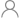
| Number of channels (#) | 8 |
| Technology Family | ABT |
| Supply voltage (Min) (V) | 4.5 |
| Supply voltage (Max) (V) | 5.5 |
| Input type | TTL-Compatible CMOS |
| Output type | 3-State |
| Clock Frequency (Max) (MHz) | 150 |
| IOL (Max) (mA) | 64 |
| IOH (Max) (mA) | -32 |
| ICC (Max) (uA) | 30000 |
| Features | Very high speed (tpd 5-10ns), Partial power down (Ioff) |
- Typical VOLP (Output Ground Bounce)
???<1 V at VCC = 5 V, TA = 25°C - High-Drive Outputs (–32-mA IOH, 64-mA IOL)
- Ioff Supports Partial-Power-Down Mode Operation
- Latch-Up Performance Exceeds 500 mA Per JEDEC Standard JESD 17
- ESD Protection Exceeds JESD 22
- 2000-V Human-Body Model (A114-A)
- 200-V Machine Model (A115-A)
These 8-bit flip-flops feature 3-state outputs designed specifically for driving highly capacitive or relatively low-impedance loads. They are particularly suitable for implementing buffer registers, I/O ports, bidirectional bus drivers, and working registers.
The eight flip-flops of the SN54ABT574 and SN74ABT574A are edge-triggered D-type flip-flops. On the positive transition of the clock (CLK) input, the Q outputs are set to the logic levels set up at the data (D) inputs.
A buffered output-enable (OE)\ input can be used to place the eight outputs in either a normal logic state (high or low logic levels) or the high-impedance state. In the high-impedance state, the outputs neither load nor drive the bus lines significantly. The high-impedance state and increased drive provide the capability to drive bus lines without need for interface or pullup components.
OE\ does not affect the internal operations of the flip-flops. Old data can be retained or new data can be entered while the outputs are in the high-impedance state.
To ensure the high-impedance state during power up or power down, OE\ should be tied to VCC through a pullup resistor; the minimum value of the resistor is determined by the current-sinking capability of the driver.
This device is fully specified for partial-power-down applications using Ioff. The Ioff circuitry disables the outputs, preventing damaging current backflow through the device when it is powered down.