

寒武纪成功适配DeepSeek-V3.2-Exp模型
描述
2025年9月29日,寒武纪已同步实现对深度求索公司最新模型DeepSeek-V3.2-Exp的适配,并开源大模型推理引擎vLLM-MLU源代码。代码地址和测试步骤见文末,开发者可以在寒武纪软硬件平台上第一时间体验DeepSeek-V3.2-Exp的亮点。
寒武纪一直高度重视大模型软件生态建设,支持以DeepSeek为代表的所有主流开源大模型。借助于长期活跃的生态建设和技术积累,寒武纪得以快速实现对DeepSeek-V3.2-Exp这一全新实验性模型架构的day 0适配和优化。
寒武纪一直重视芯片和算法的联合创新,致力于以软硬件协同的方式,优化大模型部署性能,降低部署成本。此前,我们对DeepSeek系列模型进行了深入的软硬件协同性能优化,达成了业界领先的算力利用率水平。针对本次的DeepSeek-V3.2-Exp新模型架构,寒武纪通过Triton算子开发实现了快速适配,利用BangC融合算子开发实现了极致性能优化,并基于计算与通信的并行策略,再次达成了业界领先的计算效率水平。依托DeepSeek-V3.2-Exp带来的全新DeepSeek Sparse Attention机制,叠加寒武纪的极致计算效率,可大幅降低长序列场景下的训推成本,共同为客户提供极具竞争力的软硬件解决方案。
↓ vLLM-MLU DeepSeek-V3.2-Exp适配的源码(点击文末“阅读原文”可直接跳转)↓
https://github.com/Cambricon/vllm-mlu
基于vLLM-MLU的DeepSeek-V3.2-Exp运行指南
一、环境准备
软件:需使用寒武纪训推一体镜像Cambricon Pytorch Container部署,镜像内预装运行vLLM-MLU的各项依赖。
硬件:4台8卡MLU服务器。
如需获取完整的软硬件运行环境,请通过官方渠道联系寒武纪。
二、运行步骤及结果展示
Step1:模型下载
模型文件请从Huggingface官网自行下载,后文用${MODEL_PATH}表示下载好的模型路径。
Step 2:启动容器
加载镜像,启动容器,命令如下:
# 加载镜像
docker load -i cambricon_pytorch_container-torch2.7.1-torchmlu1.28.0-ubuntu22.04-py310.tar.gz
# 启动容器
docker run -it --net=host
--shm-size '64gb' --privileged -it
--ulimit memlock=-1 ${IMAGE_NAME}
/bin/bash
# 安装社区vLLM 0.9.1版本
pushd ${VLLM_SRC_PATH}/vllm
VLLM_TARGET_DEVICE=empty pip install .
popd
# 安装寒武纪vLLM-mlu
pushd ${VLLM_SRC_PATH}/vllm-mlu
pip install .
popd
Step 3:启动Ray服务
在执行模型前,需要先启动ray服务。启动命令如下:
# 设置环境变量
export GLOO_SOCKET_IFNAME=${INFERENCE_NAME}
export NOSET_MLU_VISIBLE_DEVICES_ENV_VAR=1
# 主节点
ray start --head --port ${port}
# 从节点
ray start --address='${master_ip}:${port}'
Step 4:运行离线推理
这里提供简易的离线推理脚本`offline_inference.py`:
import sys
from vllm import LLM, SamplingParams
def main(model_path):
# Sample prompts.
prompts = [
"Hello, my name is",
"The capital of France is",
"The future of AI is",
]
sampling_params = SamplingParams(
temperature=0.6, top_p=0.95, top_k=20, max_tokens=10)
# Create an LLM.
engine_args_dict = {
"model": model_path,
"tensor_parallel_size": 32,
"distributed_executor_backend": "ray",
"enable_expert_parallel": True,
"enable_prefix_caching": False,
"enforce_eager": True,
"trust_remote_code": True,
}
llm = LLM(**engine_args_dict)
# Generate texts from the prompts.
outputs = llm.generate(prompts, sampling_params)
# Print the outputs.
for output in outputs:
prompt = output.prompt
generated_text = output.outputs[0].text
print(f"Prompt: {prompt!r}, Generated text: {generated_text!r}")
if __name__ == '__main__':
main(sys[1])
运行如下命令,完成模型离线推理:
# 运行推理命令
python offline_inference.py --model ${MODEL_PATH}
运行结果符合预期,具体结果如下:

Step 5:运行在线推理
分别启动server和client,完成推理服务,示例如下:
# server
vllm serve ${MODEL_PATH}
--port 8100
--max-model-len 40000
--distributed-executor-backend ray
--trust-remote-code
--tensor-parallel-size 32
--enable-expert-parallel
--no-enable-prefix-caching
--disable-log-requests
--enforce-eager
# client, we post a single request here.
curl -X POST http://localhost:8100/v1/completions
-H "Content-Type: application/json"
-d '{"model": ${MODEL_PATH},
"prompt": "The future of AI is",
"max_tokens": 50, "temperature": 0.7
}'
运行结果如下:
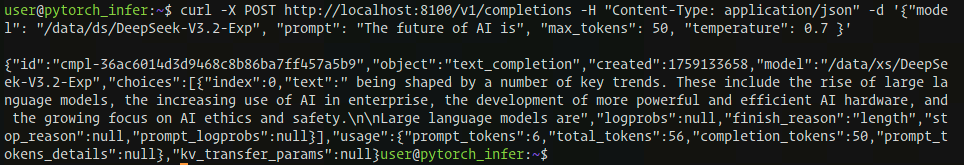
提取输入输出信息如下,符合预期。
Prompt:The future of AI is Output:being shaped by a number of key trends. These include the rise of large language models, the increasing use of AI in enterprise, the development of more powerful and efficient AI hardware, and the growing focus on AI ethics and safety. Large language models are
Step 6:运行交互式对话
使用vLLM-MLU框架,运行交互式对话demo,执行结果如下:
-
商汤科技与寒武纪达成战略合作2025-10-15 598
-
曙光AI超集群系统全面支持DeepSeek-V3.2-Exp2025-09-30 1567
-
寒武纪85后创始人陈天石身价超1500亿2025-08-26 6326
-
寒武纪增资全资子公司上海寒武纪2025-02-05 1585
-
寒武纪与智象未来联手,推动视觉大模型的技术创新与应用2024-01-24 2308
-
寒武纪与智象未来达成战略合作并完成大模型适配2024-01-23 1069
-
寒武纪的思元(MLU)云端智能加速卡与百川智能完成大模型适配,携手创新生成式AI2023-11-06 2649
-
寒武纪持续研发投入 2020年亏损收窄,营收稳步上涨2021-04-28 2551
-
寒武纪先后推出了用于终端场景的寒武纪1A寒武纪1M系列芯片2020-07-20 1995
-
寒武纪“思元220”推动边缘AI应用发展2019-11-14 5306
-
麒麟980将整合寒武纪科技的最新AI技术:“寒武纪1M”2018-05-16 7303
-
寒武纪科技生态爆发,产业伙伴展示寒武纪芯片应用2018-05-04 11383
-
寒武纪科技的股东都有谁_寒武纪科技十大股东2018-01-05 173344
-
寒武纪科技上市了吗_寒武纪科技股权结构是怎样的2017-12-29 75214
全部0条评论

快来发表一下你的评论吧 !

