

Ansible到底是个什么东西?
电子说
描述
前言
最近在重构一款命令行工具,使用 golang 重新开发,但需要继续维持原有的命令,同时增加新命令。
在重构的过程中,需要对现命令行工具和原命令行工具的命令输出结果进行比对,确保完全一致(项目要求),命令行工具需要在部署完成系统之后进行使用,每个系统完成时的部署组件又稍微有点差异。所以其实需要在多套服务主机上进行测试。
需要做这些动作:
拷贝一些配置文件到主机上:用户配置、IP和端口文件
安装命令行工具,确保使其在服务主机上可以使用
执行一堆测试命令
按理说,我不断把需要的配置和二进制文件拷贝到主机上进行测试也能完成。
但在使用的过程中存在下面几个问题:
测试发现,结果不对时需要及时修改代码,再次拷贝二进制文件到主机上
主机环境需要多次推倒,重新部署,验证版本更新问题
需要手动一个一个命令的执行
测试有几套主机
看上去手动的方法,有点费劲。
目前我从事的工作就是 PaaS 部署相关的,部署层面的脚本的运行、组件的安装、服务的启动等都是使用 Ansible 来操作。具体的脚本编写由其他同事,我只知道这个东西是干嘛的。没实质性的学习。于是想借这个机会主动学习下 Ansible.
学习之处,差点犯了老问题,即:从头开始看官方文档,而不注重当前需要解决的问题。
因为其实整个 Ansible 的内容体系很多。不注重当前需要解决的问题,会导致你抓不住重点。
意识到后专注在当前需要解决的问题上:
拷贝配置文件和安装脚本到多个主机上
在多个主机上测试命令行工具
Ansible
看了上面的事件背景,你大概知道这个 Ansible 到底是个什么东西。
Ansible 是一个配置管理和应用部署工具,即在管理主机上操作一些命令就能在节点主机上进行相应的动作。由 Python 编写,由模块化组成,即执行动作的实体,在 ansible 上都是靠着相应的模块执行动作,比如拷贝 copy 模块、执行 command 模块、shell 模块、文件 file 模块等。
Ansible 的目标有如下:
自动化部署应用
自动化管理配置
自动化的持续交付
自动化的(AWS)云服务管理。
原理
管理主机从 hosts 里读取主机清单,通过 playbook 按顺序同时对管理的主机进行相应的操作。
如图:
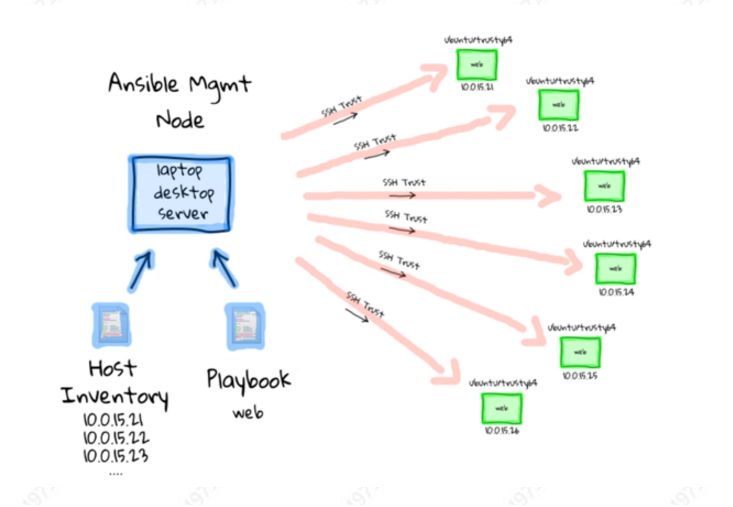
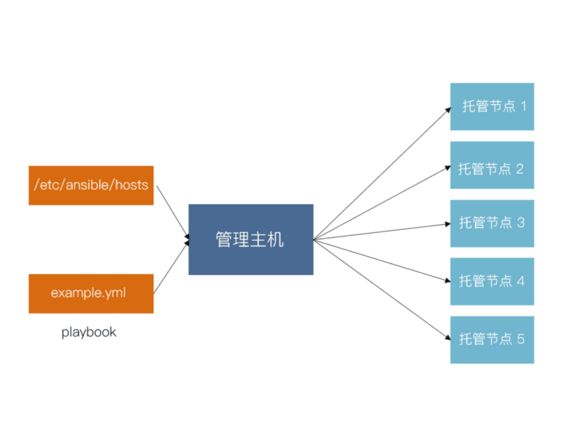
管理主机主要是对主机的定义和配置、编写 playbook(即节点主机的执行动作)。
运行:
1. 命令行
ansible all -m ping
2. playbook
ansible-playbook example.yml
主机清单
编辑文件:/etc/ansible/hosts
即:定义主机名称,变量等
主机的变量包括什么: 主机的执行用户、连接端口、密码等
类似于 ini 格式的文件
[test-new-cli] 10.62.60.72 [test-old-cli] 10.62.62.88
上面的例子:将两个主机的分为两组:test-new-cli 和 test-old-cli
主机的变量有这么些:
ansible_ssh_host将要连接的远程主机名.与你想要设定的主机的别名不同的话,可通过此变量设置.
ansible_ssh_portssh端口号.如果不是默认的端口号,通过此变量设置.
ansible_ssh_user默认的 ssh 用户名
ansible_ssh_passssh 密码(这种方式并不安全,我们强烈建议使用 —ask-pass 或 SSH 密钥)
ansible_sudo_passsudo 密码(这种方式并不安全,我们强烈建议使用 —ask-sudo-pass)
ansible_sudo_exe (new in version 1.8)sudo 命令路径(适用于1.8及以上版本)
ansible_connection与主机的连接类型.比如:local, ssh 或者 paramiko.
ansible_ssh_private_key_filessh 使用的私钥文件.适用于有多个密钥,而你不想使用 SSH 代理的情况.
ansible_shell_type目标系统的shell类型.默认情况下,命令的执行使用 ‘sh’ 语法,可设置为 ‘csh’ 或 ‘fish’.
ansible_python_interpreter目标主机的 python 路径.
看不懂怎么用:
举个例子,你想连接主机 192.168.100.100 , 切换到 root 用户下执行相应的操作。
如果你直接ssh username@192.168.100.100 会要求你输入用户名和密码。
假如我编辑主机清单使得自己不需要输入用户名密码,怎么操作?
[test-new-cli] example ansible_ssh_host=192.168.100.100 ansible_ssh_user=username ansible_ssh_pass=root
即配置好192.168.100.100 的主机别名为example, 主机的用户名和密码为:username/root
Yaml
包含三种类型:
键值对:key: value
数组
纯量:整型、字符串、布尔型
这个很好理解:如果你熟悉Python, 这三种类型就相当于:map, list, 变量
如果你熟悉golang, 这三种类型就相当于: map, 数组, 变量
示例:
--- - name: "execute command nodepool node list by { {item.name} }" shell: "{ {item.cli} } nodepool node list { {item.id} }" register: result - name: show result debug: msg: "{ {result.stdout_lines} }" with_items: - { name: "new-cli", cli: "new-cli", id: "1" } - { name: "old-cli", cli: "old-cli", id: "1" }
模块
Ad-doc
ansible 命令行式,适合执行单条命令。
# 操作 192.168.100.100 主机,看管理主机是否和192.168.100.100的主机连通 ansible example -m ping # 操作 192.168.100.100 主机,拷贝管理主机下的/root/opcli/conf 文件至节点主机/etc/opcli/conf 下 ansible test-new-cli -m copy -a="src=/root/opcli/conf dest=/etc/opcli/conf"
m: 模块
a: 接参数
可以看出适合执行单条命令
Patterns
假如你的节点主机分组很多了,Ad-hoc 如何选择特定特征的节点主机分组呢?
使用类正则表达式。
比如触发所有节点主机进行动作:
ansible all -m ping ansible * -m ping 两者等价,都是选择所有的节点主机
示例:
1. 主机别名或者IP
one.example.com one.example.com:two.example.com 192.168.1.50 192.168.1.*
2. 一个或多个groups
webservers webservers:dbservers
3. 排除一个组
webservers:!phoenix # 隶属 webservers 组但同时不在 phoenix组
4. 两个组的交集
webservers:&staging # 同时隶属于 webservers 和 staging 组
5. 列表
webservers[0] webservers[0-25]
6. 其他
有什么需求,看官方文档吧。
Playbook
编写 yaml 文件,适合执行多步操作的复杂操作。可以看成是Ad-doc 命令的集合。甚至可以看成是一门编程语言。
执行:ansible-playbook example.yml
按照 example.yml 文件里的任务集合按步执行任务。
示例
命令示例,仅举几例,有带参数、有没带参数的。
我们最终的目标是:在节点主机上执行这些命令进行比对两者结果。
新版本:
| 命令 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| command-cli nodepool list | 查询资源池 |
| command-cli nodepool node list | 查询资源池节点 |
| command-cli node list | 查询节点 |
| command-cli node show | 查询某个节点 |
| command-cli task list | 查询部署任务 |
…
旧版本:
| 命令 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| old-cli nodepool list | 查询资源池 |
| old-cli nodepool node list | 查询资源池节点 |
| old-cli node list | 查询节点 |
| old-cli node show | 查询某个节点 |
| old-cli task list | 查询部署任务 |
…
目录结构:
demo-for-ansible: ---nodepool/nodepool-list.yml ---nodepool/nodepool-node-list.yml ---node/node-list.yml ---node/node-show.yml ---task/task-list.yml ---main.yml
第一步:编写主机清单
/etc/ansible/hosts
[test_client] 192.168.100.100 ansible_ssh_user=xiewei ansible_ssh_pass=root ansible_connection=ssh 192.168.100.101 ansible_ssh_user=xiewei ansible_ssh_pass=root ansible_connection=ssh 192.168.100.102 ansible_ssh_user=xiewei ansible_ssh_pass=root ansible_connection=ssh
定义主机连接类型、用户名、密码
第二步:编写 yaml 文件
主要动作:
在节点主机上创建两个文件夹: /etc/client/conf 和 /et/client/commands
拷贝管理主机目录:/etc/client/conf 文件至节点主机: /etc/client/conf
拷贝管理主机二进制文件:/root/gosrc/src/client/command-cli 至节点主机 /etc/client/commands
软连接节点主机二进制文件:/etc/client/commands/command-cli 至节点主机 /usr/bin/command-cli
执行上表中查询命令:nodepool, node, task
main.yml
--- - hosts: test_client remote_user: root become: yes become_user: root become_method: sudo tasks: # 在节点主机上创建目录:/etc/client/conf - name: create /etc/client/conf /etc/client/commands file: path: "/etc/client/{ {item} }" owner: root group: root mode: 0755 state: directory with_items: - "conf" - "commands" # 拷贝管理主机配置文件/etc/client/conf和二进制文件至 /etc/client/conf, /etc/client/commands - name: copy /etc/client/conf copy: src="{ { item.src } }" dest="{ { item.dest } }" owner=root group=root mode=0644 with_items: - { src: "/etc/client/conf", dest: "/etc/client/conf" } - { src: "/root/gosrc/src/client/command-cli", dest: "/etc/client/commands"} # 软连接到 /usr/bin/command-cli - name: link /etc/client/commands file: src="/etc/client/commands/command-cli" dest="/usr/bin/command-cli" state=link # nodePool list - include_tasks: "nodepool/nodepool-list.yml" with_items: - { client: "new client", name: "command-cli"} - { client: "old client", name: "old-cli"} # nodePool node list
task-list.yml
--- - name: execute command task list shell: "{ {item.name} } task list" register: result - name: show result debug: msg: "{ {result.stdout_lines} }"
第三步: 检查语法
两种方法
ansible-playbook main.yml --syntax-check
先安装 pip install ansible-lint
ansible-lint main.yml
第四步: 执行
ansible-playbook main.yml
整个的编写流程大概是这样。核心是编写 yml 文件,调用 ansible 支持的各种模块完成任务。
-
ucos3移植的两个错误信息到底是什么?2019-08-11 2475
-
请教技术大佬 三态门与高阻态是个撒子东西?2021-04-07 3398
-
在ahdllib中opamp的veriloga代码中,cout是个什么东西?2021-06-24 4865
-
手机参数中的4+64G到底是什么东西2021-09-14 1748
-
ARM是什么东西?2009-03-30 2724
-
LiFePO4是什么东西?2009-10-27 3346
-
全液晶仪表到底是什么东西?2018-04-23 11305
-
CPU钎焊工艺到底是什么2018-10-23 41128
-
工业触摸屏到底是一个什么东西2019-05-24 7534
-
元宇宙到底是什么东西2021-11-02 5808
-
芯片到底是什么东西2022-01-04 22036
-
集成电路到底是什么东西2022-02-01 11356
-
Armv8-A到底是什么东西呢?2023-04-19 6766
-
脉宽调制到底是个什么东西?2023-08-30 2565
-
智能盒子到底是什么东西?昇腾310深度测评:为何能成为行业新宠?2025-04-27 1511
全部0条评论

快来发表一下你的评论吧 !

