

【教程】DNS域名解析服务systemd-resolved使用指南
描述
1. 关于DNS解析服务
DNS(Domain Name System),即域名系统。
一句话总结DNS解析服务功能就是,将域名转换为IP地址。
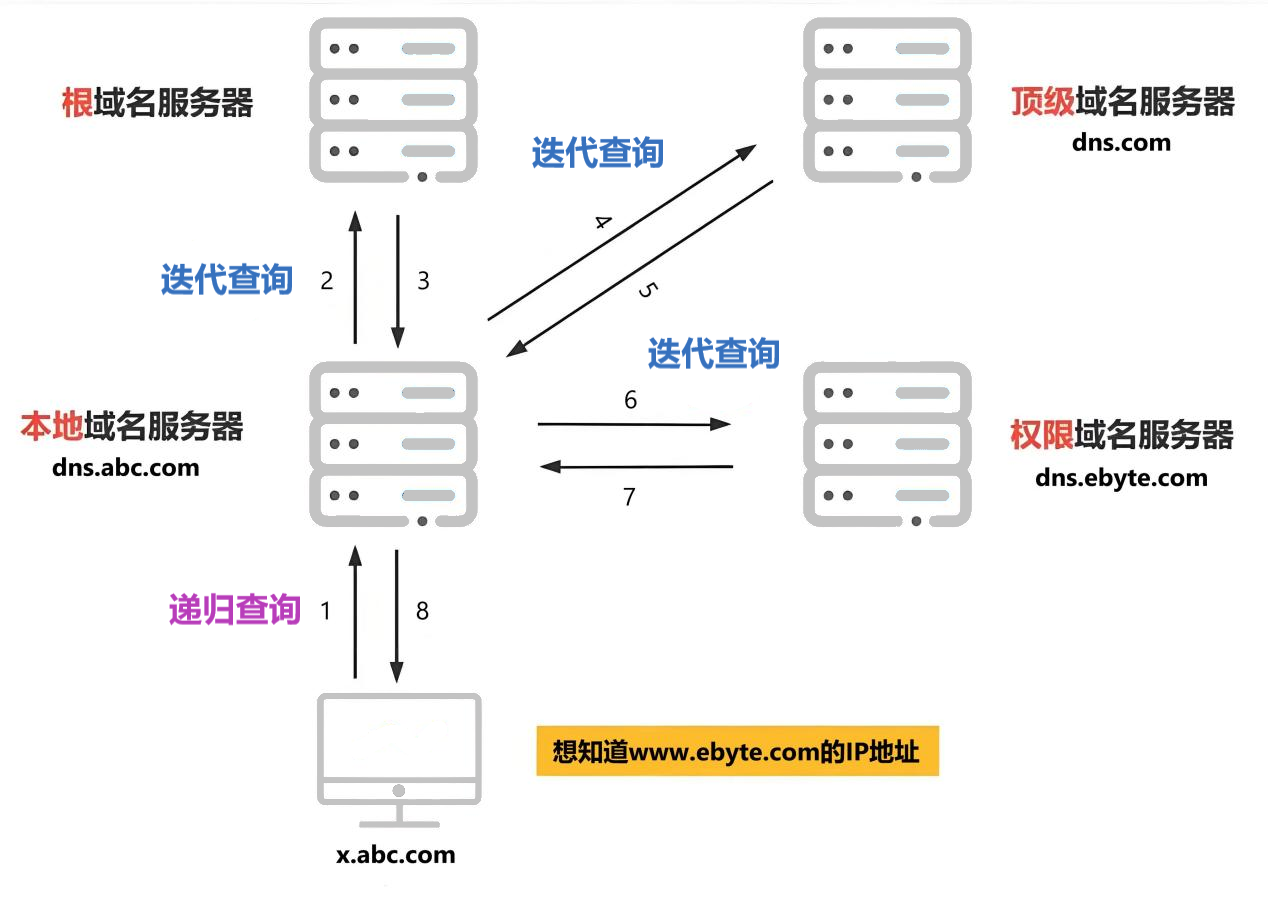
DNS解析服务过程中有如下几个角色参与:
• 待解析的域名
• DNS客户端
• DNS服务器
• 域名对应的IP地址
DNS解析大致过程:
• 用户在应用程序中使用域名
• 应用程序调用DNS客户端申请域名解析
• DNS客户端向DNS服务器发送待解析的域名(本地有解析缓存则不用再请求)
• DNS服务器将解析出的IP地址返回给客户端(服务端可能会缓存DNS解析结果,避免重复查询)
• 应用程序使用域名对应的IP地址(客户端可能会缓存DNS解析结果,加快响应速度)
Windows和Linux系统中都有常用的DNS解析服务,例如Windows中的DNS Client,Linux中的systemd-resolved、BIND等。
而其中systemd-resolved是现代Linux发行版(基于systemd)中最常用的默认DNS解析服务,今天本文将分享systemd-resolved这款DNS解析服务。
2. systemd-resolved 的常用命令
2.1 查看当前systemd-resolved的运行状态
systemctl status systemd-resolved
该服务在基于systemd的系统中是默认开启的,也可以将status字段更换为start或stop来控制该服务的开启和关闭,因为本文主要围绕systemd-resolved展开,所以systemdctl的操作命令不再详细展开。
2.2 查看systemd-resolved的统计信息,在输出中可以查看缓存命中率、缓存大小、DNSSEC 验证情况。
systemd-resolve --statistics
2.3 检查当前DNS配置:
resolvectl status或systemd-resolve --status(旧版本兼容)
2.4 清理DNS缓存,systemd-resolved会缓存在内存上,并不进行持久化保存,若缓存过大可以使用该命令清理本地缓存。
systemd-resolve --flush-caches
2.5 手动进行域名解析测试,输出中可以查看解析出来的IP、解析耗时等。
systemd-resolve www.xxx.com
2.6 临时给端口配置DNS服务器,该配置重启会失效,若想永久固定需修改/etc/systemd/resolved.conf等相关配置文件。
resolvectl dns eth0 8.8.8.8
3. systemd-resolved相关配置文件
3.1 /etc/resolv.conf配置文件
/etc/resolv.conf是最表面的DNS配置文件,systemd-resolved执行DNS解析时,会读取该文件来获取DNS服务器IP,从而进行DNS解析。所以不难看出,/etc/resolv.conf是systemd-resolved服务中最重要的文件,因此/etc/resolv.conf会被多方控制,从而达到配置DNS解析服务的目的。若用户想要临时配置系统的DNS解析服务器,可以直接修改该文件,写入对应的服务器IP:
nameserver 114.114.114.114nameserver 8.8.8.8
不过以上修改操作只能是临时的,因为/etc/resolv.conf正常情况下是动态生成的,当查看它的详细信息时会发现是一个软连接,它的状态会随着配置和用户的动作而变化。
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 37 Dec 5 14:24 /etc/resolv.conf -> /run/systemd/resolve/stub-resolv.conf
这里所指向的stub-resolv.conf文件后面再详细解释。
3.2 /etc/systemd/resolved.conf配置文件
该文件是systemd-resolved的主要配置文件,通常用于设置DNS服务器、DNS解析策略等。修改这个文件后,需要重新启动systemd-resolved服务才能生效。
[Resolve]DNS=8.8.8.8 8.8.4.4 # DNS服务器列表FallbackDNS=114.114.114.114 # 当主要DNS不可用时,使用备用DNSDomains=example.com # 域名搜索拓展列表LLMNR=no # LLMNR(本地链路多播名称解析)启用设置DNSSEC=no # 是否启用DNSSEC(域名系统安全扩展)Cache=yes # 启用DNS缓存
3.3 /run/systemd/resolve/stub-resolv.conf和/run/systemd/resolve/resolv.conf配置文件从3.1中可以发现,/etc/resolv.conf就是指向了/run/systemd/resolve/stub-resolv.conf,所以/etc/resolv.conf同样也能指向/run/systemd/resolve/resolv.conf,也证明这两个文件才是真正的DNS服务器指定文件。这两个文件实际由systemd-resolved服务直接管理和生成,其中:/run/systemd/resolve/resolv.conf文件:由systemd-resolved服务生成,其内容由3.2提到的/etc/systemd/resolved.conf配置文件进行指定,如下:
# This file is managed by man:systemd-resolved(8). Do not edit.## This is a dynamic resolv.conf file for connecting local clients directly to# all known uplink DNS servers. This file lists all configured search domains.## Third party programs must not access this file directly, but only through the# symlink at /etc/resolv.conf. To manage man:resolv.conf(5) in a different way,# replace this symlink by a static file or a different symlink.## See man:systemd-resolved.service(8) for details about the supported modes of# operation for /etc/resolv.conf.nameserver 8.8.8.8nameserver 8.8.4.4search example.com
/run/systemd/resolve/stub-resolv.conf文件:由systemd-resolved服务生成,配置使用DNS stub解析器,这种情况下应用程序不会与systemd-resolved直接通信,而是由stub解析器转发,一般情况下应用程序只需要向127.0.0.53查询即可,由stub解析器转发给systemd-resolved,避免了紧耦合:
# This file is managed by man:systemd-resolved(8). Do not edit.## This is a dynamic resolv.conf file for connecting local clients to the# internal DNS stub resolver of systemd-resolved. This file lists all# configured search domains.## Run "resolvectl status" to see details about the uplink DNS servers# currently in use.## Third party programs must not access this file directly, but only through the# symlink at /etc/resolv.conf. To manage man:resolv.conf(5) in a different way,# replace this symlink by a static file or a different symlink.## See man:systemd-resolved.service(8) for details about the supported modes of# operation for /etc/resolv.conf.nameserver 127.0.0.53options edns0 trust-adsearch example.com
4. 总结
在实际使用过程中,可以只关注/etc/resolv.conf文件即可:
• 想临时修改系统DNS服务器,直接修改/etc/resolv.conf文件即可(或使用resolvectl命令修改,可以更好的控制);• 想持久化修改系统DNS服务器,配置/run/systemd/resolve/resolv.conf文件,并确保 /etc/resolv.conf 符号链接指向 /run/systemd/resolve/resolv.conf;• 想使用DNS Stub解析器,配置/run/systemd/resolve/resolv.conf文件,并确保 /etc/resolv.conf 符号链接指向 /run/systemd/resolve/stub-resolv.conf。在操作上,了解systemd-resolved是如何管理DNS请求,了解配置文件如何影响DNS解析行为,已经足以完成日常的配置和故障排查。在理论上,若想要使用DNS解析服务更高级的功能可以深入了解DNS工作原理以及DNS协议的高级特性,并深入学习systemd-resolved服务相关的高级命令和安全防护等。
-
深度解析Linux中的DNS服务2025-04-09 747
-
域名解析是什么 为什么要进行域名解析2024-11-22 1468
-
域名解析是什么意思?2023-11-21 3346
-
ip地址是从哪来的呢 DNS技术详解2023-07-24 4459
-
DNS劫持的工作原理和解决方案2020-07-07 6250
-
使用JavaScript代码在Rapid板子上实现DNS解析域名得到IP地址操作分享!2019-08-15 3732
-
如何解决DNS解析错误故障2018-09-29 4158
-
汉邦高科域名解析教程2017-01-04 745
-
如何在 Linux 上从 NetworkManager 切换为 systemd2015-11-25 7679
-
华为mu509支持域名解析吗?2014-07-12 2933
-
[讨论]域名解析了,网站却打不开的原因2010-11-25 3259
-
什么是域名DNS2010-07-19 2376
-
动态域名解析、E-mail的工作原理2009-08-06 706
全部0条评论

快来发表一下你的评论吧 !

