

基于ACP平行视觉理论的车道线检测系统设计
电子说
描述
过去,车道线检测性能多依赖于人工视觉验证的方法。然而这种方法不能客观量化车道线检测系统的性能。同时,由于车道线检测系统的复杂性,不同的硬件与算法,不同的数据采集方式和采集环境(天气,道路)等,都会影响测试结果。因此,目前尚没有一种统一的车道线评价方法。本文介绍了一种基于ACP平行视觉理论的车道线检测系统设计,将有效地解决车道线性能评价和测试问题,实现精确且稳定的车道线检测。
1 引言
研究发现,交通事故大多由驾驶员人为因素造成,例如驾驶员注意力不集中,错误判断与执行[1]。车道线检测技术是高级驾驶员辅助系统 (ADAS) 中至关重要的功能,并促成了自动车道偏移预警与车道保持等系统[2]-[3]。车道线的检测精度与稳定性是车道线检测技术的两个重要性能指标。车道线检测系统应该具有评估检测结果并识别不合理检测的能力[4]-[5]。对于传统车来说,当发现不合理的车道线检测结果应及时示意驾驶员注意当前路况。对于具有ADAS或自动驾驶功能的汽车,汽车要负责对检测结果进行评估,应保证在没有驾驶员参与的情况下做出安全的行驶策略。
如何提高车道线检测技术的可靠性以应对复杂多变的行车环境是目前所面临重要的挑战。采用数据融合与功能融合可以有效构造准确且稳定的车道线检测系统。功能融合是指将多个检测功能相结合,如将道路可行区域检测与车辆检测技术融合进来。数据融合利用激光雷达,GPS等设备来弥补摄像头的不足,进而提高车道线检测的精度及稳定性[4]。同时,本文在论述了多种传统车道线检测系统的评价方法之后。针对现有方法在性能与评估方面的不足,提出一种基于ACP平行视觉理论的平行车道线检测方法。平行车道线检测方法利用人工平行系统提供海量数据,将有效弥补传统车道线检测算法因数据不足所造成的无法充分训练与评估的缺陷。
2 基于视觉的车道线算法概述
2.1 车道线检测基本过程
基于视觉的车道线检测技术主要包含图像预处理,车道线检测与追踪三个过程,如图1。最常见的图像预处理技术有感兴趣区域提取,消失点检测,图像灰度化,噪声处理,逆透视变换,图像分割和边缘检测等。车道线特征主要包括其颜色和边缘等信息。当车道线被识别和建模后,为了提高车道线的实时检测精度和稳定性,车道线模型参数可以利用跟踪算法进行滤波以提高车道线的检测精度和稳定性。
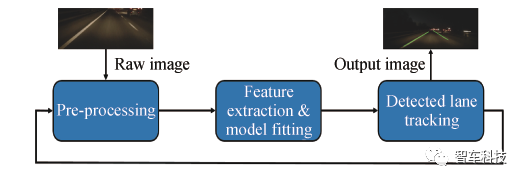
图1. 基本车道线检测过程
2.2 传统车道线检测算法
基于视觉的车道线检测技术可分为两类:基于特征的检测方法[9]-[19]与基于模型的检测方法[20]-[29]。基于特征的车道线检测算法利用车道线的颜色、纹理与边缘等特征进行检测。文献[10]利用车道线像素点强度与边缘特征,通过自适应阈值的方法检测车道线。文献[11]利用车道线的空间特征和霍夫变换进行车道线检测。文献[12]利用粒子滤波器识别车道线。文中指出,严格的车道线模型在实际运用中难以满足稳定性要求。基于粒子滤波的车道线检测算法无需对车道线进行精确建模,只需要通过车道线特征跟踪即可获得良好效果。文献[13]将RGB彩色图片变换为YUV格式,利用车道线边缘与车道线宽度进行车道线检测。文献[14]通过将彩色图片变换到HSV格式以增强车道线色彩的对比度,进而根据像素点强度完成车道线检测。文献[16]给出一种基于频域特征的车道线检测方法。综上所述,基于特征的车道线检测算法更加直接,也较为简便,适合车道线清晰的场景。然而,基于特征的车道线检测算法难以应对车道线复杂或可视条件不好的场景下。
基于模型的车道线检测算法通常将将车道线假设为直线模型,抛物线模型,或高阶曲线模型。除此之外还需要对道路的假设,例如道路应该是平坦且连续的。文献[21]提出一种可以拟合任意形状车道线的B-Snake模型。文献[22]将该模型进一步改进,变为一种平行snake模型。文献[23]将车道线模型分为两部分,近视野端为直线模型,远视野端曲线模型利用B-snake拟合。[25]提出一种基于霍夫变换,RANSAC以及B-Spline的集成车道线检测方法。首先利用霍夫变换粗略检测,之后再利用RANSAC和B-spline模型进一步拟合。文献[33]给出了一种基于RANSAC模型拟合的多段车道线自动切换建模的方法。基于模型的车道线检测方法通常比基于特征的方法更加稳定和精确,同时利用滤波算法估计模型参数也更加简便。但是,基于模型的方法通常也需要更多的计算需求来拟合出模型参数。
2.3 基于机器学习的车道线检测算法
近年来,深度学习技术被广泛应用于图像识别、分割、与物体检测。文献[36]指出,深度卷积网络可以显著的将车道线检测精度提高到90%以上。文献[37]提出一种基于深度卷积网络与循环神经网络的车道线检测方法。卷积神经网络负责判断每副图片是否包含车道线,并输出车道线的位置与走向。循环神经网络负责识别视频中的车道线结构,可以有效识别出被周围车辆或物体所遮盖的车道线。文献[38]利用卷积神经网络对来自两个侧视摄像头的图像进行处理,利用真实图像与合成图像训练端到端的车道线检测算法。文献[41]采用前视与俯视图像结合的方法,将两类图像利用不同的卷积网络分别处理,最后利用全局策略依据车道线物理特性做出预测。除此之外,研究人员也开发了基于进化和启发式算法的车道线搜索方法。文献[42]提出一种受驾驶员行为启发的置信度网路和多机构检测模型。文献[43]提出基于蚁群算法的最优化车道线搜索方法。文献[44]给出了一种基于随机游走模型的多车道检测方法。使用基于马尔科夫概率矩阵的有向随机游走算法连接候选车道线特征。综上所述,基于机器学习与智能算法的车道线检测算法已经体现出较传统方法更强大的性能。虽然基于学习的方法对车载控制器的计算性能要求更多,但是随着硬件系统的不断升级,基于机器学习的检测算法将会因其强大的计算能力而成为主要的车道线检测方法。
3 车道线检测的集成方法
3.1 集成方法概述
车道线检测系统的稳定性和适应性是真正制约车道线系统应用的核心问题。对于汽车企业来说,单一的外部环境传感器不足以提供安全有效的环境感知。像Tesla, Mobileye和Delphi公司等都采用传感器融合的方法(摄像头,激光雷达,毫米波雷达等)来提高车辆对周围环境感知的能力。本文回顾了传统车道线集成的方法,并将其分为算法层集成,系统级集成以及传感器层集成,如图2。
3.2 算法集成方式
传统算法层集成主要有串行和并行两种结构。串行集成方法较为常见[20][21][25]。如文献[25]将霍夫变换,RANSAC算法和模型拟合依次用于车道线检测,逐步提高检测精度。另外,许多文献也使用在车道线检测模块之后加入跟踪算法的串行结构提高车道线检测精度[21][22][45]-[47]。文献[50][51]给出了并行车道线检测的方法。文献[50]提出将两个相对独立且方法不同的车道线检测算法并行运行。通过对比两个检测结果判断合理的车道线位置。如果两种不同算法给出了相似的结果则视为当前车道线检测合理。相较而言,虽然并行集成引入冗余算法提高了检测精度,但是提高了系统运算量,降低了系统的实时性。
3.3 系统集成方式
现实道路中的障碍物很有可能影响车道线检测精度。例如,护栏就因具有较强的类车道线特征极易造成车道线的误检测[54]-[56]。因此,将车道线检测系统与其他障碍物检测有机结合有利于提高车辆的整体环境感知能力。临近车辆也会因为相似的颜色、遮挡或阴影问题带来车道线误检测。文献[30][57]-[60]指出,前车检测有利于区分车道线与车辆阴影以及降低车辆遮挡影响,可以提高车道线检测精度。道路标志与道路可行区域检测也可以提高车道线检测精度[4][7][66]-[68]。Tesla与Mobileye也都提出道路识别可以增强车道线检测的稳定性[69][70]。通常道路检测先于车道线检测,准确的道路检测可以优化感兴趣区域的选择,提高车道线检测效率。另外,因为道路边界与车道线有相同走向,道路检测可以辅助车道线置信度评估系统完成对所检测车道线的验证。
3.3 传感器集成方式
传感器融合方法可以最大程度上提高车道线检测系统的精度和稳定性。文献[76]通过RADAR检测周围车辆来精确划分车辆边缘像素获得只含有车道线的道路图片。文献[77][78]结合GPS 和道路图像,利用GPS获得道路形状,边缘和走向以优化车道线检测算法。激光雷达具有高精度,大范围的环境感知能力,因此,将激光雷达与摄像头结合,可以弥补摄像头系统的不足。激光雷达可通过道路与车道线标志的不同反射效应来获得车道线位置[88]。文献[89]利用激光雷达探测前方障碍物以获得精确的可行区域作为车道线检测的依据。文献[56]给出一种基于多摄像头与激光雷达融合的方法检测城市道路车道线。虽然传感器融合的方法比以上两种方法更加精确,然而,传感器之间需要复杂的标定过程,同时,硬件系统的增加也提高了系统成本。
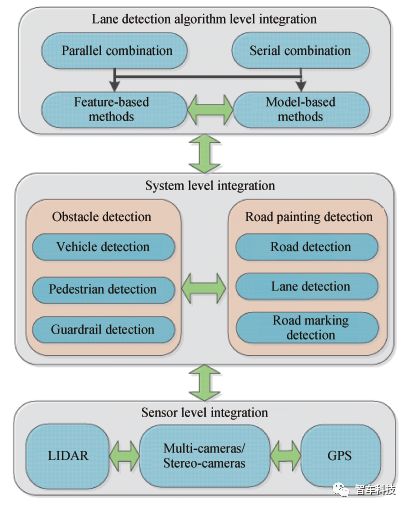
图2. 车道线检测的集成方法
4 车道线检测的评价方法
过去,检测性能多依赖于人工视觉验证的方法。然而这种方法不能客观量化车道线检测系统的性能。同时,由于车道线检测系统的复杂性,不同的硬件与算法,不同的数据采集方式和采集环境(天气,道路)等,都会影响测试结果。因此,目前尚没有一种统一的车道线评价方法。本节探讨了影响车道线系统精度的各种因素,并总结了车道线检测系统评估框架,如图3。将车道线评价算法分为两类在线评价和离线评价两类。
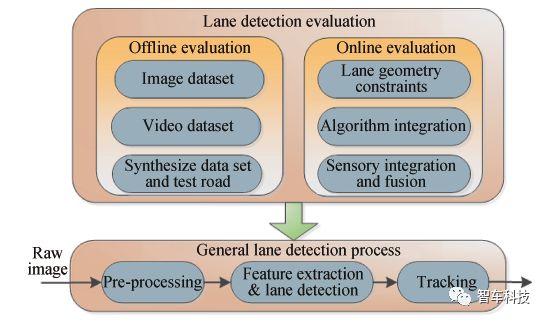
图3. 车道线系统评价体系
4.1 车道线系统精度的影响因素
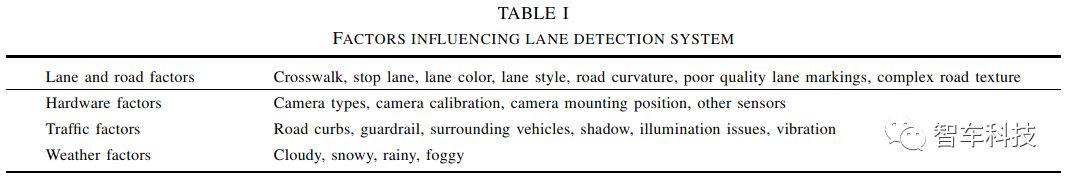
车道线检测系统精度通常受限于多种因素。在高速道路上精确的车道线系统不能保证在市区环境也有效,因为市区交通状况和车道线标识更加复杂。因此车道线系统性能需要综合评价,而不是只考虑某一指标。如表1,车道线评价系统需要考虑尽可能多的影响因素。最理想的检测方式是采用统一的检测平台和量化指标,然而这在现实情况下难以实现。
4.2 离线检测方法
基于图片和视频数据的离线检测是常用的车道线检测方法。著名的开放数据集有KITTI和Caltech Road[7][25]。图像数据集更易发布,但需要在每张图片上人工标注出车道线位置。人工标注需要消耗大量的时间,不适合大规模数据集。同时,图片无法有效反应行车环境与综合衡量车道线算法。基于视频数据的评价方法则更能反应真实的行车环境和算法性能。然而这也显著提升了数据标注的难度。对此,文献[95]给出一种半自动视频标注的方法,截取每帧中固定的几行,按照时间顺序和行序连成时序图片,通过在时序图片上标注车道线像素点较为准确的还原视频中车道线的位置。学者们还提出基于人工生成场景的车道线评估方法[28][56],通过仿真软件自动产生带有标注的类似真实道路环境的图像。
4.3 在线评价方法
车道线在线评价的方法通常通过融合其他检测系统或传感器来综合评价车道线检测结果的置信度。通过道路检测得到的道路几何信息有利于实时检测车道线的合理性。文献[96]提出一种实时车道线检测算法,该算法采用车道线斜率,道路宽度和消失点三个指标计算车道线检测结果的可信度。文献[5]利用车辆侧方安装摄像头的方法,为车道线检测结果提供真实的参考位置。此外,文献[56]利用摄像头与激光雷达建立车道线检测置信度概率网络。文献[56][77]提出利用GPS,Lidar和高精度地图的方式,通过所获得的道路宽度与方向作为检测车道线的指标。文献[97]提出利用消失点、道路旋转信息和建立帧间相似度模型的方法检测车道线的连续性。
4.4评价指标
传统车道线评价指标多基于主观观测的方法,尚没有形成一种统一有效的车道线系统测试指标。文献[98]设计了一个完善的智能车评价系统,该方法主要侧重于评价车辆的整体智能化程度。文献[20]提出车道线检测系统应该满足以下五点要求:克服道路阴影,可应对无明显车道标识的道路,可识别曲线道路,满足车道线形状约束以及稳定监测。文献[101]提出,车道线系统性能评价不能局限于检测率,应该采用检测值与真实值误差的方差及变化率,平均绝对值误差作为性能评价指标。文献[102]进一步提出五种评价指标,分别是:车道线特征测量精度,本车自身定位,车道线位置变化率,计算效率及精度,累计时间误差。
5 基于ACP平行理论的车道线检测系统
由于无法有效模拟各种真实场景和环境,车道线检测性能在未知场景下难以预测。虽然建立在线评价与置信度估计系统可以实时评价当前检测结果的正确性。当发现有不合理的检测结果时,可以及时通知驾驶员应对当前问题。然而,这还不足以完全解决车道线检测算法在设计与评价方面所面临的问题。
为解决这类问题,本文提出基于ACP平行理论的车道线检测系统设计框架。平行理论是先进控制理论和计算机仿真系统的产物。平行控制理论首先由王飞跃研究员提出并已成功应用到各类复杂系统控制与管理领域[105]-[107]。建立平行系统的主要目的是连接现实世界与一个或多个人工社会以解决解决模型建模和测试困难问题。建立平行系统依赖于ACP理论支持。ACP(ArtificialSociety, Computational Experiments, Parallel Execution)由人工社会,计算实验,和平行执行三部分组成。首先对一个复杂系统进行整体建模,在计算空间形成一个对现实系统的虚拟映射。之后利用计算实验在人工社会中对系统进行大量的仿真实验,使得虚拟系统可以面对在现实世界中较少或难以出现的场景。通过大量的实验计算,获得较为完善的系统模型和控制方法,并将模型参数反馈到现实物理层。最后,在现实世界和人工社会平行运行和测试该复杂系统使之不断完善,最终使难以建模的复杂系统得到良好控制。基于ACP平行理论,文献[109]给出了平行视觉系统的构建方法。通过利用计算机仿真软件建立与现实世界相似的人工场景,利用高性能计算平台解决计算机视觉问题。
将车道线检测系统引入平行视觉框架,本文设计了平行车道线检测系统框架,如图4。首先利用仿真软件建立类似真实世界的虚拟交通环境。之后通过计算实验,将大量计算机标注过的道路图像和有限的现实图像结合起来,训练和验证高精度的车道线检测模型。最后,在平行执行阶段,通过不断的在虚拟世界和现实世界中的测试,将结果反馈给车道线检测模型,利用在线学习和自我优化实现安全稳定的车道线检测系统。将车道线检测引入ACP平行视觉框架,利用平行系统模拟所产生的各种环境下的标注数据,将有效解决车道线检测系统评价与测试这一困境,彻底实现车道线系统的完整测试,使之更加安全稳定,并更好的应对现实世界中的突发情况。

图4. 基于ACP理论的平行车道线检测方法
6 结论
本文在算法,集成,和测试三方面论述了车道线检测技术的发展。整体而言,车道线检测算法可分为基于传统计算机视觉和机器学习两种方法。作为可以有效提高车道线检测精度与稳定性的技术手段,车道线检测的集成方法又分为算法层集成,系统功能层集成和信号层集成。通过分析现阶段车道线系统性能评价与测试的局限性,本文提出了基于ACP平行理论的平行车道线检测系统设计方法。平行车道线检测技术将有效地解决车道线性能评价和测试问题,实现精确且稳定的车道线检测。
7 Reference
[1] Bellis, Elizabeth, and JimPage. National motor vehicle crash causation survey (NMVCCS) SAS analyticaluser’s manual. No. HS-811 053. 2008.
[2] Gayko, Jens E. "Lanedeparture and lane keeping." Handbookof Intelligent Vehicles. Springer London, 2012. 689-708.
[3] Visvikis C, Smith T L, PitcherM, et al. Study on lane departurewarning and lane change assistant systems. TransportResearch Laboratory Project Rpt PPR, 2008, 374.
[4] Bar Hillel, Aharon, et al."Recent progress in road and lane detection: a survey." Machine vision and applications (2014):1-19.
[5] McCall, Joel C., and Mohan M.Trivedi. "Video-based lane estimation and tracking for driver assistance:survey, system, and evaluation." IEEETransactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems 7.1 (2006): 20-37.
[6] Yenikaya,Sibel, Gökhan Yenikaya, and Ekrem Düven. "Keeping the vehicle on the road:A survey on on-road lane detection systems." ACM Computing Surveys(CSUR) 46.1 (2013): 2.
[7] Fritsch,Jannik, Tobias Kuhnl, and Andreas Geiger. "A new performance measure andevaluation benchmark for road detection algorithms." IntelligentTransportation Systems-(ITSC), 2013 16th International IEEE Conference on.IEEE, 2013.
[8] Beyeler,Michael, Florian Mirus, and Alexander Verl. "Vision-based robust road lanedetection in urban environments." Robotics and Automation (ICRA), 2014IEEE International Conference on. IEEE, 2014.
[9] Kang, Dong-Joong, and Mun-Ho Jung. "Roadlane segmentation using dynamic programming for active safety vehicles." Pattern Recognition Letters 24.16(2003): 3177-3185.
[10] Suddamalla, Upendra, et al."A novel algorithm of lane detection addressing varied scenarios of curvedand dashed lanemarks." ImageProcessing Theory, Tools and Applications (IPTA), 2015 International Conferenceon. IEEE, 2015.
[11] Collado, Juan M., et al. "Adaptiveroad lanes detection and classification." International Conference on Advanced Concepts for Intelligent VisionSystems. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2006.
[12] Sehestedt, Stephan, et al."Robust lane detection in urban environments." Intelligent Robots and Systems, 2007. IROS 2007. IEEE/RSJ InternationalConference on. IEEE, 2007.
[13] Lin, Qing, Young joon Han, andHernsoo Hahn. "Real-time lane departure detection based on extendededge-linking algorithm." ComputerResearch and Development, 2010 Second International Conference on. IEEE,2010.
[14] Cela, Andrés F., et al."Lanes Detection Based on Unsupervised and Adaptive Classifier."Computational Intelligence, Communication Systems and Networks (CICSyN), 2013Fifth International Conference on. IEEE, 2013.
[15] Borkar, Amol, et al. "Alayered approach to robust lane detection at night." Computational Intelligencein Vehicles and Vehicular Systems, 2009. CIVVS'09. IEEE Workshop on. IEEE,2009.
[16] Kreucher,Chris, and Sridhar Lakshmanan. "LANA: a lane extraction algorithm thatuses frequency domain features." IEEETransactions on Robotics and Automation 15.2 (1999): 343-350.
[17] Jung,Soonhong, Junsic Youn, and Sanghoon Sull. "Efficient lane detection basedon spatiotemporal images." IEEETransactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems 17.1 (2016): 289-295.
[18] Xiao,Jing, Shutao Li, and Bin Sun. "A Real-Time System for Lane Detection Basedon FPGA and DSP." Sensing andImaging 17.1 (2016): 1-13.
[19] Ozgunalp, Umar, and NaimDahnoun. "Lane detection based on improved feature map and efficientregion of interest extraction." Signaland Information Processing (GlobalSIP), 2015 IEEE Global Conference on.IEEE, 2015.
[20] Wang, Yue, Dinggang Shen, andEam Khwang Teoh. "Lane detection using spline model." Pattern Recognition Letters 21.8 (2000):677-689.
[21] Wang, Yue, Eam Khwang Teoh, andDinggang Shen. "Lane detection and tracking using B-Snake." Image andVision Computing 22.4 (2004): 269-280.
[22] Li, Xiangyang, et al."Lane detection and tracking using a parallel-snake approach." Journal of Intelligent & Robotic Systems77.3-4 (2015): 597.
[23] Lim,King Hann, Kah Phooi Seng, and Li-Minn Ang. "River flow lane detection andKalman filtering-based B-spline lane tracking." International Journal of Vehicular Technology 2012 (2012).
[24] Jung, Cláudio Rosito, andChristian Roberto Kelber. "An improved linear-parabolic model for lanefollowing and curve detection." ComputerGraphics and Image Processing, 2005. SIBGRAPI 2005. 18th Brazilian Symposium on.IEEE, 2005.
[25] Aly, Mohamed. "Real timedetection of lane markers in urban streets." Intelligent Vehicles Symposium, 2008 IEEE. IEEE, 2008.
[26] Borkar, Amol, Monson Hayes, and Mark T. Smith."Robust lane detection and tracking with ransac and kalman filter." Image Processing (ICIP), 2009 16th IEEEInternational Conference on. IEEE, 2009.
[27] Lopez, A., et al. "Detectionof Lane Markings based on Ridgeness and RANSAC." Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2005. Proceedings. 2005 IEEE.IEEE, 2005.
[28] López, A., et al. "Robustlane markings detection and road geometry computation." International Journal of Automotive Technology11.3 (2010): 395-407.
[29] Chen, Qiang, and Hong Wang."A real-time lane detection algorithm based on a hyperbola-pairmodel." Intelligent VehiclesSymposium, 2006 IEEE. IEEE, 2006.
[30] Tan, Huachun, et al. "Improved river flow and random sampleconsensus for curve lane detection." Advancesin Mechanical Engineering 7.7 (2015): 1687814015593866.
[31] Hur,Junhwa, Seung-Nam Kang, and Seung-Woo Seo. "Multi-lane detection in urbandriving environments using conditional random fields." Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV), 2013IEEE. IEEE, 2013
[32] Bounini,Farid, et al. "Autonomous Vehicle and Real Time Road Lanes Detection andTracking." Vehicle Power andPropulsion Conference (VPPC), 2015 IEEE. IEEE, 2015.
[33] Wu, Dazhou, Rui Zhao, and Zhihua Wei. "Amulti-segment lane-switch algorithm for efficient real-time lanedetection." Information andAutomation (ICIA), 2014 IEEE International Conference on. IEEE, 2014.
[34] Zhou,Shengyan, et al. "A novel lane detection based on geometrical model andgabor filter." Intelligent Vehicles Symposium(IV), 2010 IEEE. IEEE, 2010.
[35] Niu, Jianwei, et al."Robust Lane Detection using Two-stage Feature Extraction with CurveFitting." Pattern Recognition 59(2016): 225-233.
[36] He, Bei, et al. "Lanemarking detection based on Convolution Neural Network from point clouds." Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC),2016 IEEE 19th International Conference on. IEEE, 2016.
[37] Li,Jun, Xue Mei, and Danil Prokhorov. "Deep neural network for structuralprediction and lane detection in traffic scene." IEEE transactions on neural networks and learning systems (2016).
[38] Gurghian,Alexandru, et al. "DeepLanes: End-To-End Lane Position Estimation UsingDeep Neural Networks." Proceedingsof the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops.2016
[39] Li, Xue, et al. "Lanedetection based on spiking neural network and hough transform." Image and Signal Processing (CISP), 2015 8thInternational Congress on. IEEE, 2015.
[40] Kim, Jihun, et al. "Fastlearning method for convolutional neural networks using extreme learningmachine and its application to lane detection." Neural Networks (2016).
[41] He, Bei, et al. "Accurate and robust lane detectionbased on Dual-View Convolutional Neural Network." Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV), 2016 IEEE. IEEE, 2016.
[42] Revilloud, Marc, Dominique Gruyer, and Mohamed-CherifRahal. "A new multi-agent approach for lane detection and tracking." Robotics and Automation (ICRA), 2016 IEEEInternational Conference on. IEEE, 2016.
[43] Bertozzi,Massimo, et al. "An evolutionary approach to lane markings detection inroad environments." Atti del 6 (2002): 627-636.
[44] Tsai, Luo-Wei, et al."Lane detection using directional random walks." Intelligent Vehicles Symposium, 2008 IEEE. IEEE, 2008.
[45] Bai, Li, and Yan Wang."Road tracking using particle filters with partition sampling andauxiliary variables." ComputerVision and Image Understanding 115.10 (2011): 1463-1471.
[46] Danescu, Radu, and SergiuNedevschi. "Probabilistic lane tracking in difficult road scenarios usingstereovision." IEEE Transactions onIntelligent Transportation Systems 10.2 (2009): 272-282.
[47] Kim, ZuWhan. "Robust lanedetection and tracking in challenging scenarios." IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems 9.1 (2008):16-26.
[48] Shin, Bok-Suk, Junli Tao, andReinhard Klette. "A super particle filter for lane detection." Pattern Recognition 48.11 (2015):3333-3345.
[49] Das,Apurba, Siva Srinivasa Murthy, and Upendra Suddamalla. "Enhanced Algorithmof Automated Ground Truth Generation and Validation for Lane Detection Systemby M2BMT" IEEE Transactions onIntelligent Transportation Systems (2016).
[50] Labayrade, Raphael, S. S. Leng,and Didier Aubert. "A reliable road lane detector approach combining twovision-based algorithms." IntelligentTransportation Systems, 2004. Proceedings. The 7th International IEEEConference on. IEEE, 2004.
[51] Labayrade, Raphaël, et al. "A reliable and robust lanedetection system based on the parallel use of three algorithms for drivingsafety assistance." IEICEtransactions on information and systems 89.7,2006: 2092-2100.
[52] Hernández, Danilo Cáceres,Dongwook Seo, and Kang-Hyun Jo. "Robust lane marking detection based onmulti-feature fusion." Human SystemInteractions (HSI), 2016 9th International Conference on. IEEE, 2016.
[53] Yim, Young Uk, and Se-Young Oh."Three-feature based automatic lane detection algorithm (TFALDA) forautonomous driving." IEEETransactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems 4.4 (2003): 219-225.
[54] Felisa, Mirko, and Paolo Zani."Robust monocular lane detection in urban environments." Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV), 2010IEEE. IEEE, 2010.
[55] Bertozzi, Massimo, and AlbertoBroggi. "GOLD: A parallel real-time stereo vision system for genericobstacle and lane detection." IEEEtransactions on image processing 7.1 (1998): 62-81.
[56] Huang, Albert S., et al. "Finding multiple lanes inurban road networks with vision and lidar." Autonomous Robots 26.2 (2009): 103-122.
[57] Cheng, Hsu-Yung, et al. "Lane detection with moving vehicles inthe traffic scenes." IEEETransactions on intelligent transportation systems 7.4 (2006): 571-582.
[58] Sivaraman, Sayanan, and MohanManubhai Trivedi. "Integrated lane and vehicle detection, localization,and tracking: A synergistic approach." IEEETransactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems 14.2 (2013): 906-917.
[59] Wu, Chi-Feng, Cheng-Jian Lin,and Chi-Yung Lee. "Applying a functional neurofuzzy network to real-timelane detection and front- vehicle distancemeasurement." IEEE Transactions onSystems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part C (Applications and Reviews) 42.4(2012): 577-589.
[60] Huang,Shih-Shinh, et al. "On-board vision system for lane recognition andfront-vehicle detection to enhance driver's awareness." Robotics and Automation, 2004. Proceedings.ICRA'04. 2004 IEEE International Conference on. Vol. 3. IEEE, 2004.
[61] Satzoda, Ravi Kumar, and MohanM. Trivedi. "Efficient lane and vehicle detection with integratedsynergies (ELVIS)." Computer Visionand Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), 2014 IEEE Conference on. IEEE,2014.
[62] Kim, Huieun, et al. "Integration of vehicle and lanedetection for forward collision warning system." Consumer Electronics-Berlin (ICCE-Berlin), 2016 IEEE 6th InternationalConference on. IEEE, 2016.
[63] Qin, B., et al. "A generalframework for road marking detection and analysis." Intelligent Transportation Systems-(ITSC), 2013 16th International IEEEConference on. IEEE, 2013.
[64] Kheyrollahi, Alireza, and TobyP. Breckon. "Automatic real-time road marking recognition using a featuredriven approach." Machine Vision andApplications 23.1 (2012): 123-133.
[65] Greenhalgh, Jack, and MajidMirmehdi. "Detection and Recognition of Painted Road SurfaceMarkings." ICPRAM (1). 2015.
[66] Oliveira, Gabriel L., WolframBurgard, and Thomas Brox. "Efficient deep models for monocular roadsegmentation." Intelligent Robotsand Systems (IROS), 2016 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on. IEEE, 2016.
[67] Kong, Hui, Jean-Yves Audibert,and Jean Ponce. "Vanishing point detection for road detection." Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition,2009. CVPR 2009. IEEE Conference on. IEEE, 2009.
[68] Levi, Dan, et al."StixelNet: A Deep Convolutional Network for Obstacle Detection and RoadSegmentation." BMVC. 2015.
[69] Stein, Gideon P., YoramGdalyahu, and Amnon Shashua. "Stereo-assist: Top-down stereo for driverassistance systems." IntelligentVehicles Symposium (IV), 2010 IEEE. IEEE, 2010.
[70] Raphael, Eric, et al. "Development of a camera-based forwardcollision alert system." SAEInternational Journal of Passenger Cars-Mechanical Systems 4.2011-01-0579,2011: 467-478.
[71] Ma, Bing, S. Lakahmanan, andAlfred Hero. "Road and lane edge detection with multisensor fusionmethods." Image Processing, 1999. ICIP 99. Proceedings. 1999 InternationalConference on. Vol. 2. IEEE, 1999.
[72] Beyeler,Michael, Florian Mirus, and Alexander Verl. "Vision-based robust road lanedetection in urban environments." Roboticsand Automation (ICRA), 2014 IEEE International Conference on. IEEE, 2014.
[73] Ozgunalp,Umar, et al. "Multiple Lane Detection Algorithm Based on Novel DenseVanishing Point Estimation." IEEETransactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems 18.3 (2017): 621-632.
[74] Lipski, Christian, et al."A fast and robust approach to lane marking detection and lanetracking." Image Analysis andInterpretation, 2008. SSIAI 2008. IEEE Southwest Symposium on. IEEE, 2008.
[75] Kim, Dongwook, et al."Lane-level localization using an AVM camera for an automated drivingvehicle in urban environments." IEEE/ASMETransactions on Mechatronics 22.1 (2017): 280-290.
[76] Jung, H. G., et al."Sensor fusion-based lane detection for LKS+ ACC system." International journal of automotivetechnology 10.2 (2009): 219-228.
[77] Cui, Dixiao, Jianru Xue, andNanning Zheng. "Real-Time Global Localization of Robotic Cars in LaneLevel via Lane Marking Detection and Shape Registration." IEEE Transactions on IntelligentTransportation Systems 17.4 (2016): 1039-1050.
[78] Jiang, Yan, Feng Gao, andGuoyan Xu. "Computer vision-based multiple-lane detection on straight roadand in a curve." Image Analysis andSignal Processing (IASP), 2010 International Conference on. IEEE, 2010.
[79] Rose, Christopher, et al."An integrated vehicle navigation system utilizing lane-detection andlateral position estimation systems in difficult environments for GPS." IEEE Transactions on IntelligentTransportation Systems 15.6 (2014): 2615-2629.
[80] Li, Qingquan, et al. "Asensor-fusion drivable-region and lane-detection system for autonomous vehiclenavigation in challenging road scenarios." IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology 63.2 (2014): 540-555.
[81] Kammel, Soren, and BenjaminPitzer. "Lidar-based lane marker detection and mapping." Intelligent Vehicles Symposium, 2008 IEEE.IEEE, 2008.
[82] Manz, Michael, et al. "Detection and tracking of road networksin rural terrain by fusing vision and LIDAR." Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), 2011 IEEE/RSJ InternationalConference on. IEEE, 2011.
[83] Schreiber, Markus, CarstenKnöppel, and Uwe Franke. "Laneloc: Lane marking based localization usinghighly accurate maps." IntelligentVehicles Symposium (IV), 2013 IEEE. IEEE, 2013.
[84] Clanton J M, Bevly D M, Hodel AS. A low-cost solution for an integrated multisensor lane departure warningsystem[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2009,10(1): 47-59.
[85] Montemerlo, Michael, et al."Junior: The stanford entry in the urban challenge." Journal of field Robotics 25.9 (2008):569-597.
[86] Buehler, Martin, Karl Iagnemma, and Sanjiv Singh, eds. The DARPA urban challenge: autonomous vehiclesin city traffic. Vol. 56. Springer, 2009.
[87] Lindner, Philipp, et al. "Multi-channel lidarprocessing for lane detection and estimation." Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2009. ITSC'09. 12th InternationalIEEE Conference on. IEEE, 2009.
[88] Shin,Seunghak, Inwook Shim, and In So Kweon. "Combinatorial approach for lanedetection using image and LIDAR reflectance." Ubiquitous Robots andAmbient Intelligence (URAI), 2015 12th International Conference on. IEEE,2015.
[89] Amaradi, Phanindra, et al."Lane following and obstacle detection techniques in autonomous drivingvehicles." Electro InformationTechnology (EIT), 2016 IEEE International Conference on. IEEE, 2016.
[90] Dietmayer, Klaus, et al."Roadway detection and lane detection using multilayer laser scanner."Advanced Microsystems for AutomotiveApplications 2005. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2005. 197-213.
[91] Hernandez, Danilo Caceres,Van-Dung Hoang, and Kang-Hyun Jo. "Lane surface identification based onreflectance using laser range finder." SystemIntegration (SII), 2014 IEEE/SICE International Symposium on. IEEE, 2014.
[92] Sparbert, Jan, Klaus Dietmayer,and Daniel Streller. "Lane detection and street type classification usinglaser range images." IntelligentTransportation Systems, 2001. Proceedings. 2001 IEEE. IEEE, 2001.
[93] Broggi, Alberto, et al. "Alaser scanner-vision fusion system implemented on the terramax autonomousvehicle." Intelligent Robots andSystems, 2006 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on. IEEE, 2006.
[94] Zhao, Huijing, et al. "A laser-scanner-based approach towarddriving safety and traffic data collection." IEEE Transactions on intelligent transportation systems 10.3(2009): 534-546.
[95] Borkar, Amol, Monson Hayes, and Mark T. Smith. "Anovel lane detection system with efficient ground truth generation." IEEE Transactions on IntelligentTransportation Systems 13.1 (2012): 365-374.
[96] Lin,Chun-Wei, Han-Ying Wang, and Din-Chang Tseng. "A robust lane detection andverification method for intelligent vehicles." Intelligent Information Technology Application, 2009. IITA 2009. ThirdInternational Symposium on. Vol. 1. IEEE, 2009.
[97] Yoo, Ju Han, et al. "ARobust Lane Detection Method Based on Vanishing Point Estimation Using theRelevance of Line Segments." IEEETransactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems (2017).
[98] Li, Li, et al."Intelligence Testing for Autonomous Vehicles: A New Approach." IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Vehicles 1.2(2016): 158166.
[99] Kluge, Karl C."Performance evaluation of vision-based lane sensing: Some preliminarytools, metrics, and results." IntelligentTransportation System, 1997. ITSC'97., IEEE Conference on. IEEE, 1997.
[100]Veit,Thomas, et al. "Evaluation of road marking feature extraction."Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2008. ITSC 2008. 11th International IEEEConference on. IEEE, 2008.
[101]McCall, Joel C., and Mohan M. Trivedi. "Performance evaluationof a vision based lane tracker designed for driver assistance systems." Intelligent Vehicles Symposium, 2005.Proceedings. IEEE. IEEE, 2005.
[102]Satzoda, Ravi Kumar, and Mohan M. Trivedi. "On performanceevaluation metrics for lane estimation." Pattern Recognition (ICPR), 2014 22nd International Conference on.IEEE, 2014.
[103]Jung, Claudio Rosito, and Christian Roberto Kelber. "A robustlinear-parabolic model for lane following." Computer Graphics and Image Processing, 2004. Proceedings. 17thBrazilian Symposium on. IEEE, 2004.
[104]Haloi, Mrinal, and Dinesh Babu Jayagopi. "A robust lanedetection and departure warning system." Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV), 2015 IEEE. IEEE, 2015.
[105]F. Y. Wang, “Parallel system methods for management and control of complexsystems,” Control Decision, vol. 19,no. 5, pp. 485-489, 514, May 2004.
[106]F. Y. Wang, “Parallel control and management for intelligenttransportation systems: Concepts, architectures, and applications,” IEEE Trans .Intell. Transp. Syst., vol.11, no. 3, pp. 630-638, Sep. 2010.
[107]F. Y. Wang, “Artificial societies, computational experiments, andparallel systems: A discussion on computational theory of complex socialeconomic systems,” Complex Syst.Complexity Sci., vol. 1, no. 4, pp.25-35, Oct.
[108]L. Li, Y. L. Lin, D. P. Cao, N. N. Zheng, and F. Y. Wang, “Parallellearning-a new framework for machine learning,” Acta Automat. Sin., vol. 43, no. 1, pp. 1-18, Jan. 2017.
[109]K. F. Wang, C. Gou, N. N. Zheng, J. M. Rehg, and F. Y. Wang,“Parallel vision for perception and understanding of complex scenes: methods,framework, and perspectives,” Artif. Intell. Rev., vol. 48, no. 3, pp.298-328, Oct. 2017.
[110]Wang,F.Y., Zheng, N.N., Cao, D., et al. Parallel driving in CPSS: a unified approachfor transport automation and vehicle intelligence. IEEE/CAA Journal of AutomaticaSinica, 2017, 4(4), pp.577-587.
[111] Lv, C., Liu, Y., Hu, X., Guo, H., Cao, D. andWang, F.Y. Simultaneous observation of hybrid states for cyber-physicalsystems: A case study of electric vehicle powertrain. IEEE transactions oncybernetics, 2017.
[112]Silver,David, et al. "Mastering the game of Go with deep neural networks and treesearch." Nature 529.7587 (2016):484-489.
- 相关推荐
- 热点推荐
- ACP
-
汽车电子的lidar检测车道线原理分析2023-02-07 1169
-
基于树莓派设计的道路车道检测系统2022-03-31 5260
-
单片机车道线检测模型的相关资料分享2021-11-25 1036
-
基于图像的车道线检测2021-07-20 1008
-
怎么实现单目视觉车道偏离报警系统的设计?2021-05-13 1227
-
如何实现车道线分割2020-05-22 2010
-
基于雷达扫描检测车道线的四种方法2019-03-07 3527
-
汽车先进驾驶员辅助系统ADAS:车道偏离告警系统资料分享2018-11-06 3614
-
利用激光雷达检测车道线的4种方法2018-05-25 11665
-
一套车道线检测系统2018-01-31 1336
-
单目视觉车道线识别算法及其ARM实现2017-09-24 970
-
基于边界特征的车道标识线检测方法2012-01-13 716
-
基于分形理论的高效机器视觉检测系统2010-05-30 929
-
基于机器视觉的车道偏离预警系统的实现2009-12-24 1611
全部0条评论

快来发表一下你的评论吧 !

