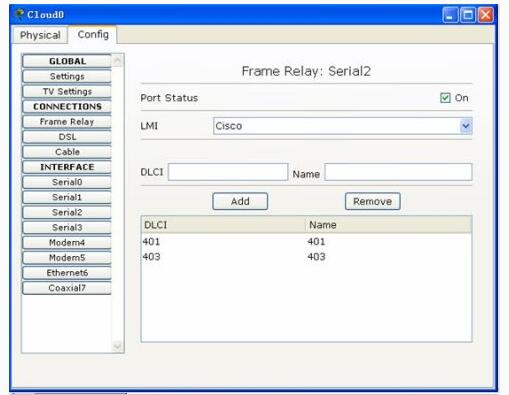
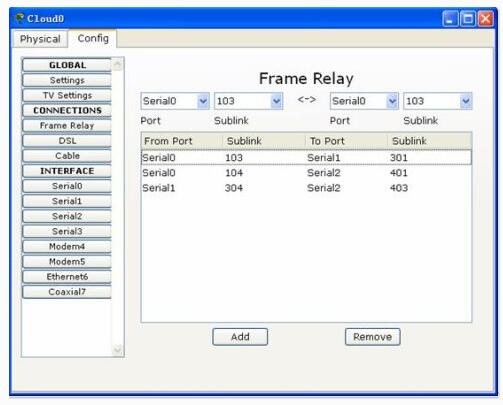
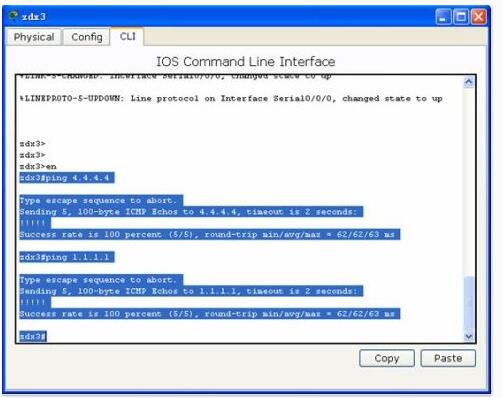
测试:
帧中继点到点与点到多点的区别
点对点连接类型:
使用单一子接口建立到达远程路由器上的另一个物理接口或多子接口的单一PVC连接。在这种情况下,一条PVC连接两端的接口必须位于相同的子网,且每个接口各自有一个DLCI。每个点对点连接都有自己的子网。在此环境中,因为路由器是点对点连接且运作方式类似于专线,所以广播不成问题。
点对多点连接类型:
使用单一子接口建立到达远程路由器上的多个物理接口和子接口的多重PVC连接。在这种情况下,所有参与的接口必须位于相同的子网内,且每个接口具有自己的本地DLCI。在此环境中,由于子接口的运作方式类似于一般的NBMA帧中继网络物理接口,因为路由更新广播信息依照SplitHorizon(水平分割)的方式进行。
点到点和点到多点的应用:
多数和在帧中继上运行的网络协议有关系,在点到多点的情况下,必须要关闭水平分割,而在点到点的情况下没必要关闭水平分割。也就是说点到点稍微简单一些,并且不发送广播包,有利于提升路由器的吞吐量,点到多点的优势则在于不用配置那么多的子接口。
自己顺便查看了一些资料,发现配置方面的差别:
物理接口配置相同,不同的是在子接口上
PS:帧中继类型有:NBMA/BMA/点到点/点到多点
nbma一定要选举dr和bdr,应不支持广播,是用组播发,所以必须用neighbor命令指定邻居
首先将物理接口封装为cisco模式,
ints0/0
encapframe-relay
noshut
点到点的配置(一个子接口对端连接的是一个物理接口)
ints0/0.1pointtopoint
ipadd10.1.1.1255.255.255.248
frame-relayinterface-dlci101
ints0/0.2pointtopoint
ipadd10.1.1.2255.255.255.248
frame-relayinterface-dlci102
ints0/0.3pointtopoint
ipadd10.1.1.3255.255.255.248
frame-relayinterface-dlci103
点到多点的配置(一个子接口对端连接多个子接口)
ints0/0.1multipoint
ipadd10.2.1.1255.255.255.248
frame-relayinterface-dlci102
以下3行也可以用frame-relaymapip10.2.1.2102broadcast
frame-relayinterface-dlci103frame-relaymapip10.2.1.3103broadcast
frame-relayinterface-dlci104frame-relaymapip10.2.1.4104broadcast
ipospfnetworkpoint-to-multipoint
在未开启IARP的前提下,需要手动分配帧中继的静态地址,并且这里的IP地址为远端接口的IP
- 相关推荐
- 热点推荐
- 帧中继
-
点到多点无源光网络有哪些优点2024-09-23 1226
-
小鹏汽车:今年智驾实现国内全范围、点到点,明年研发全球范围XNGP2024-01-31 1335
-
基于UDP协议和FPGA的点到点数据传输方案2021-06-01 1167
-
点到点和端到端通讯2019-01-18 1807
-
帧中继和路由协议详解(帧中继的作用及特点)2018-03-02 21740
-
帧中继接入,什么是帧中继接入2010-04-06 2130
-
帧中继,帧中继是什么意思2010-03-18 5141
-
帧中继交换机的配置2010-03-01 2474
-
帧中继协议2009-06-24 1244
-
什么是帧中继2009-06-11 3078
-
高速、多路LVDS交叉开关,减少点到点链路并节省成本2008-10-01 1374
全部0条评论

快来发表一下你的评论吧 !

