

分支限界法与回溯法算法的详细资料概述
描述
分支限界法与回溯法
(1)求解目标:回溯法的求解目标是找出解空间树中满足约束条件的所有解,而分支限界法的求解目标则是找出满足约束条件的一个解,或是在满足约束条件的解中找出在某种意义下的最优解。 (2)搜索方式的不同:回溯法以深度优先的方式搜索解空间树,而分支限界法则以广度优先或以最小耗费优先的方式搜索解空间树。
分支限界法的基本思想
分支限界法常以广度优先或以最小耗费(最大效益)优先的方式搜索问题的解空间树。在分支限界法中,每一个活结点只有一次机会成为扩展结点。活结点一旦成为扩展结点,就一次性产生其所有儿子结点。在这些儿子结点中,导致不可行解或导致非最优解的儿子结点被舍弃,其余儿子结点被加入活结点表中。 此后,从活结点表中取下一结点成为当前扩展结点,并重复上述结点扩展过程。这个过程一直持续到找到所需的解或活结点表为空时为止。
常见的两种分支限界法
(1)队列式(FIFO)分支限界法 按照队列先进先出(FIFO)原则选取下一个结点为扩展结点。 (2)优先队列式分支限界法 按照优先队列中规定的优先级选取优先级最高的结点成为当前扩展结点。
一、单源最短路径问题
1、问题描述
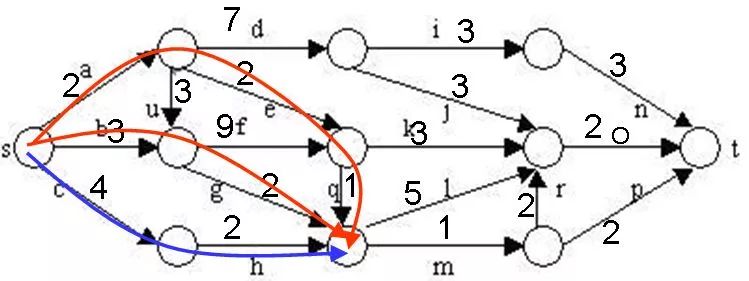
在下图所给的有向图G中,每一边都有一个非负边权。要求图G的从源顶点s到目标顶点t之间的最短路径。
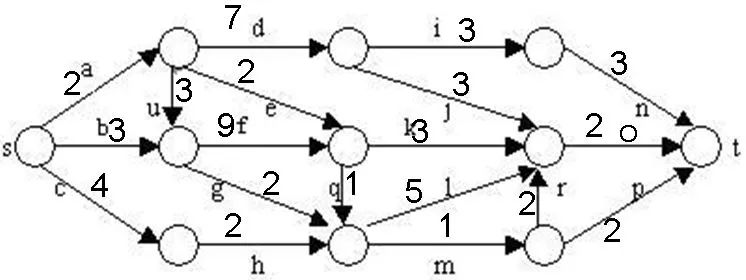
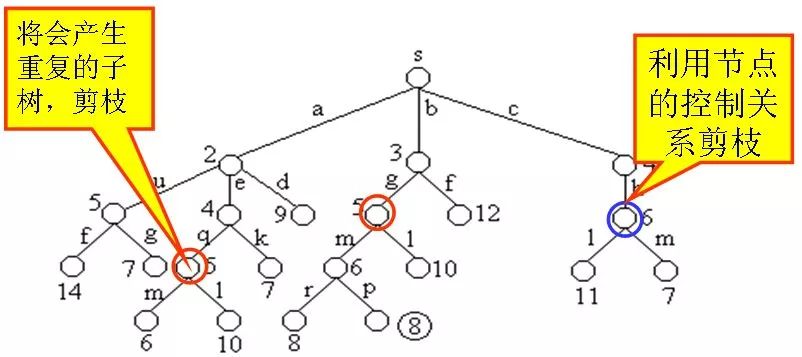
下图是用优先队列式分支限界法解有向图G的单源最短路径问题产生的解空间树。其中,每一个结点旁边的数字表示该结点所对应的当前路长。
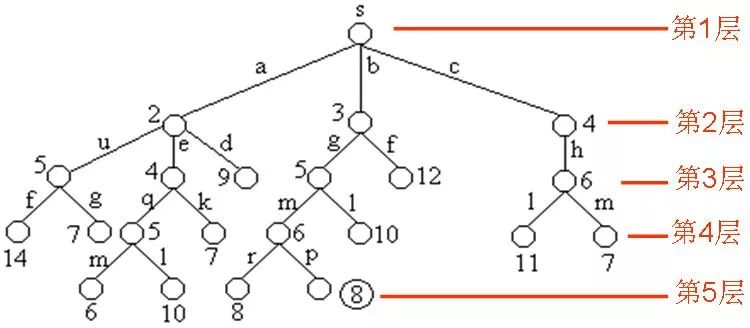
找到一条路径:
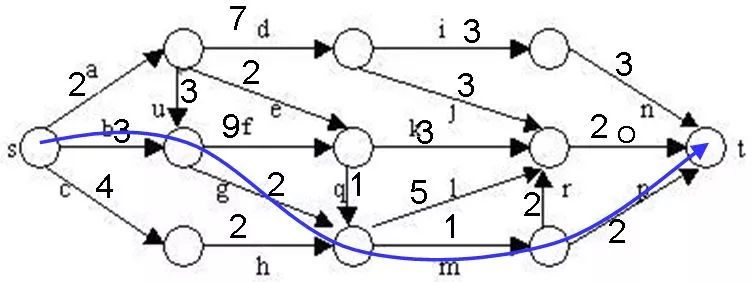
目前的最短路径是8,一旦发现某个结点的下界不小于这个最短路进,则剪枝:
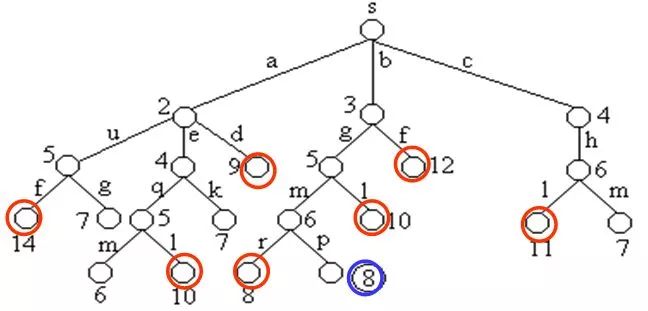
同一个结点选择最短的到达路径:
2.剪枝策略
在算法扩展结点的过程中,一旦发现一个结点的下界不小于当前找到的最短路长,则算法剪去以该结点为根的子树。
在算法中,利用结点间的控制关系进行剪枝。从源顶点s出发,2条不同路径到达图G的同一顶点。由于两条路径的路长不同,因此可以将路长长的路径所对应的树中的结点为根的子树剪去。
3.算法思想
解单源最短路径问题的优先队列式分支限界法用一极小堆来存储活结点表。其优先级是结点所对应的当前路长。
算法从图G的源顶点s和空优先队列开始。结点s被扩展后,它的儿子结点被依次插入堆中。此后,算法从堆中取出具有最小当前路长的结点作为当前扩展结点,并依次检查与当前扩展结点相邻的所有顶点。如果从当前扩展结点i到顶点j有边可达,且从源出发,途经顶点i再到顶点j的所相应的路径的长度小于当前最优路径长度,则将该顶点作为活结点插入到活结点优先队列中。这个结点的扩展过程一直继续到活结点优先队列为空时为止。
实现
* 作者:chinazhangjie
* 邮箱:chinajiezhang@gmail.com
* 开发语言:C++
* 开发环境:Mircosoft Virsual Studio 2008
* 时间: 2010.11.01
*/
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespacestd;
structnode_info
{
public:
node_info(inti,intw)
: index(i),weight(w){}
node_info()
: index(0),weight(0){}
node_info(constnode_info & ni)
: index(ni.index),weight(ni.weight){}
friend
booloperator < (constnode_info& lth,constnode_info& rth){
returnlth.weight > rth.weight;// 为了实现从小到大的顺序
}
public:
intindex;// 结点位置
intweight;// 权值
};
structpath_info
{
public:
path_info()
: front_index(0),weight(numeric_limits
public:
intfront_index;
intweight;
};
// single source shortest paths
classss_shortest_paths
{
public:
ss_shortest_paths(constvector
:no_edge(-1),end_node(end_location),node_count(g.size()),graph(g)
{}
// 打印最短路径
voidprint_spaths()const{
cout << "min weight : " << shortest_path << endl;
cout << "path: ";
copy(s_path_index.rbegin(),s_path_index.rend(),
ostream_iterator
cout << endl;
}
// 求最短路径
voidshortest_paths(){
vector
priority_queue
min_heap.push(node_info(0,0)); // 将起始结点入队
while(true){
node_info top = min_heap.top(); // 取出最大值
min_heap.pop();
// 已到达目的结点
if(top.index == end_node){
break;
}
// 未到达则遍历
for(inti = 0;i < node_count; ++ i){
// 顶点top.index和i间有边,且此路径长小于原先从原点到i的路径长
if(graph[top.index][i] != no_edge &&
(top.weight + graph[top.index][i]) < path[i].weight){
min_heap.push(node_info(i,top.weight + graph[top.index][i]));
path[i].front_index = top.index;
path[i].weight = top.weight + graph[top.index][i];
}
}
if(min_heap.empty()){
break;
}
}
shortest_path = path[end_node].weight;
intindex = end_node;
s_path_index.push_back(index);
while(true){
index = path[index].front_index;
s_path_index.push_back(index);
if(index == 0){
break;
}
}
}
private:
vector
int node_count; // 结点个数
constint no_edge; // 无通路
constint end_node; // 目的结点
vector
int shortest_path; // 最短路径
};
intmain()
{
constintsize = 11;
vector
for(inti = 0;i < size; ++ i){
graph[i].resize(size);
}
for(inti = 0;i < size; ++ i){
for(intj = 0;j < size; ++ j){
graph[i][j] = -1;
}
}
graph[0][1] = 2;
graph[0][2] = 3;
graph[0][3] = 4;
graph[1][2] = 3;
graph[1][5] = 2;
graph[1][4] = 7;
graph[2][5] = 9;
graph[2][6] = 2;
graph[3][6] = 2;
graph[4][7] = 3;
graph[4][8] = 3;
graph[5][6] = 1;
graph[5][8] = 3;
graph[6][9] = 1;
graph[6][8] = 5;
graph[7][10] = 3;
graph[8][10] = 2;
graph[9][8] = 2;
graph[9][10] = 2;
ss_shortest_paths ssp(graph,10);
ssp.shortest_paths();
ssp.print_spaths();
return0;
}
测试数据(图)
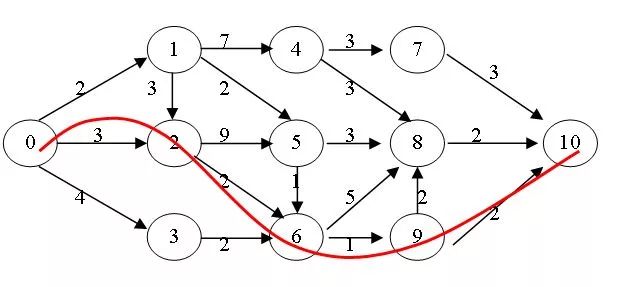
测试结果
-
求allegro高速信号蛇形走线和10度线的走法详细资料2014-07-06 13708
-
调制解调器和积分器算法程序的详细资料概述2018-04-28 1512
-
五大常用算法之回溯法2018-05-02 6381
-
TI的基于DSP兼容的第三方算法协议的详细资料概述2018-05-07 1086
-
PID程序算法的详细资料概述免费下载2018-07-24 1114
-
SV601187的详细资料合集包括了电路图,原理图和介绍等详细资料概述2018-07-30 1699
-
十一个经典的滤波算法的介绍和示例程序详细资料免费下载2018-11-06 1107
-
线性系统的频域分析频率特性法的详细资料免费下载2018-11-22 1113
-
5500极谱法DO探头校准及维护的资料说明2019-01-03 1549
-
单片机有哪些常用滤波算法详细资料说明2019-07-29 1017
-
分形插值算法的详细资料说明2019-06-05 966
-
龙格-库塔法的MATLAB代码及含义的详细资料说明2019-07-17 1120
-
python的内置函数详细资料概述2019-11-18 1177
-
EMC HF垫圈的详细资料概述2020-09-07 1299
-
如何使用回溯法实现网络设计问题算法的设计2020-12-11 1007
全部0条评论

快来发表一下你的评论吧 !

