

鸿蒙元服务实战-笑笑五子棋(4)
电子说
描述
鸿蒙元服务实战-笑笑五子棋(4)
我们在这一章节主要实现五子棋的基本逻辑
核心目录结构
├─ets
│ ├─entryability
│ │ EntryAbility.ets
│ │
│ ├─entryformability
│ │ EntryFormAbility.ets
│ │
│ ├─pages
│ │ Index.ets
│ │
│ ├─views
│ │ About.ets
│ │ Home.ets
│ │
│ └─widget
│ └─pages
│ WidgetCard.ets
│
└─resources
├─base
│ ├─element
│ │ color.json
│ │ float.json
│ │ string.json
│ │
│ ├─media
│ │ right.svg
│ │ startIcon.png
│ │
│ └─profile
│ form_config.json
│ main_pages.json
│
├─en_US
│ └─element
│ string.json
│
├─rawfile
└─zh_CN
└─element
string.json
## 沉浸式设计

1. `entry/src/main/ets/entryability/EntryAbility.ets` 中统一设置
```javascript
onWindowStageCreate(windowStage: window.WindowStage): void {
windowStage.getMainWindow()
.then(windowClass = > {
// 设置沉浸式
windowClass.setWindowLayoutFullScreen(true)
// 顶部状态栏
const topAvoidArea = windowClass.getWindowAvoidArea(window.AvoidAreaType.TYPE_SYSTEM);
const topRectHeight = topAvoidArea.topRect.height;
// px转vp
const vpTopHeight = px2vp(topRectHeight)
// 底部导航条
const bottomAvoidArea = windowClass.getWindowAvoidArea(window.AvoidAreaType.TYPE_NAVIGATION_INDICATOR);
const bottomRectHeight = bottomAvoidArea.bottomRect.height;
const vpBottomHeight = px2vp(bottomRectHeight)
AppStorage.setOrCreate('topRect', vpTopHeight)
AppStorage.setOrCreate('bottomRect', vpBottomHeight)
})
windowStage.loadContent('pages/Index', (err) = > {
// ...
});
}
页面通过 padding 避开顶部和底部
@StorageProp("topRect") topRect: number = 0 @StorageProp("bottomRect") bottomRect: number = 0 build() { Column() { // ... } .width('100%') .height('100%') .linearGradient({ colors: [["#DEF9ED", 0], ["#F4F5F7", 0.4]] }) .padding({ top: this.topRect, bottom: this.bottomRect }) }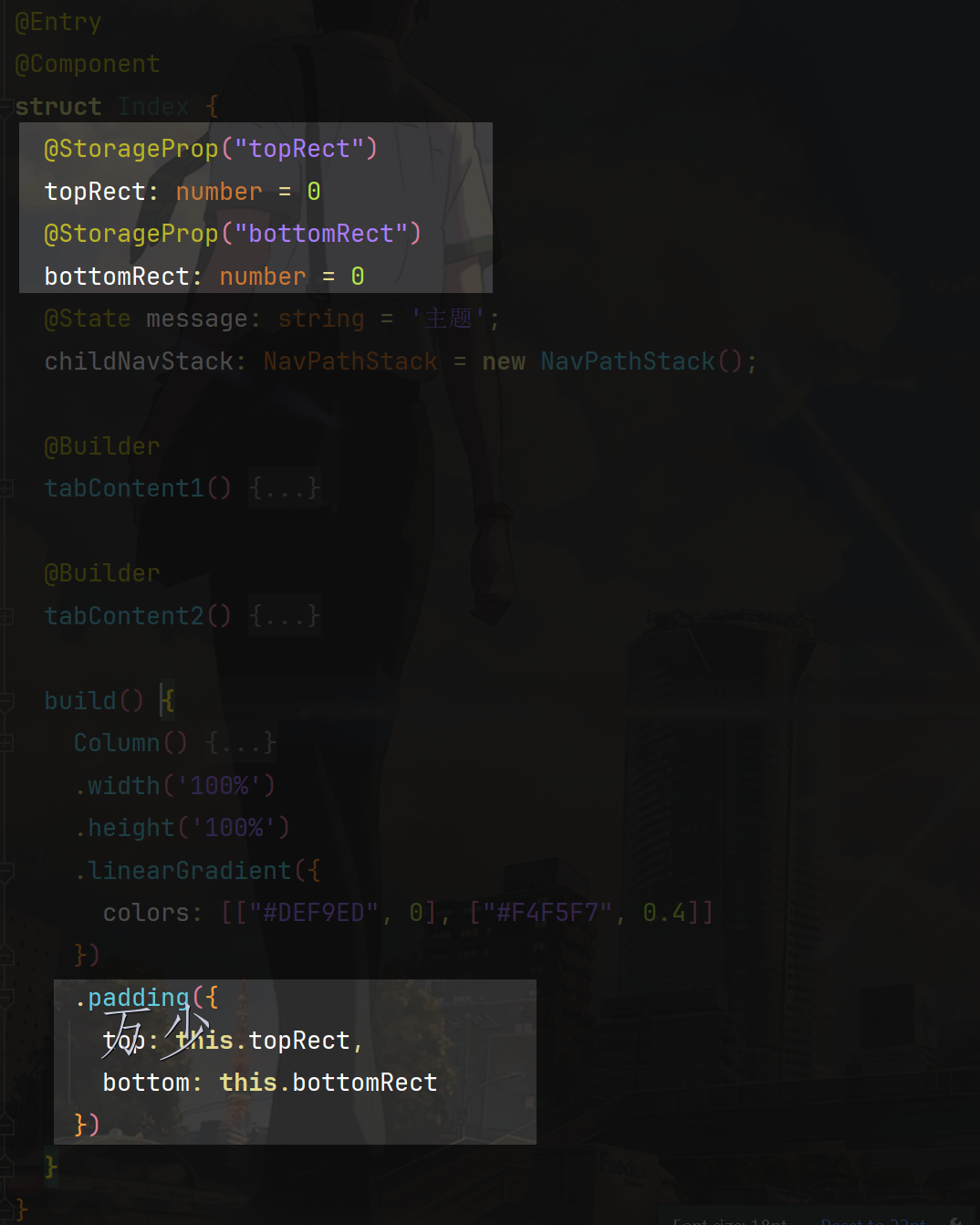
AtomicServiceTabs
AtomicServiceTabs是元服务独有的 tab 组件。Tabs组件后续不再支持在元服务中进行使用。,对 Tabs 组件一些不需提供给用户自定义设计的属性进行简化,限制最多显示 5 个页签,固定页签样式,位置和大小。

基本用法
AtomicServiceTabs({
// 内容
tabContents: [
() = > {
// 自定义构建函数
this.tabContent1();
},
() = > {
// 自定义构建函数
this.tabContent2();
},
],
// 标题
tabBarOptionsArray: [
new TabBarOptions(
$r("sys.media.save_button_picture"),
"玩吧",
"#666",
"#07C160"
),
new TabBarOptions($r("sys.media.AI_keyboard"), "关于", "#666", "#07C160"),
],
// 标题显示的位置
tabBarPosition: TabBarPosition.BOTTOM,
// 背景颜色
barBackgroundColor: 0xffffff,
});
Home 和 About
Home 表示首页,用来显示主要内容
About 表示关于,用来存放项目的基本信息
他们目前都是普通的组件,分别放在 tabContent1 和 tabContent2 内
引入 canvas
在 Home 中开始引入canvas
@Component
export struct Home {
settings: RenderingContextSettings = new RenderingContextSettings(true);
ctx: CanvasRenderingContext2D = new CanvasRenderingContext2D(this.settings);
build() {
Column() {
Canvas(this.ctx)
.width(width)
.height(width)
.backgroundColor(Color.Orange)
}
.width("100%")
.height("100%")
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
}
}
绘制棋盘
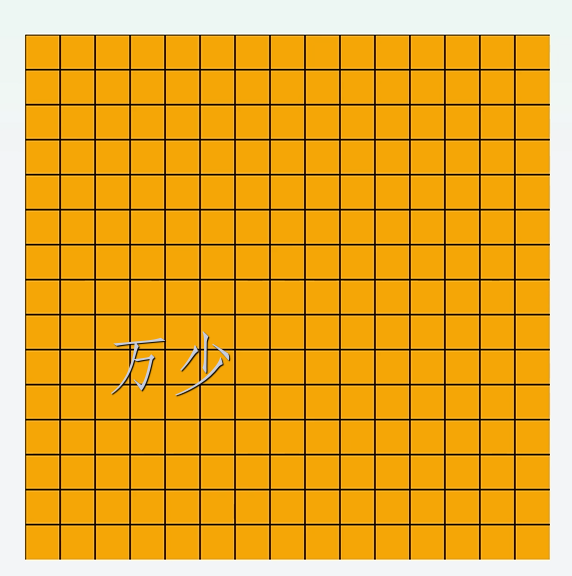
绘制棋盘的思路如下:
- 确定要绘制多少个格子。
- 每一个格子多大
这里的想法比较简单:
- 确定要绘制的格子是 15 个。
gridSize: number = 15; - 每一个格多大,由屏幕宽度决定。比如屏幕宽度的 90%,然后分成 15 份。每一份就是格子的宽度
// 获取屏幕的宽度的 90% const width = px2vp(display.getDefaultDisplaySync().availableWidth) * 0.9; // 棋盘是正方形的,所以高度和宽度相等 const height = width; cellSize: number = width / this.gridSize; - 然后封装描绘画面的方法
drawBoard
// 绘制棋盘
drawBoard = () = > {
this.ctx.clearRect(0, 0, width, height);
// 绘制网格
this.ctx.strokeStyle = "#000";
this.ctx.lineWidth = 1;
for (let i = 0; i < this.gridSize; i++) {
this.ctx.beginPath();
this.ctx.moveTo(this.cellSize * i, 0);
this.ctx.lineTo(this.cellSize * i, height);
this.ctx.stroke();
this.ctx.beginPath();
this.ctx.moveTo(0, this.cellSize * i);
this.ctx.lineTo(width, this.cellSize * i);
this.ctx.stroke();
}
};
- canvas 准备好的时候开始绘制
Canvas(this.ctx) .width(width) .height(width) .backgroundColor(Color.Orange) .onReady(() = > { this.drawBoard(); });
点击下棋
点击下棋要是做挺多的处理的,比如:
- 当前是下黑棋还是白棋
- 下完这一子之后,胜利了还是继续下。
我们开始吧:
- 初始化棋盘数据,它是一个二维数组,下棋的时候,其实也是往里面填充内容
// 棋盘数据 board: number[][] = [] - 初始化当前下棋的角色 设定 1:黑旗 ,2:白旗
currentPlayer: number = 1; // 当前玩家 (1: 黑子, 2: 白子) - 声明初始化棋盘的函数,负责初始化棋盘数据和描绘棋盘
initGame = () = > { this.board = [] for (let index = 0; index < this.gridSize; index++) { const arr: number[] = [] for (let index2 = 0; index2 < this.gridSize; index2++) { // 0 表示当前没有人在下棋 arr.push(0) } this.board.push(arr) } // this.currentPlayer = 1; // this.gameOver = false; // this.textContent = '轮到黑子落子'; this.drawBoard(); } ------------------- Canvas(this.ctx) .width(width) .height(width) .backgroundColor(Color.Orange) .onReady(() = > { this.initGame() }) - 声明点击棋盘事件,事件中执行下棋逻辑
handleClick = async (event: ClickEvent) = > { const x = event.x; const y = event.y; const col = Math.floor(x / this.cellSize); const row = Math.floor(y / this.cellSize); if (this.board[row] && this.board[row][col] === 0) { this.board[row][col] = this.currentPlayer; this.drawBoard(); this.currentPlayer = this.currentPlayer === 1 ? 2 : 1; } else { promptAction.showToast({ message: `请点击中棋盘对位位置` }); } }; - 调整
drawBoard函数,根据this.board[row][col]描绘出旗子// 绘制棋盘 drawBoard = () = > { this.ctx.clearRect(0, 0, width, height); // 绘制网格 this.ctx.strokeStyle = "#000"; this.ctx.lineWidth = 1; for (let i = 0; i < this.gridSize; i++) { this.ctx.beginPath(); this.ctx.moveTo(this.cellSize * i, 0); this.ctx.lineTo(this.cellSize * i, height); this.ctx.stroke(); this.ctx.beginPath(); this.ctx.moveTo(0, this.cellSize * i); this.ctx.lineTo(width, this.cellSize * i); this.ctx.stroke(); } // 绘制已落的棋子 for (let row = 0; row < this.gridSize; row++) { for (let col = 0; col < this.gridSize; col++) { if (this.board[row][col] !== 0) { this.ctx.beginPath(); this.ctx.arc( col * this.cellSize + this.cellSize / 2, row * this.cellSize + this.cellSize / 2, this.radius, 0, 2 * Math.PI ); this.ctx.fillStyle = this.board[row][col] === 1 ? "black" : "white"; this.ctx.fill(); this.ctx.stroke(); } } } }; - 效果
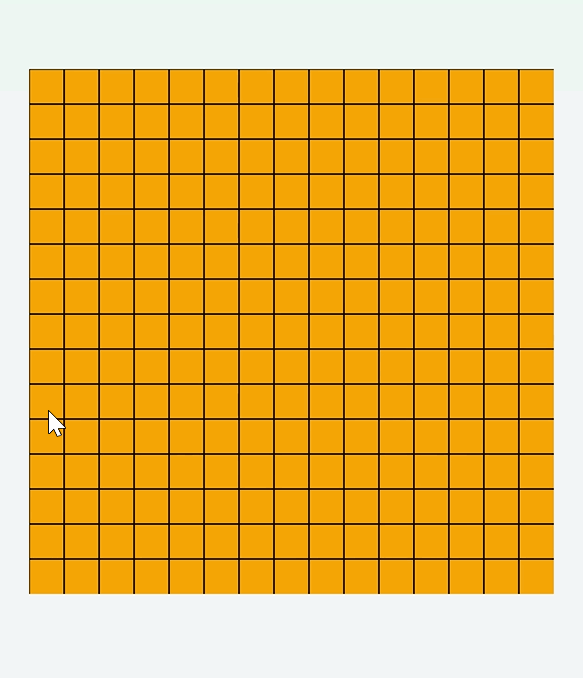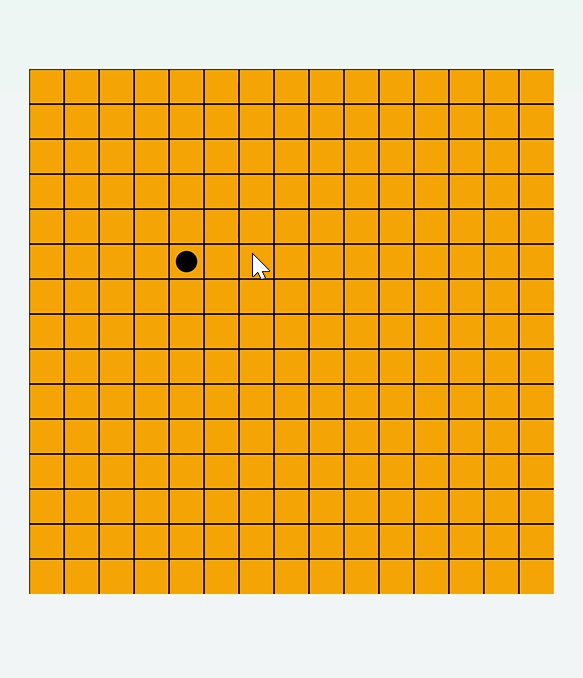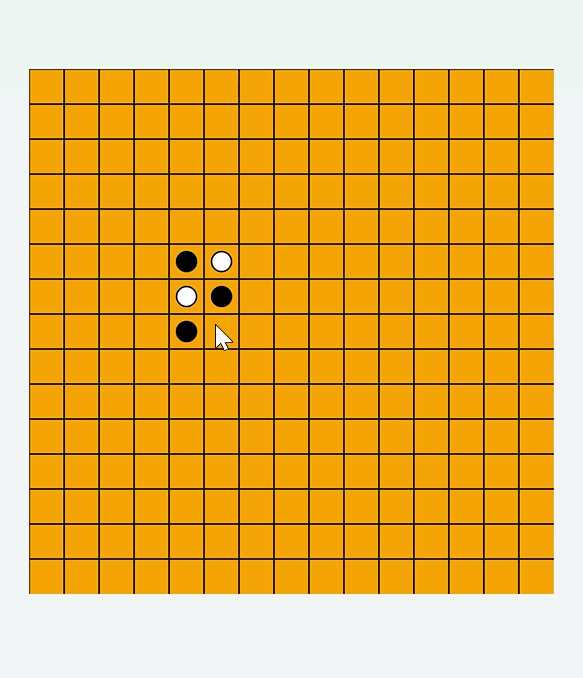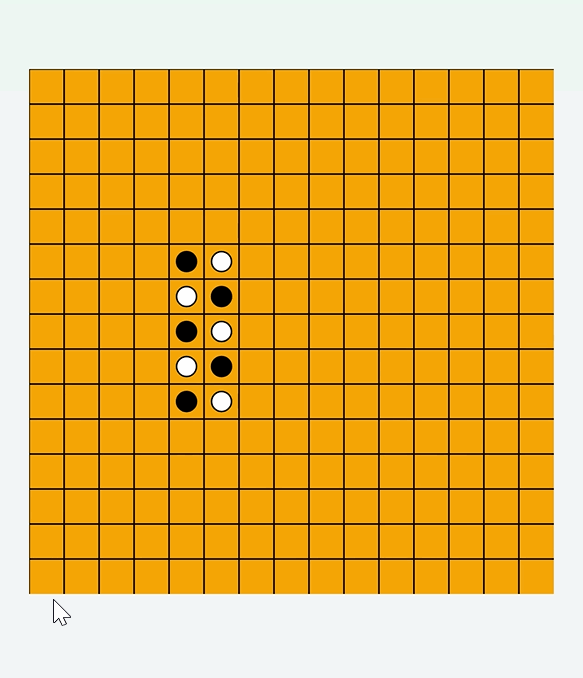
判断输赢
五子棋判断输赢的方法比较简单,只需要知道是否有五子连珠就行
定义判断输赢的方法
checkWin// 判断是否有五子连珠 checkWin = (row: number, col: number) = > { // 定义一个接口abc,用于表示方向相关的偏移量,dr表示行方向的偏移量,dc表示列方向的偏移量 interface abc { dr: number dc: number } // 定义一个包含四个方向偏移量信息的数组,分别对应不同的检查方向 const directions: abc[] = [ { dr: 0, dc: 1 }, // 水平方向,行偏移量为0,列偏移量为1,即向右检查 { dr: 1, dc: 0 }, // 垂直方向,行偏移量为1,列偏移量为0,即向下检查 { dr: 1, dc: 1 }, // 主对角线方向,行和列偏移量都为1,向右下方向检查 { dr: 1, dc: -1 }// 副对角线方向,行偏移量为1,列偏移量为 -1,即向右上方向检查 ]; // 遍历四个不同的方向,依次检查每个方向上是否有五子连珠情况 for (let i = 0; i < directions.length; i++) { const dr = directions[i].dr; const dc = directions[i].dc; let count = 1; // 向一个方向检查(从当前落子位置开始,沿着指定方向向前检查) // 循环尝试查找连续相同颜色的棋子,最多查找连续4个(因为已经有当前落子算1个了,凑够5个判断赢) for (let i = 1; i < 5; i++) { let r = row + dr * i; let c = col + dc * i; // 判断当前位置是否在棋盘范围内,并且此位置的棋子颜色是否和当前玩家的棋子颜色相同 if (r >= 0 && r < this.gridSize && c >= 0 && c < this.gridSize && this.board[r][c] === this.currentPlayer) { count++; } else { break; } } // 向另一个方向检查(从当前落子位置开始,沿着指定方向的反方向检查) // 同样循环尝试查找连续相同颜色的棋子,最多查找连续4个 for (let i = 1; i < 5; i++) { let r = row - dr * i; let c = col - dc * i; if (r >= 0 && r < this.gridSize && c >= 0 && c < this.gridSize && this.board[r][c] === this.currentPlayer) { count++; } else { break; } } // 如果在当前方向(正方向和反方向结合起来)上连续相同颜色的棋子数量达到或超过5个,则表示当前玩家胜利 if (count >= 5) { return true; } } // 如果遍历完所有方向都没有出现五子连珠的情况,则返回false,表示当前落子未形成胜利局面 return false; }在点击下棋时 判断是否输赢
handleClickif (this.board[row] && this.board[row][col] === 0) { this.board[row][col] = this.currentPlayer; this.drawBoard(); if (this.checkWin(row, col)) { // 执行后续逻辑在
handleClick中判断输赢后,再做后续的一些小逻辑- 如 还没决定输赢,继续下棋
- 决定输赢了,弹出对话框恭喜胜利者, 询问是否还要再下一盘。。
- 完整代码
// 处理玩家落子 handleClick = async (event: ClickEvent) = > { if (this.gameOver) { return; } const x = event.x; const y = event.y; const col = Math.floor(x / this.cellSize); const row = Math.floor(y / this.cellSize); if (this.board[row] && this.board[row][col] === 0) { this.board[row][col] = this.currentPlayer; this.drawBoard(); if (this.checkWin(row, col)) { this.textContent = this.currentPlayer === 1 ? "黑子胜利!" : "白子胜利!"; this.gameOver = true; // AlertDialog.show({ message: this.textContent }) const res = await promptAction.showDialog({ title: this.textContent, message: "重新再来一盘吗", buttons: [ { text: "不了", color: "#000" }, { text: "来吧", color: "#0094ff" }, ], }); if (res.index === 1) { this.initGame(); } } else { this.currentPlayer = this.currentPlayer === 1 ? 2 : 1; this.textContent = this.currentPlayer === 1 ? "轮到黑子落子" : "轮到白子落子"; } } else { promptAction.showToast({ message: `请点击中棋盘对位位置` }); } };效果
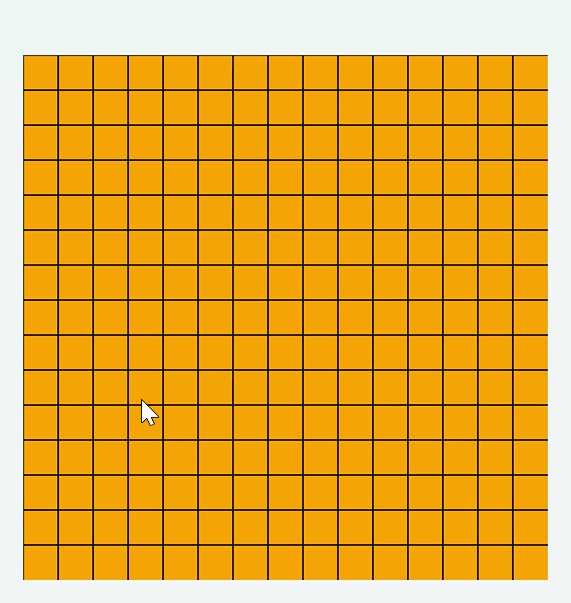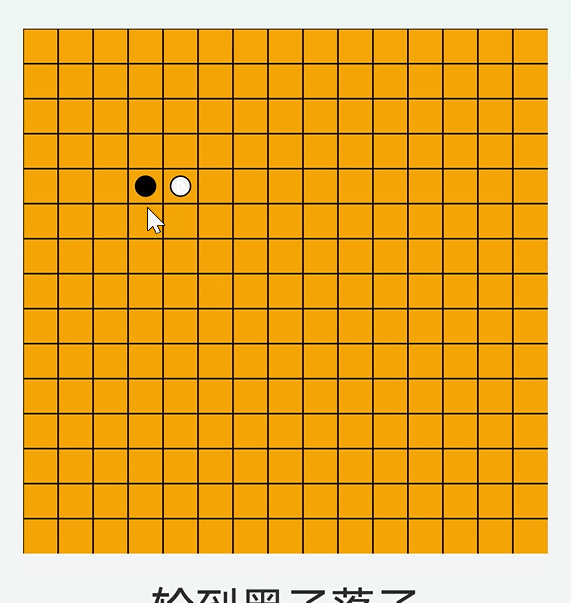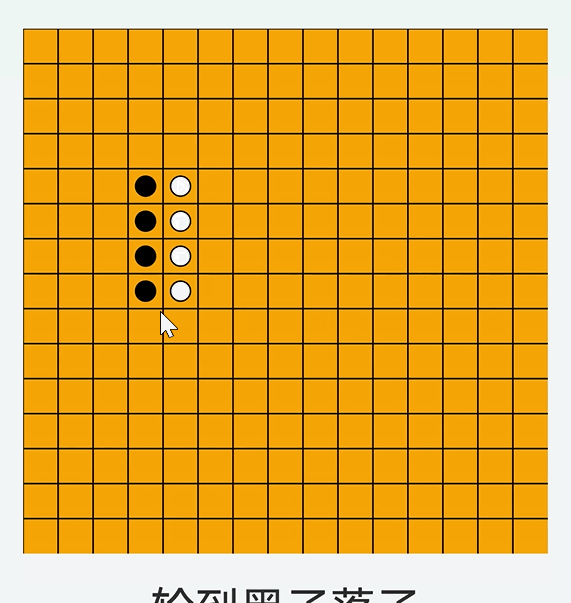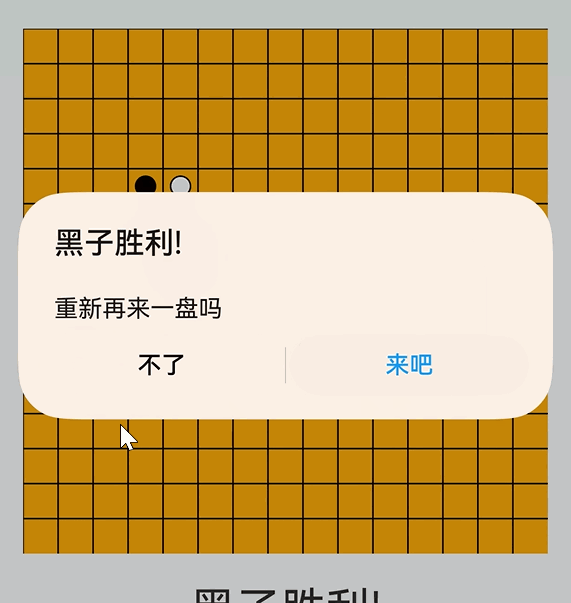
总结
本章节多了一些业务的具体实现,尤其是下棋的一些逻辑处理上。
如果你兴趣想要了解更多的鸿蒙应用开发细节和最新资讯,欢迎在评论区留言或者私信或者看我个人信息,可以加入技术交流群。
审核编辑 黄宇
-
鸿蒙元服务实战-笑笑五子棋(1)2025-03-31 646
-
怎么实现基于STM32的五子棋游戏的设计?2021-11-26 1179
-
怎样去设计一种人机对弈五子棋程序2021-09-29 2350
-
labview 虚拟五子棋2020-06-16 3241
-
基于LabVIEW的五子棋博弈算法2017-12-17 1047
-
C语言教程之五子棋游戏的问题2016-04-25 557
-
Delphi教程_使用DrawGrid控件制作五子棋2016-03-16 1369
-
C语言五子棋2016-01-12 481
-
五子棋2015-06-26 4499
-
用Verilog写的一个五子棋2014-06-15 15398
-
五子棋主程序前面板怎么设计2013-07-03 3078
-
五子棋的棋盘怎么么做2013-07-02 6429
-
labview五子棋程序2012-06-10 48327
-
用java语言编写的智能五子棋源程序2008-10-30 682
全部0条评论

快来发表一下你的评论吧 !

