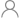
| Configuration | Serial-in, Parallel-out |
| Bits (#) | 8 |
| Technology Family | LS |
| Supply voltage (Min) (V) | 4.75 |
| Supply voltage (Max) (V) | 5.25 |
| Input type | Bipolar |
| Output type | Push-Pull |
| Clock Frequency (MHz) | 25 |
| IOL (Max) (mA) | 24 |
| IOH (Max) (mA) | -2.6 |
| ICC (Max) (uA) | 80000 |
| Features | High speed (tpd 10-50ns), Output register |
- 'LS673
- 16-Bit Serial-In, Serial-Out Shift Register with 16-Bit Parallel-Out Storage Register
- Performs Serial-to-Parallel Conversion
- 'LS674
- 16-Bit Parallel-In, Serial-Out Shift Register
- Performs Parallel-to-Serial Conversion
SN54LS673, SN74LS673
The 'LS673 is a 16-bit shift register and a 16-bit storage register in a single 24-pin package. A three-state input/output (SER/Q15) port to the shift register allows serial entry and/or reading of data. The storage register is connected in a parallel data loop with the shift register and may be asynchronously cleared by taking the store-clear input low. The storage register may be parallel loaded with shift-register data to provide shift-register status via the parallel outputs. The shift register can be parallel loaded with the storage-register data upon commmand.
A high logic level at the chip-level (CS\) input disables both the shift-register clock and the storage register clock and places SER/Q15 in the high-impedance state. The store-clear function is not disabled by the chip select.
Caution must be exercised to prevent false clocking of either the shift register or the storage register via the chip-select input. The shift clock should be low during the low-to-high transition of chip select and the store clock should be low during the high-to-low transition of chip select.
SN54LS674, SN74LS674
The 'LS674 is a 16-bit parallel-in, serial-out shift register. A three-state input/output (SER/Q15) port provides access for entering a serial data or reading the shift-register word in a recirculating loop.
The device has four basic modes of operation:
- Hold (do nothing)
- Write (serially via input/output)
- Read (serially)
- Load (parallel via data inputs)
Low-to-high-level changes at the chip select input should be made only when the clock input is low to prevent false clocking.