

介绍MATLAB一种算法实现方式
电子说
描述
本篇文章要分享的是基于MATLAB的腐蚀膨胀算法实现,腐蚀膨胀是形态学图像处理的基础,腐蚀在二值图像的基础上做“收缩”或“细化”操作,膨胀在二值图像的基础上做“加长”或“变粗”的操作。
什么是二值图像呢?把一幅图片看做成一个二维的数组,那么二值图像是一个只有0和1的逻辑数组,我们前面Sobel边缘检测后的图像输出边缘效果,设置个阈值,大于阈值输出为1,小于阈值输出为0,最后输出就是一幅二值图像了。
腐蚀
腐蚀是一种消除边界点,使边界向内部收缩的过程。可以用来消除小且无意义的物体。用3X3的结构元素,扫描图像的每一个像素,用结构元素与其覆盖的二值图像做“与”操作,如果都为1,结果图像的该像素为1。否则为0。结果会使二值图像小一圈。
有一个形象的比喻来可以说明该运算,用0表示蛀虫,1表示大米。蛀虫腐蚀大米的过程便是腐蚀运算,
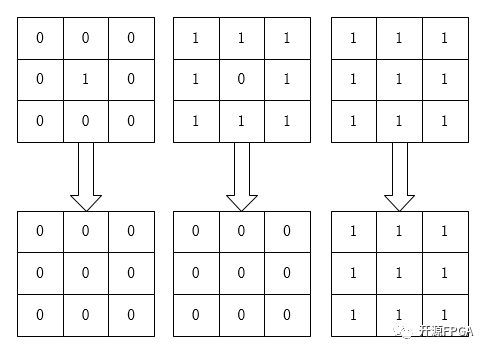
腐蚀
如图所示,对于一个像素矩阵而言,只要有蛀虫(0)的存在,大米(1)就会被腐蚀掉了,即使只存在一个蛀虫(0),但是还是会被蛀虫腐蚀完毕,最后一幅图上面由于没有蛀虫(0)所以大米完好无损。
关于算法的实现,可以用下式子来表示,即3x3像素的运算:
P = P11 & P12 & P13 & P21 & P22 & P23 & P31 & P32 & P33
在FPGA中,为了通过面积去换速度,我们将上式改变如下:
P1 = P11 & P12 & P13
P2 = P21 & P22 & P23
P3 = P31 & P32 & P33
P = P1 & P2 & P3
MATLAB中可以直接写一个按位或运算。
膨胀
膨胀是将与物体接触的所有背景点合并到该物体中,使边界向外部扩张的过程。可以用来填补物体中的空洞。用3X3的结构元素,扫描图像的每一个像素,用结构元素与其覆盖的二值图像做“与”操作,如果都为0,结果图像的该像素为0,。否则为1。结果使二值图像扩大一圈。
先腐蚀后膨胀的过程称为开运算。用来消除小物体、在纤细点处分离物体、平滑较大物体的边界的同时并不明显的改变其面积。先膨胀后腐蚀的过程称为比运算,用来填充物体内细小空间、连接邻近物体、平滑其边界的同时并不明显改变其面积。
膨胀算法用最简单的比喻来描述:0表示害虫,1表示青蛙,青蛙吃了害虫表示膨胀运算,我们用3*3像素阵列来解释:
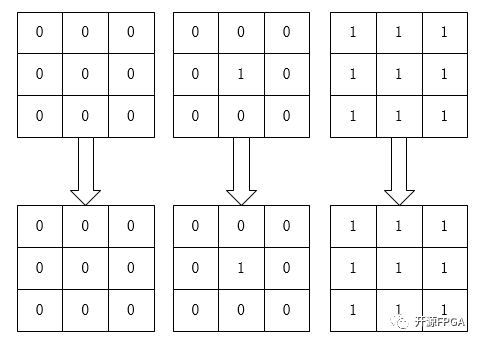
膨胀
如图所示,图左只有害虫(0),所以害虫都活着,中间那个图,虽然只有一个害虫,但是还是会被青蛙全部吃掉,最右边的那幅图,都是青蛙,所以青蛙始终是青蛙。
关于算法的实现,可以用下式子来表示,即3x3像素的运算:
P = P11 | P12 | P13 | P21 | P22 | P23 | P31 | P32 | P33
在HDL中,为了通过面积去换速度,我们将上式改变如下:
P1 = P11 | P12 | P13
P2 = P21 | P22 | P23
P3 = P31 | P32 | P33
P = P1 | P2 | P3
MATLAB中可以直接写一个按位与运算。
开运算闭运算
先腐蚀后膨胀叫开运算,开运算的作用是清除图像边缘周围非边缘的细小的点。先膨胀后腐蚀为闭运算,闭运算的作用是清除图像内部的空洞,
如果我们的目标物体外面有很多无关的小区域,就用开运算去除掉;如果物体内部有很多小黑洞,就用闭运算填充掉。
MATLAB逻辑运算函数
bitand(), 对十进制数进行逐位逻辑与运算:先将十进制数转换成二进制数,然后逐位与运算,其运算结果转换为十进制。
bitor(), 对十进制数进行逐位逻辑或运算:先将十进制数转换成二进制数,然后逐位与运算,其运算结果转换为十进制。
MATLAB代码实现
1 %RGB_YCbCr 2 clc; 3 clear all; 4 close all; 5 6 RGB_data = imread('lena.jpg'); 7 8 R_data = RGB_data(:,:,1); 9 G_data = RGB_data(:,:,2); 10 B_data = RGB_data(:,:,3); 11 12 %imshow(RGB_data); 13 14 [ROW,COL, DIM] = size(RGB_data);
15 16 Y_data = zeros(ROW,COL); 17 Cb_data = zeros(ROW,COL); 18 Cr_data = zeros(ROW,COL); 19 Gray_data = RGB_data; 20 21 for r = 1:ROW
22 for c = 1:COL 23 Y_data(r, c) = 0.299*R_data(r, c) + 0.587*G_data(r, c) + 0.114*B_data(r, c); 24 Cb_data(r, c) = -0.172*R_data(r, c) - 0.339*G_data(r, c) + 0.511*B_data(r, c) + 128; 25 Cr_data(r, c) = 0.511*R_data(r, c) - 0.428*G_data(r, c) - 0.083*B_data(r, c) + 128; 26 end 27 end
28 29 Gray_data(:,:,1)=Y_data; 30 Gray_data(:,:,2)=Y_data; 31 Gray_data(:,:,3)=Y_data; 32 33 figure; 34 imshow(Gray_data); 35 36 %Median Filter 37 imgn = imnoise(Gray_data,'salt & pepper',0.02);
38 39 figure; 40 imshow(imgn); 41 42 Median_Img = Gray_data; 43 for r = 2:ROW-1 44 for c = 2:COL-1 45 median3x3 =[imgn(r-1,c-1) imgn(r-1,c) imgn(r-1,c+1) 46 imgn(r,c-1) imgn(r,c) imgn(r,c+1) 47 imgn(r+1,c-1) imgn(r+1,c) imgn(r+1,c+1)]; 48 sort1 = sort(median3x3, 2, 'descend'); 49 sort2 = sort([sort1(1), sort1(4), sort1(7)], 'descend'); 50 sort3 = sort([sort1(2), sort1(5), sort1(8)], 'descend'); 51 sort4 = sort([sort1(3), sort1(6), sort1(9)], 'descend'); 52 mid_num = sort([sort2(3), sort3(2), sort4(1)], 'descend'); 53 Median_Img(r,c) = mid_num(2); 54 end 55 end 56 57 figure; 58 imshow(Median_Img); 59 60 %Sobel_Edge_Detect 61 62 Median_Img = double(Median_Img); 63 Sobel_Threshold = 150; 64 Sobel_Img = zeros(ROW,COL); 65 66 for r = 2:ROW-1 67 for c = 2:COL-1 68 Sobel_x = Median_Img(r-1,c+1) + 2*Median_Img(r,c+1) + Median_Img(r+1,c+1) - Median_Img(r-1,c-1) - 2*Median_Img(r,c-1) - Median_Img(r+1,c-1); 69 Sobel_y = Median_Img(r-1,c-1) + 2*Median_Img(r-1,c) + Median_Img(r-1,c+1) - Median_Img(r+1,c-1) - 2*Median_Img(r+1,c) - Median_Img(r+1,c+1); 70 Sobel_Num = abs(Sobel_x) + abs(Sobel_y); 71 %Sobel_Num = sqrt(Sobel_x^2 + Sobel_y^2); 72 if(Sobel_Num > Sobel_Threshold) 73 Sobel_Img(r,c)=255; 74 else 75 Sobel_Img(r,c)=0; 76 end 77 end 78 end 79 80 figure; 81 imshow(Sobel_Img); 82 83 %imopen Erosion_Dilation 84 %Erosion 85 % Erosion_img = zeros(ROW,COL); 86 % for r = 2:ROW-1 87 % for c = 2:COL-1 88 % and1 = bitand(Sobel_Img(r-1, c-1), bitand(Sobel_Img(r-1, c), Sobel_Img(r-1, c+1))); 89 % and2 = bitand(Sobel_Img(r, c-1), bitand(Sobel_Img(r, c), Sobel_Img(r, c+1))); 90 % and3 = bitand(Sobel_Img(r+1, c-1), bitand(Sobel_Img(r+1, c), Sobel_Img(r+1, c+1))); 91 % Erosion_img(r, c) = bitand(and1, bitand(and2, and3)); 92 % end 93 % end 94 95 % figure; 96 % imshow(Erosion_img); 97 98 % %Dilation 99 % Dilation_img = zeros(ROW,COL);100 % for r = 2:ROW-1101 % for c = 2:COL-1102 % or1 = bitor(Erosion_img(r-1, c-1), bitor(Erosion_img(r-1, c), Erosion_img(r-1, c+1)));103 % or2 = bitor(Erosion_img(r, c-1), bitor(Erosion_img(r, c), Erosion_img(r, c+1)));104 % or3 = bitor(Erosion_img(r+1, c-1), bitor(Erosion_img(r+1, c), Erosion_img(r+1, c+1)));105 % Dilation_img(r, c) = bitor(or1, bitor(or2, or3));106 % end107 % end108 109 % figure;110 % imshow(Dilation_img);111 112 %imclose Erosion_Dilation113 %Dilation114 Dilation_img = zeros(ROW,COL);115 for r = 2:ROW-1116 for c = 2:COL-1117 or1 = bitor(Sobel_Img(r-1, c-1), bitor(Sobel_Img(r-1, c), Sobel_Img(r-1, c+1)));118 or2 = bitor(Sobel_Img(r, c-1), bitor(Sobel_Img(r, c), Sobel_Img(r, c+1)));119 or3 = bitor(Sobel_Img(r+1, c-1), bitor(Sobel_Img(r+1, c), Sobel_Img(r+1, c+1)));120 Dilation_img(r, c) = bitor(or1, bitor(or2, or3));121 end122 end123 124 figure;125 imshow(Dilation_img);126 127 %Erosion128 Erosion_img = zeros(ROW,COL);129 for r = 2:ROW-1130 for c = 2:COL-1131 and1 = bitand(Dilation_img(r-1, c-1), bitand(Dilation_img(r-1, c), Dilation_img(r-1, c+1)));132 and2 = bitand(Dilation_img(r, c-1), bitand(Dilation_img(r, c), Dilation_img(r, c+1)));133 and3 = bitand(Dilation_img(r+1, c-1), bitand(Dilation_img(r+1, c), Dilation_img(r+1, c+1)));134 Erosion_img(r, c) = bitand(and1, bitand(and2, and3));135 end136 end137 138 figure;139 imshow(Erosion_img);
处理后结果对比
为了可以清晰的看到图像边缘的变化,我们把黑色作为背景,白色作为边缘。
Sobel边缘检测后的lena
腐蚀后的lena
膨胀后的lena
先腐蚀后膨胀开运算lena
先膨胀后腐蚀闭运算lena
- 相关推荐
- 热点推荐
- matlab
-
在MATLAB/simulink中建模时的两种不同实现方式2022-09-15 2809
-
一文详解限流算法的实现方式2022-05-25 1933
-
果蝇优化算法MATLAB实现2021-08-17 2382
-
如何去实现一种方波控制算法2021-08-10 1499
-
如何去实现一种错误控制编码的算法?2021-06-21 1852
-
介绍一种基于Winpcap的网络视频流识别算法2021-06-03 2126
-
介绍一种防止相位假信号的具体算法2021-04-30 969
-
如何实现一种改进的Bayer图像彩色恢复差值算法2021-04-02 821
-
一种基于FPGA的实时视频图像处理算法研究与实现2019-06-28 3880
-
Matlab关于Apriori算法设计2018-02-02 5435
-
BP算法及其matlab实现2017-12-02 546
-
FFT 算法的一种 FPGA 实现2017-11-21 4071
-
一种多核混合分区调度算法设计与实现2017-01-07 603
-
一种解决函数优化问题的免疫算法2009-11-08 787
全部0条评论

快来发表一下你的评论吧 !

