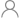
| Number of channels (#) | 16 |
| Technology Family | ALVC |
| Supply voltage (Min) (V) | 1.65 |
| Supply voltage (Max) (V) | 3.6 |
| Input type | Standard CMOS |
| Output type | 3-State |
| Clock Frequency (Max) (MHz) | 150 |
| IOL (Max) (mA) | 12 |
| IOH (Max) (mA) | -12 |
| ICC (Max) (uA) | 40 |
| Features | Balanced outputs, Very high speed (tpd 5-10ns), Over-voltage tolerant inputs, Damping resistors, Bus-hold |
- Member of the Texas Instruments Widebus? Family
- Bus Hold on Data Inputs Eliminates the Need for External Pullup/Pulldown Resistors
- Output Ports Have Equivalent 26-
 Series Resistors, So No External Resistors Are Required
Series Resistors, So No External Resistors Are Required - Latch-Up Performance Exceeds 250 mA Per JESD 17
- ESD Protection Exceeds JESD 22
- 2000-V Human-Body Model (A114-A)
- 200-V Machine Model (A115-A)
Widebus is a trademark of Texas Instruments.
This 16-bit edge-triggered D-type flip-flop is designed for 1.65-V to 3.6-V VCC operation.
The SN74ALVCH162374 is particularly suitable for implementing buffer registers, I/O ports, bidirectional bus drivers, and working registers. It can be used as two 8-bit flip-flops or one 16-bit flip-flop. On the positive transition of the clock (CLK) input, the Q outputs of the flip-flop take on the logic levels set up at the data (D) inputs.
The output-enable (OE)\ input can be used to place the eight outputs in either a normal logic state (high or low logic levels) or a high-impedance state. In the high-impedance state, the outputs neither load nor drive the bus lines significantly. The high-impedance state and the increased drive provide the capability to drive bus lines without need for interface or pullup components. OE\ does not affect internal operations of the flip-flop. Old data can be retained or new data can be entered while the outputs are in the high-impedance state.
The outputs, which are designed to sink up to 12 mA, include equivalent 26- resistors to reduce overshoot and undershoot.
resistors to reduce overshoot and undershoot.
To ensure the high-impedance state during power up or power down, OE\ should be tied to VCC through a pullup resistor; the minimum value of the resistor is determined by the current-sinking capability of the driver.
Active bus-hold circuitry holds unused or undriven inputs at a valid logic state. Use of pullup or pulldown resistors with the bus-hold circuitry is not recommended.