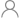
| Number of full bridges | 1 |
| Vs (Min) (V) | 4.5 |
| Vs ABS (Max) (V) | 40 |
| Peak output current (A) | 10 |
| RDS(ON) (HS + LS) (mOhms) | 150 |
| Sleep current (uA) | 15 |
| Control mode | Independent 1/2-Bridge, PH/EN, PWM |
| Control interface | Hardware (GPIO), SPI |
| Features | Current Sense Amplifier, Integrated Current Sensing, Open-Load Detection |
| Rating | Catalog |
| Operating temperature range (C) | -40 to 125 |
- H-Bridge Motor Driver
- Drives One DC Motor, One Winding of a Stepper Motor, or Solenoid Loads
- 4.5-V to 38-V Operating Voltage Range
- 10-A Peak Current Drive
- Low HS + LS RDS(ON)
- 150 m? at TJ = 25°C, 13.5 V
- 250 m? at TJ = 150°C, 13.5 V
- Current Mirror for Output Current Sensing
- Configurable Control Interface
- PH/EN
- PWM (IN1/IN2)
- Independent Half-Bridge Control
- Supports 1.8-V, 3.3-V, 5-V Logic Inputs
- SPI or Hardware Interface Options
- Low-Power Sleep Mode (10 μA)
- Small Package and Footprint
- 24 HTSSOP PowerPAD? IC Package
- Protection Features
- VM Undervoltage Lockout (UVLO)
- Charge Pump Undervoltage (CPUV)
- Overcurrent Protection (OCP)
- Output short to battery and short to ground protection
- Open Load Detection
- Thermal Shutdown (TSD)
- Fault Condition Output (nFAULT / SPI)
The DRV8873 device is an integrated driver IC for driving a brushed DC motor in industrial applications. Two logic inputs control the H-bridge driver, which consists of four N-channel MOSFETs that drive motors bi-directionally with up to 10-A peak current. The device operates from a single power supply and supports a wide input supply range from 4.5 V to 38 V.
A PH/EN or PWM interface allows simple interfacing to controller circuits. Alternatively, independent half-bridge control is available to drive two solenoid loads.
A current mirror allows the controller to monitor the load current. This mirror approximates the current through the high-side FETs, and does not require a high-power resistor for sensing the current.
A low-power sleep mode is provided to achieve very-low quiescent current draw by shutting down much of the internal circuitry. Internal protection functions are provided for undervoltage lockout, charge pump faults, overcurrent protection, short-circuit protection, open-load detection, and overtemperature. Fault conditions are indicated on an nFAULT pin and through the SPI registers.