

使用VSCode编译Apollo项目,使用VSCode本地调试Apollo项目
电子说
描述
前言
1. 我已将本文所述的配置文件上传到Apollo项目的GitHub仓库,大家直接下载使用即可。
2. 我之前已写过一篇博客《使用Visual Studio Code编译Apollo项目》(https://blog.csdn.net/davidhopper/article/details/79349927),这篇文章内容不够全面,这里给出更为详细的阐述。
Apollo项目以其优异的系统架构、完整的模块功能、良好的开源生态及规范的代码风格,受到众多开发者的喜爱和好评。然而,该项目使用命令行编译和调试,不能使用IDE开发,既不直观,也不利于提高效率。我有点追求完美,必须想办法让Apollo项目能在IDE中编译、调试。
Visual Studio Code(以下简称VSCode)是微软第一款支持Linux的轻量级代码编辑器,其功能介于编辑器与IDE之间,但更倾向于一个编辑器。优点是运行速度快,占用内存少,使用方法与Visual Stuio类似。缺点在于,与Visual Studio、QT等IDE相比,功能还不够强大。我认为,Windows中最强大的C++ IDE为Visual Studio,Linux中最强大的C++ IDE为QT。
Apollo项目目前只支持Ubuntu系统(Mac OS系统部分支持),Windows系统中的Visual Studio自然排除在外;此外,Apollo项目使用Bazel编译,而QT目前只支持QMake和CMake工程,因此只能忍痛割爱。在无法使用上述两种IDE的前提下,退而求次选用VSCode。
我写了几个配置文件,允许使用VSCode编译、调试Apollo项目,下面对其进行具体阐述,希望能给广大开发者带来一定的帮助。
{ 一 }
使用VSCode编译Apollo项目
首先从GitHub网站(https://github.com/ApolloAuto/apollo)下载Apollo源代码,可以使用git命令下载,也可以直接通过网页下载压缩包。源代码下载完成后,将其放置到合适的目录。使用VSCode编译Apollo项目有一个前提,就是在你的机器上已经顺利安装了Docker。Apollo之前版本提供了一个“install_docker.sh”脚本文件,因为很多开发者反映可能出错,Apollo项目组已将该文件移除。现在要安装Docker就只能参考Docker官方网站(https://www.docker.com/)的帮助文档了。
1.1编译方法
打开“Visual Studio Code”,执行菜单命令“文件->打开文件夹”,在弹出的对话框中,选择“Apollo”项目源文件夹,点击“确定”,如下图所示:


之后,执行菜单命令“任务->运行生成任务”或直接按快捷键“Ctrl+Shift+B”(与Visual Studio和QT的快捷键一致)构建工程,若之前没有启动过Docker,则编译时会启动Docker,需在底部终端窗口输入超级用户密码,如下图所示:
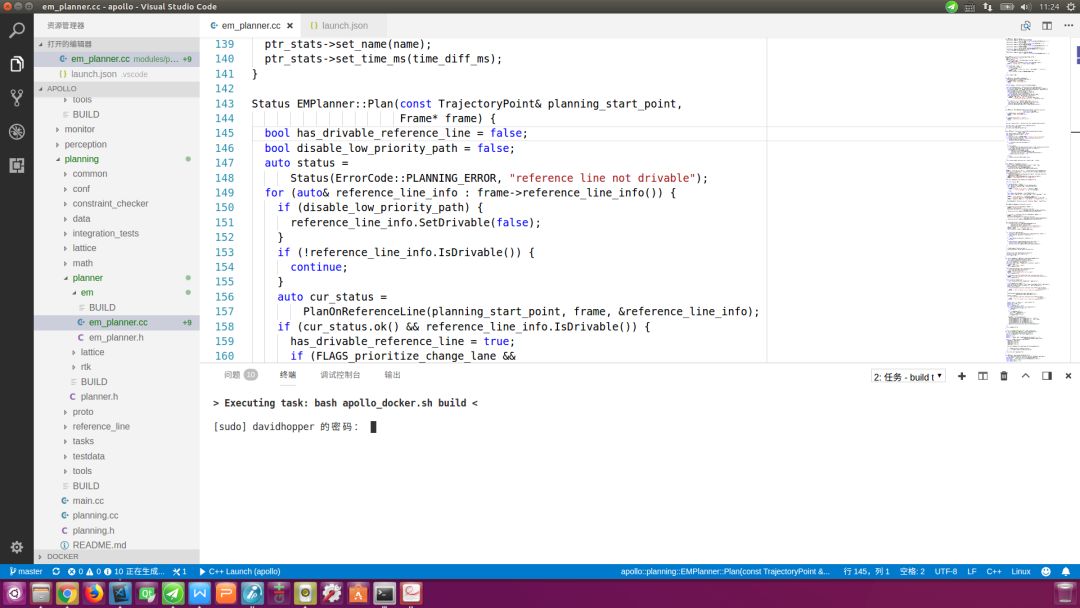
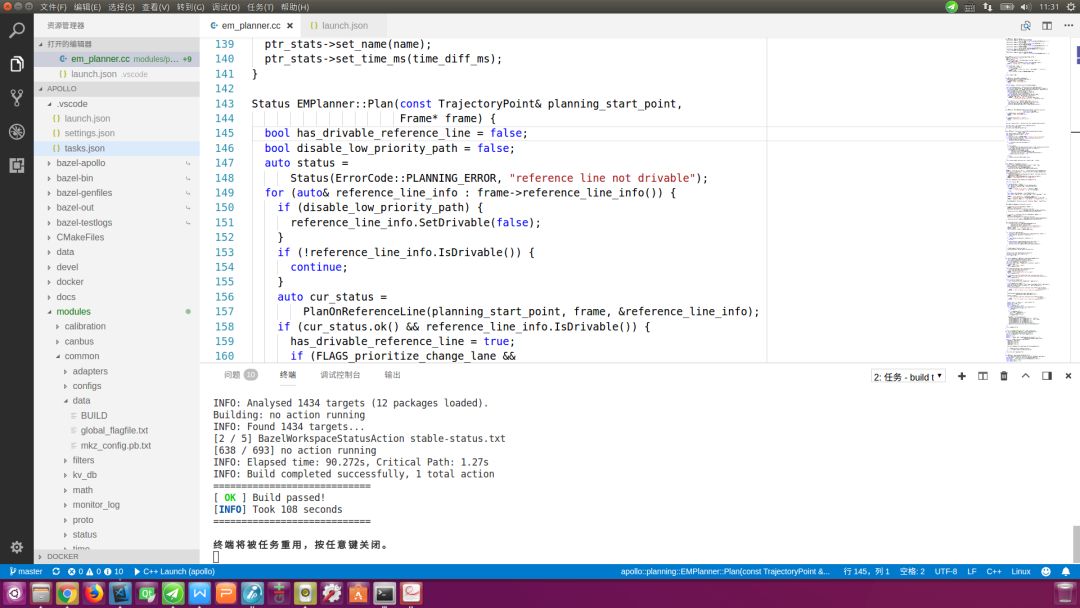
命令执行完毕,若在底部终端窗口出现“终端将被任务重用,按任意键关闭。”信息(如下图所示),则表示构建成功。整个过程一定要保持网络畅通,否则无法下载依赖包。
1.2配置文件解析
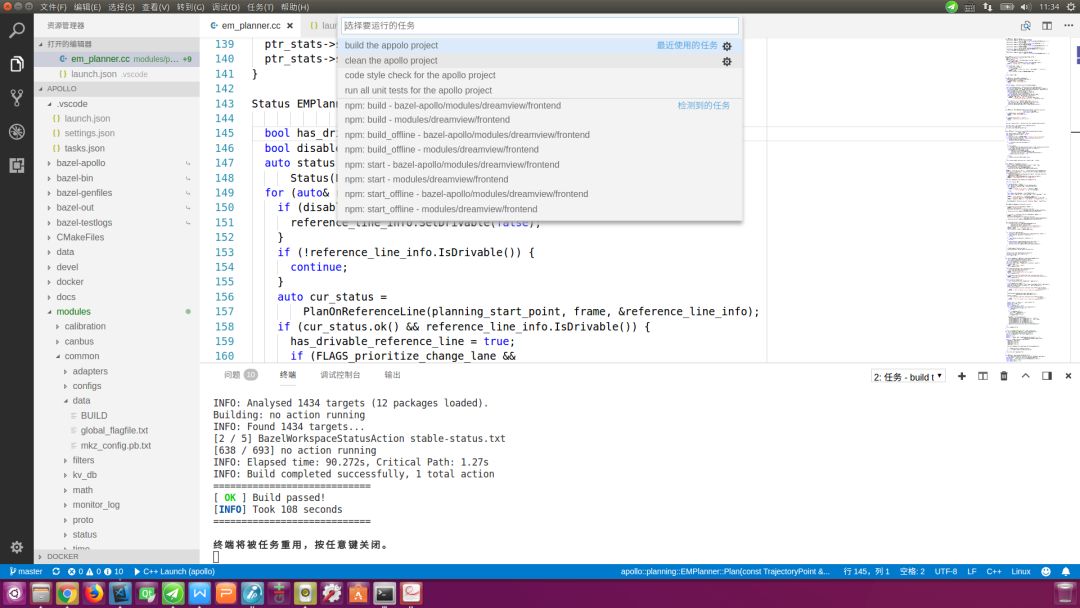
我在.vscode/tasks.json文件中总共配置了四个常见的任务:build the apollo project(构建Apollo项目)、run all unit tests for the apollo project(运行Apollo项目的所有单元测试)、code style check for the apollo project(Apollo项目的代码风格检查)、clean the apollo project(清理Apollo项目)。其中第一个任务是默认生成任务,可以直接按快捷键“Ctr+Shift+B”调用,其他任务可通过执行菜单命令:任务->运行任务(R)…,在弹出的窗口中,选择对应选项即可,如下图所示:
下面是具体的配置内容,请参考里面的注释来调整编译任务以满足你的构建需求:
{ “version”: “2.0.0”,
“tasks”: [
{
“label”: “build the apollo project”,
“type”: “shell”,
// 可根据“apollo.sh”提供的选项来调整编译任务,例如:build_gpu
“command”: “bash apollo_docker.sh build”,
“group”: {
“kind”: “build”,
“isDefault”: true // default building task invoked by “Ctrl+Shift+B”
},
// 格式化错误信息
“problemMatcher”: {
“owner”: “cc”,
“fileLocation”: [
“relative”,
“${workspaceFolder}”
],
“pattern”: {
“regexp”: “^(.*):(\d+):(\d+):\s+(warning|error):\s+(.*)$”,
“file”: 1,
“line”: 2,
“column”: 3,
“severity”: 4,
“message”: 5
}
}
},
{
“label”: “run all unit tests for the apollo project”,
“type”: “shell”,
“command”: “bash apollo_docker.sh test”,
“problemMatcher”: {
“owner”: “cc”,
“fileLocation”: [
“relative”,
“${workspaceFolder}”
],
“pattern”: {
“regexp”: “^(.*):(\d+):(\d+):\s+(warning|error):\s+(.*)$”,
“file”: 1,
“line”: 2,
“column”: 3,
“severity”: 4,
“message”: 5
}
}
},
{
“label”: “code style check for the apollo project”,
“type”: “shell”,
“command”: “bash apollo_docker.sh lint”,
“problemMatcher”: {
“owner”: “cc”,
“fileLocation”: [
“relative”,
“${workspaceFolder}”
],
“pattern”: {
“regexp”: “^(.*):(\d+):(\d+):\s+(warning|error):\s+(.*)$”,
“file”: 1,
“line”: 2,
“column”: 3,
“severity”: 4,
“message”: 5
}
}
},
{
“label”: “clean the apollo project”,
“type”: “shell”,
“command”: “bash apollo_docker.sh clean”,
“problemMatcher”: {
“owner”: “cc”,
“fileLocation”: [
“relative”,
“${workspaceFolder}”
],
“pattern”: {
“regexp”: “^(.*):(\d+):(\d+):\s+(warning|error):\s+(.*)$”,
“file”: 1,
“line”: 2,
“column”: 3,
“severity”: 4,
“message”: 5
}
}
}
]}
1.3可能存在的问题及解决方法1.3.1 编译时遇到“ERROR: query interrupted”错误
这是由于bazel内部缓存不一致造成的。
解决方法:
按任意键退出编译过程,在VSCode的命令终端窗口(如果未打开,按快捷键“Ctrl + `”开启)执行如下命令进入Docker环境:
| 1 | bash docker/scripts/dev_into.sh |
在Docker环境中输入如下命令,执行bazel的清理缓存任务(一定要保持网络畅通,以便成功下载依赖包,否则该命令即使执行一万次也不会奏效):
| 1 | bazel query //... |
最后输入exit命令退出Docker环境,按快捷键“Ctrl+Shift+B”,重新执行构建任务。
1.3.2 编译时长时间停留在“Building: no action running”界面
这是由于当前系统中存在多个不同版本的Docker或者是bazel内部缓存不一致造成的。
解决方法:
按快捷键“Ctrl+C”键终止当前构建过程,在VSCode的命令终端窗口(如果未打开,按快捷键“Ctrl + `”开启),使用下述方法中的任意一种,停止当前运行的Docker:
| 1234 | # 方法1:停止当前所有的Apollo项目Dockerdocker stop $(docker ps -a | grep apollo | awk '{print $1}')# 方法2:停止当前所有的Dockerdocker stop $(docker ps -aq) |
执行VSCode的菜单命令:任务->运行任务(R)…,在弹出的窗口中,选择 “clean the apollo project”(清理Apollo项目)。待清理完毕后,按快捷键“Ctrl+Shift+B”,重新构建Apollo项目。
1.3.3 编译时出现类似“Another command (pid=2466) is running. Waiting for it to complete…”的错误
这是由于在其他命令行终端进行编译或是在之前编译时按下“Ctrl+C”键强行终止但残留了部分编译进程所引起的。
解决方法:
按快捷键“Ctrl+C”键终止当前构建过程,在VSCode的命令终端窗口(如果未打开,按快捷键“Ctrl + `”开启),使用如下命令终止残留的编译进程:
| 123456789 | # 1.进入Dockerbash docker/scripts/dev_into.sh# 2.杀死Docker中残留的编译进程pkill bazel-real# 3.查看Docker中是否残留bazel-real进程,若有则按“q”退出,再次执行步骤2。# 也可使用“ps aux | grep bazel-real”查看top# 4.退出Dockerexit |
按快捷键“Ctrl+Shift+B”,重新执行构建任务。
{ 二 }
使用VSCode本地调试Apollo项目
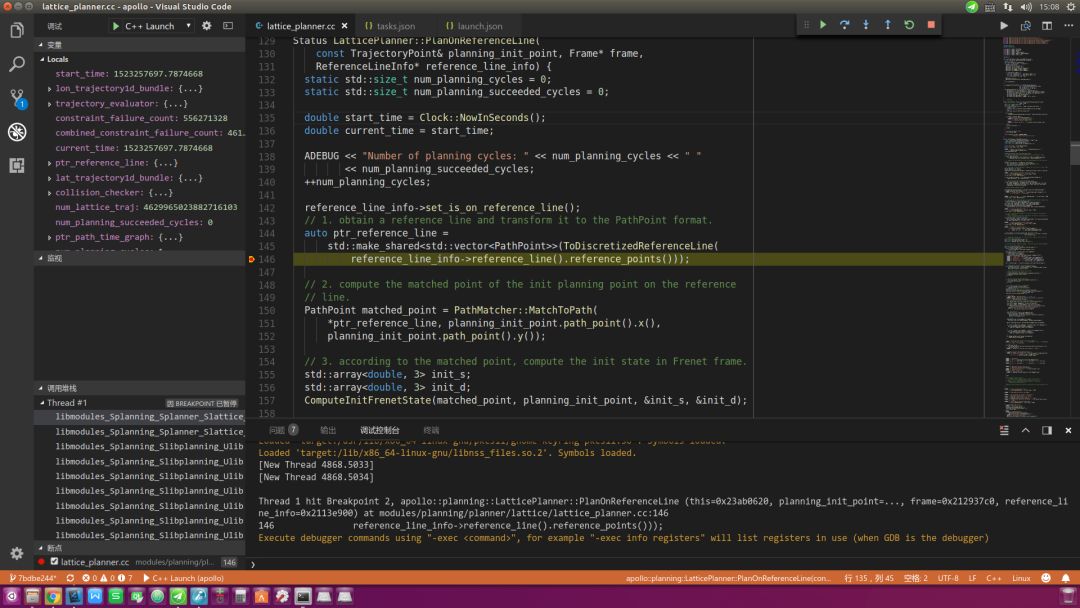
Apollo项目运行于Docker中,不能在宿主机(所谓宿主机就是运行Docker的主机,因为Docker服务像寄宿于主机中,故有此称呼)中直接使用GDB调试,而必须先在Docker中借助GDBServer创建调试服务进程,再在宿主机中使用GDB连接Docker中的调试服务进程来完成。下面介绍具体操作方法:
2.1前提条件2.1.1 编译Apollo项目需带调试信息
编译Apollo项目时需使用build或build_gpu等带调试信息的选项,而不能使用build_opt或build_opt_gpu等优化选项。
2.2.2 Docker内部已安装GDBServer
进入Docker后,可使用如下命令查看:
| 1 | gdbserver --version |
若提示类似如下信息:
| 1234 | GNU gdbserver (Ubuntu 7.7.1-0ubuntu5~14.04.3) 7.7.1Copyright (C) 2014 Free Software Foundation, Inc.gdbserver is free software, covered by the GNU General Public License.This gdbserver was configured as "x86_64-linux-gnu" |
则表示Docker内部已安装了GDBServer(我已请Apollo项目组老师将GDBServer预装至Docker内部,正常情况下应该能看到上述提示信息)。若提示如下信息:
| 1 | bash: gdbserver: command not found |
则表示Docker内部未安装GDBServer,可使用如下命令安装:
| 1 | sudo apt-get install gdbserver |
2.2Docker内部的操作2.2.1 启动Dreamview后台服务程序
进入Docker,启动Dreamview,命令如下:
| 1234567 | cd your_apollo_project_root_dir# 如果没有启动Docker,首先启动,否则忽略该步bash docker/scripts/dev_start.sh -C# 进入Dockerbash docker/scripts/dev_into.sh# 启动Dreamview后台服务bash scripts/bootstrap.sh |
2.2.2 启动待调试模块
启动待调试模块,既可使用命令行操作,也可借助Dreamview界面完成。我肯定喜欢使用Dreamview界面操作了,下面以调试“planning”模块为例进行说明。
打开Chrome浏览器,输入网址:http://localhost:8888/,打开Dreamview界面,打开“SimControl”选项,如下图所示:

点击左侧工具栏“Module Controler”标签页,选中“Routing”和“Planning”选项,如下图所示:

点击左侧工具栏“Default Routing”标签页,选中“Route: Reverse Early Change Lane”或其中任意一个选项,发送“Routing Request”请求,生成全局导航路径,如下图所示:

2.2.3 查看“Planning”进程ID
使用如下命令,查看“Planning”进程ID:
| 1 | top |
结果类似下图,可以看到“Planning”进程ID为4147,请记住该ID。按“q”退出“top”界面。

还可使用如下命令查看:
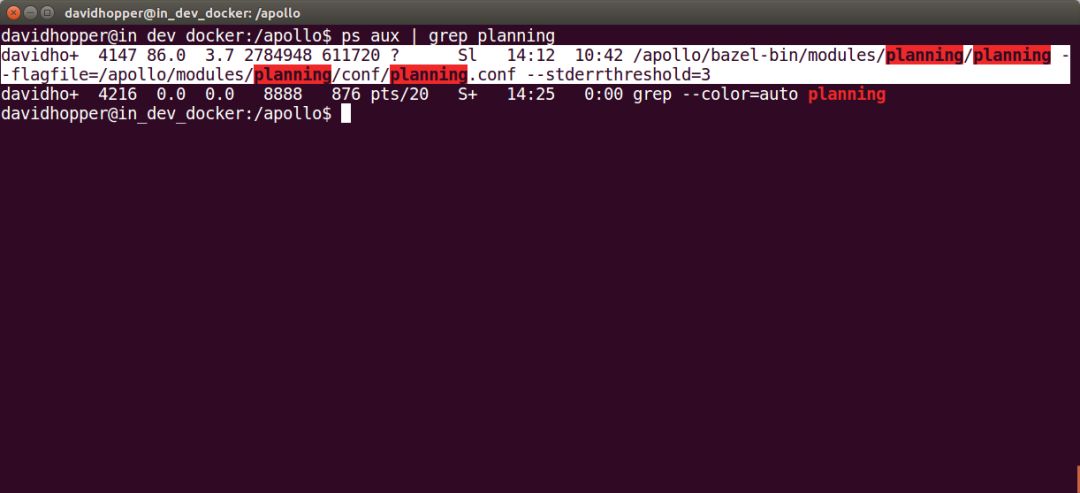
| 1 | ps aux | grep planning |
结果类似下图,可以看到“Planning”进程ID为4147。
2.2.4 使用GDBServer附加调试“Planning”进程
接下来需要进行我们的关键操作了,使用GDBServer附加调试“Planning”进程,命令如下:
| 1 | sudo gdbserver :1111 --attach 4147 |
上述命令中,“:1111”表示开启端口为“1111”的调试服务进程,“4147”表示步骤2.2.3中查到的“Planning”进程ID。若结果如下图所示,则表示操作成功。

重新开启一个命令终端,进入Docker后,使用如下命令可看到“gdbserver”进程已正常运行:
| 1 | ps aux | grep gdbserver |

2.2.5 使用脚本文件启动GDBServer
我写了两个脚本文件:scripts/start_gdb_server.sh、docker/scripts/dev_start_gdb_server.sh,其中前者用于在Docker内部启动GDBServer,后者直接在宿主机(Docker外部)启动GDBServer。
假设调试planning模块,端口号为1111,scripts/start_gdb_server.sh的使用方法为:
| 1234 | # 进入Dockerbash docker/scripts/dev_into.sh# 启动gdbserverbash scripts/start_gdb_server.sh planning 1111 |
假设调试planning模块,端口号为1111,docker/scripts/dev_start_gdb_server.sh的使用方法为:
| 12 | # 在宿主机中(Docker外部)直接启动gdbserverbash docker/scripts/dev_start_gdb_server.sh planning 1111 |
在2.3节我还将继续配置VSCode文件,以便在VSCode中直接按快捷键“F5”就可启动调试。
start_gdb_server.sh的内容如下:
#!/usr/bin/env bashfunction print_usage()
{
RED=‘�33[0;31m’
BLUE=‘�33[0;34m’
BOLD=‘�33[1m’
NONE=‘�33[0m’
echo -e “ ${RED}Usage${NONE}:
.${BOLD}/start_gdb_server.sh${NONE} MODULE_NAME PORT_NUMBER”
echo -e “${RED}MODULE_NAME${NONE}:
${BLUE}planning${NONE}: debug the planning module.
${BLUE}control${NONE}: debug the control module.
${BLUE}routing${NONE}: debug the routing module.
。..,
and so on.”
echo -e “${RED}PORT_NUMBER${NONE}:
${NONE}a port number, such as ‘1111’
。”}if [ $# -lt 2 ];then
print_usage
exit 1fiDIR=“$( cd ”$( dirname “${BASH_SOURCE[0]}” )“
&& pwd )”source “${DIR}/apollo_base.sh”MODULE_NAME=$1PORT_NUM=$2shift 2# If there is a gdbserver process running, stop it first.
GDBSERVER_NUMS=$(pgrep -c -x “gdbserver”)if [ ${GDBSERVER_NUMS} -ne 0 ]; then
sudo pkill -f “gdbserver”fi# Because the “grep ${MODULE_NAME}” always generates a process with the name of # “${MODULE_NAME}”,
I added another grep to remove grep itself from the output.# The following command got a wrong result and I can‘t find the reason.
#PROCESS_ID=$(ps -eo pid,command | grep “${MODULE_NAME}”
| grep -v “grep” | awk ’{print $1}‘)# This one is OK.PROCESS_ID=$(pgrep -o -x “${MODULE_NAME}”)#echo ${PROCESS_ID}# If the moudle is not started, start it first.
if [ -z ${PROCESS_ID} ]; then
#echo “The ’${MODULE_NAME}‘
module is not started, please start it in the dreamview first. ”
#exit 1
# run function from apollo_base.sh
# run command_name module_name
run ${MODULE_NAME} “$@” PROCESS_ID=$(pgrep -o -x “${MODULE_NAME}”)fi sudo gdbserver
:${PORT_NUM} --attach ${PROCESS_ID}
dev_start_gdb_server.sh的内容如下:
#!/usr/bin/env bashfunction check_docker_open() { docker ps --format “{{.Names}}” | grep apollo_dev 1》/dev/null 2》&1 if [ $? != 0 ]; then
echo “The docker is not started, please start it first. ”
exit 1 fi}function print_usage() { RED=‘�33[0;31m’
BLUE=‘�33[0;34m’ BOLD=‘�33[1m’ NONE=‘�33[0m’
echo -e “ ${RED}Usage${NONE}:
.${BOLD}/dev_debug_server.sh${NONE} MODULE_NAME PORT_NUMBER” echo -e “${RED}MODULE_NAME${NONE}: ${BLUE}planning${NONE}: debug the planning module.
${BLUE}control${NONE}: debug the control module.
${BLUE}routing${NONE}: debug the routing module.
。。.,
and so on.”
echo -e “${RED}PORT_NUMBER${NONE}:
${NONE}a port number, such as ‘1111’。”}if [ $# -lt 2 ];then
print_usage
exit 1ficheck_docker_openDIR=“$( cd ”$( dirname “${BASH_SOURCE[0]}” )“ && pwd )”cd “${DIR}/。。/。。”
# pwdxhost +local:root 1》/dev/null 2》&1#echo $@docker exec -u $USER
-it apollo_dev /bin/bash scripts/start_gdb_server.sh $@xhost -local:root 1》/dev/null 2》&1
2.3宿主机上VSCode内部的操作
在宿主机上使用VSCode打开Apollo项目(必须是你刚才构建的版本),打开需要调试的文件,在指定位置设置断点,按“F5”键启动调试。注意:由于VSCode使用脚本语言编写,因此启动过程会较慢,若加上网速不够快,甚至出现一分钟等待也有可能。调试方法和Visual Studio类似,此处不再赘述。如下图所示:
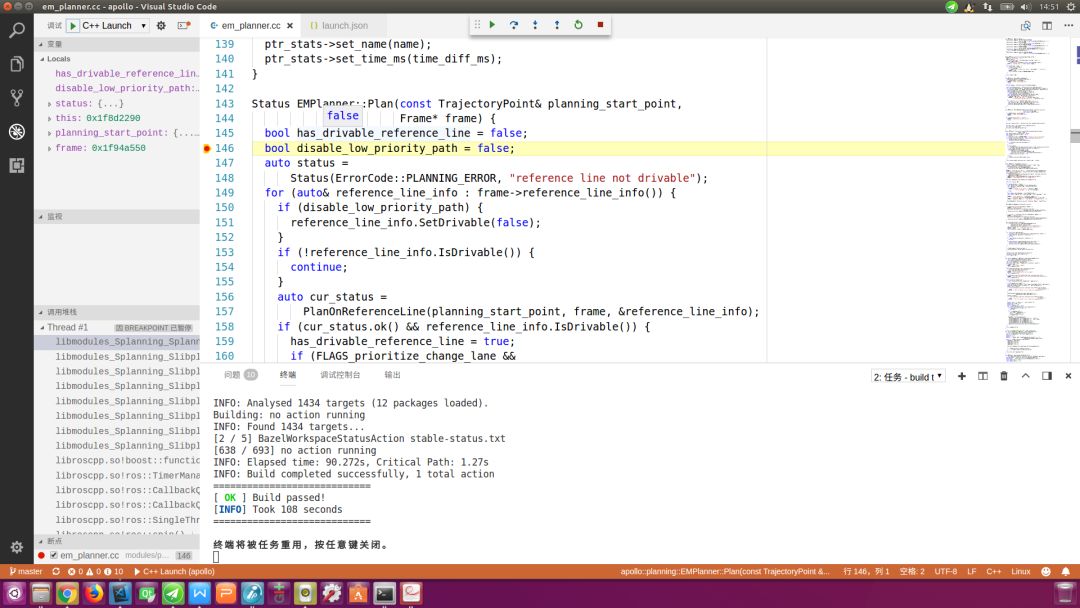
2.4配置文件解析
我对.vscode/launch.json文件作出配置以便能在VSCode中连接Docker中的调试服务进程。此外,为了能在VSCode中直接启动GDBServer,我在.vscode/launch.json文件中添加了一个调试前启动任务:"preLaunchTask": "start gdbserver",该任务对应于.vscode/tasks.json文件中的一个启动GDBServer的任务,因为GDBServer启动后会一直阻塞命令行窗口,且无法通过在命令后面添加&的方式进行后台启动,我只能将其配置为一个VSCode的后台运行任务。
.vscode/launch.json文件的配置内容如下:
{ “version”: “0.2.0”, “configurations”: [
{
“name”: “C++ Launch”,
“type”: “cppdbg”,
“request”: “launch”,
// You can change the “planning” to your module name, but it should be
// same as in gdbserver of the docker container.
“program”: “${workspaceRoot}/bazel-bin/modules/planning/planning”,
// You can change “localhost:1111” to another “IP:port” name, but it
// should be same as in gdbserver of the docker container.
“miDebuggerServerAddress”: “localhost:1111”,
// You can change the task to meet your demands in the
// “.vscode/tasks.json” file (search the label:
// “start gdbserver”, but the module name and the port
// number should be consistent with this file.
“preLaunchTask”: “start gdbserver”,
“args”: [],
“stopAtEntry”: false,
“cwd”: “${workspaceRoot}”,
“environment”: [],
“externalConsole”: true,
“linux”: {
“MIMode”: “gdb”
},
“osx”: {
“MIMode”: “gdb”
},
“windows”: {
“MIMode”: “gdb”
}
}
]
}
.vscode/tasks.json文件中用于启动GDBServer的任务配置如下:
{
“label”: “start gdbserver”,
“type”: “shell”,
// you can change the “planning” module name to another one and
// change the “1111” to another port number.
// Note: the module name and port number should be same as in
// the “launch.json” file.
“command”: “bash docker/scripts/dev_start_gdb_server.sh planning 1111”,
“isBackground”: true,
“problemMatcher”: {
“owner”: “custom”,
“pattern”: {
“regexp”: “__________”
},
“background”: {
“activeOnStart”: true,
// Don‘t change the following two lines, otherwise the
// gdbserver can’t run in the background.
“beginsPattern”: “^Listening on port$”,
“endsPattern”: “^$”
}
}
}
2.5可能碰到的问题及解决方法.vscode/tasks.json文件中用于启动GDBServer的任务配置如下:
调试过程中,可能会碰到以下问题:
一是Docker内部待调试进程崩溃,无法在VSCode中调试(如下图所示),解决办法是:重启Docker内部的调试进程;
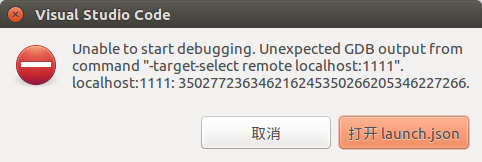
二是网络连接不畅,无法在VSCode中调试,解决办法是:确保网络畅通,并停用代理工具;
三是在VSCode内部关闭调试后,会同时将Docker内部的调试服务进程关闭,可能会出现无法直接在VSCode再次启动调试服务里程的情形,解决办法是:在Docker内部重启调试服务进程,再在VSCode中按“F5”键启动调试。
{ 三 }
使用VSCode远程调试Apollo项目
研发过程中,我们还需远程调试车内工控机上的Apollo项目,即在调试电脑上借助SSH服务连接车内工控机,启动工控机内相关进程,然后在调试电脑上进行远程调试。下面以调试planning模块为例进行具体阐述:
3.1查看车内工控机IP地址
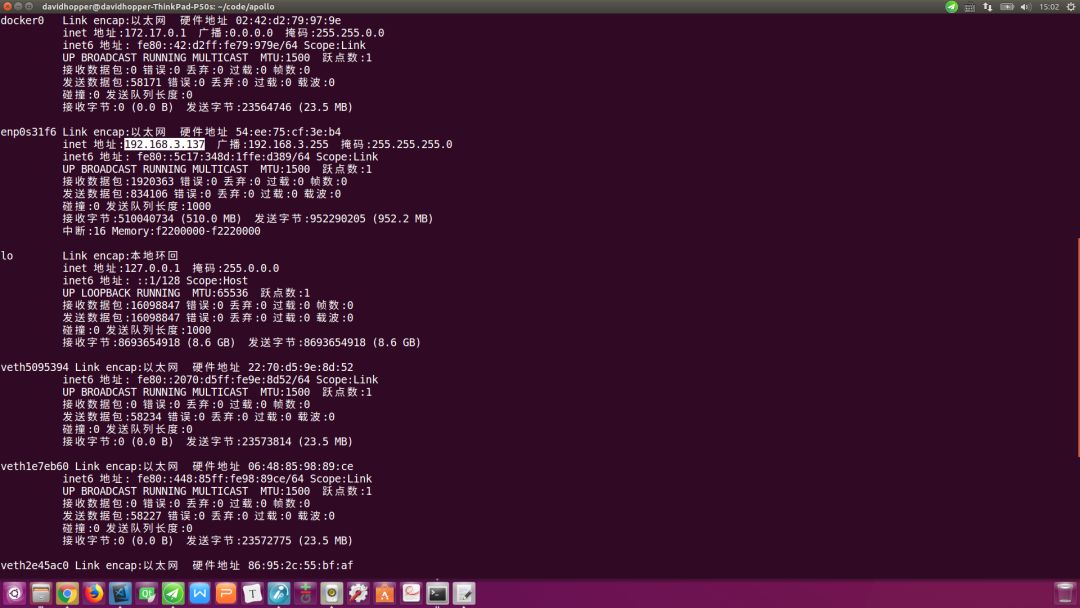
在车内工控机上,通过如下命令查看本机IP:
| 1 | ifconfig |
如下图所示,白色选中部分:192.168.3.137即为车内工控机的局域网IP地址。
3.2在调试电脑的浏览器中打开Dreamview并启动待调试模块
假设车内工控机局域网IP地址为:192.168.3.137,打开Chrome或Firefox浏览器,输入如下网址:http://192.168.3.137:8888/,按照2.2.2节中的方法,启动待调试的planning及其依赖的routing模块。

3.3使用SSH命令远程登录车内工控机并启动工控机的gdbserver服务
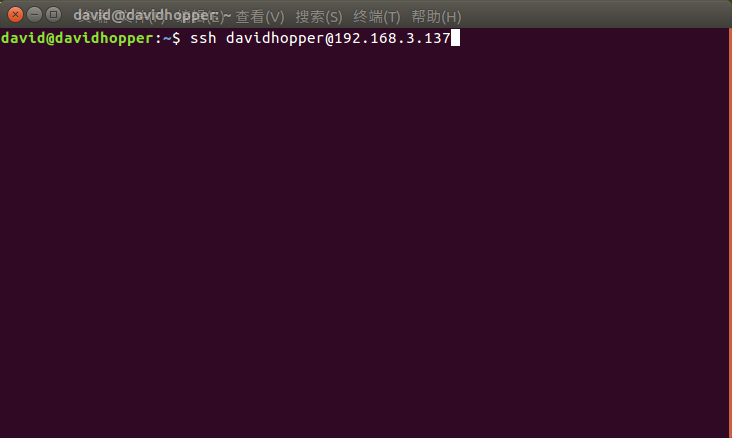
假设车内工控机的用户名为:davidhopper,局域网IP地址为:192.168.3.137,使用如下命令远程登录车内工控机:
| 1 | ssh davidhopper@192.168.3.137 |
成功进入工控机后,假设需调试planning模块,端口号为1111,使用如下命令启动车内工控机的gdbserver服务:
| 1234 | # 切换到工控机上Apollo项目根目录cd ~/code/apollo# 在Docker外部启动gdbserver服务bash docker/scripts/dev_start_gdb_server.sh planning 1111 |
如下图所示,如看到类似Listening on port 1111的提示,表示gdbserver服务顺利启动。

3.4在调试电脑上使用VSCode远程调试工控机上的planning模块
在调试电脑上使用VSCode打开Apollo项目,注意项目版本应与工控机上的版本一致,否则调试起来会输出许多不一致的信息。首先,将配置文件.vscode/launch.json中的调试前加载任务行:"preLaunchTask": "start gdbserver",注释掉,再将远程调试服务地址修改为:"miDebuggerServerAddress": "192.168.3.137:1111",,如下图所示:
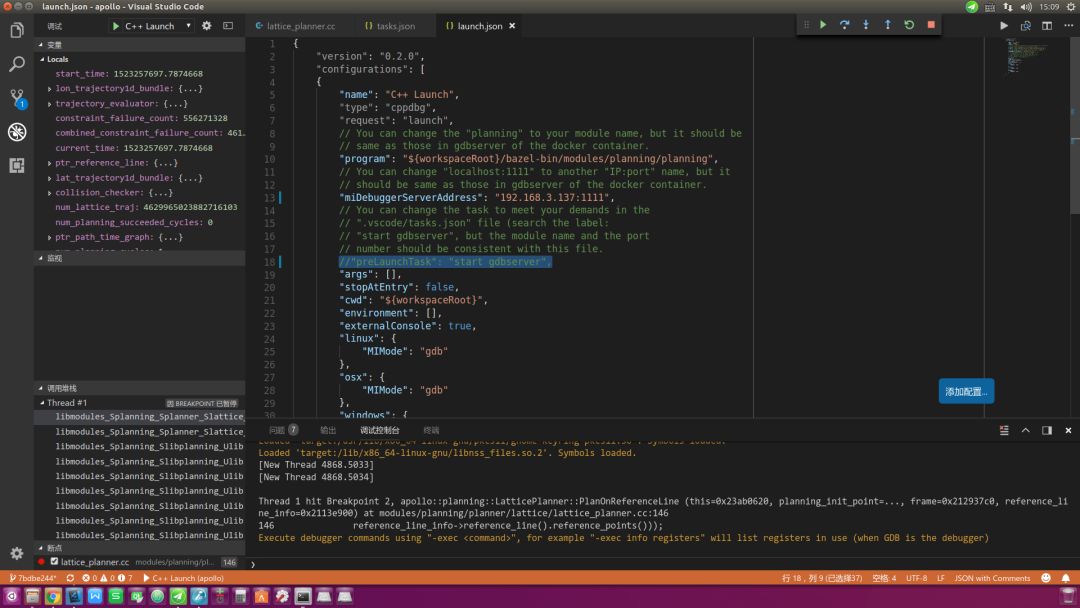
在需要的位置设置断点,按F5键启动调试,因为是远程连接,启动等待的时间会更长,甚至会超过1分钟。下图是远程调试界面。注意:每次在VSCode中中止调试后,需再次启动调试时,一定要再次在命令行终端执行3.3节的操作,重启工控机内的gdbserver服务进程。在本机调试时,因为我配置了一个preLaunchTask任务,就可省略此步骤。
自Apollo平台开放已来,我们收到了大量开发者的咨询和反馈,越来越多开发者基于Apollo擦出了更多的火花,并愿意将自己的成果贡献出来,这充分体现了Apollo『贡献越多,获得越多』的开源精神。为此我们开设了『开发者说』板块,希望开发者们能够踊跃投稿,更好地为广大自动驾驶开发者营造一个共享交流的平台!
-
如何使用VSCode+gdbserver远程调试ZMC900E2025-05-22 663
-
imx8mp项目在Vscode中编译时报错怎么解决?2025-04-01 706
-
首创ubuntu下cw32l031的vscode+gcc工程创建、下载、调试2023-06-25 25637
-
VSCode使用-搭建python运行调试环境2023-05-04 1835
-
vscode无法使用的原因及其解决办法2023-04-11 13842
-
如何NAS上搭建web端vscode2023-02-17 1464
-
Apollo Heritage版音频接口附带的插件2022-01-24 4629
-
Linux使用VScode编译调试C/C++程序的过程是怎样的2021-12-24 1019
-
在ubuntu中用vscode编译调试C\C++2021-12-22 1361
-
如何在ubuntu中用vscode编译调试C\C++2021-12-14 907
-
配置VScode编译、调试STM32(二)Cortex-Debug插件2021-12-01 1600
-
单片机编程vscode EIDE插件新环境2021-11-23 913
-
如何对Apollo2.5 CANBUS进行全面调试?2021-08-30 1012
-
stm32cubeMX+vscode开发编译调试2021-08-05 1014
全部0条评论

快来发表一下你的评论吧 !

