| Number of series cells | 1, 2, 3, 4 |
| Charge current (Max) (A) | 2 |
| Operating Vin (Max) (V) | 6 |
| Cell chemistry | NiCd, NiMH |
| Battery charge voltage (Min) (V) | 0 |
| Battery charge voltage (Max) (V) | 6 |
| Absolute Vin (safety rating) (Max) ((V)) | 7 |
| Control interface | Standalone (RC-Settable) |
| Features | BAT temp thermistor monitoring (hot/cold profile) |
| Operating Vin (Min) (V) | 4 |
| Rating | Catalog |
- Fast charge of nickel cadmium or nickel-metal hydride batteries
- Direct LED output displays charge status
- Fast-charge termination by -
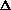 V, maximum voltage, maximum temperature, and maximum time
V, maximum voltage, maximum temperature, and maximum time - Internal band-gap voltage reference
- Optional top-off charge
- Selectable pulse trickle charge rates
- Low-power mode
- 8-pin 300-mil DIP or 150-mil SOIC
The bq2002E and bq2002G Fast-Charge ICs are low-cost CMOS battery-charge controllers providing reliable charge termination for both NiCd and NiMH battery applications. Controlling a current-limited or constant-current supply allows the bq2002E/G to be the basis for a cost-effective stand-alone or system-integrated charger. The bq2002E/G integrates fast charge with optional top-off and pulsed-trickle control in a single IC for charging one or more NiCd or NiMH battery cells.
Fast charge is initiated on application of the charging supply or battery replacement. For safety, fast charge is inhibited if the battery temperature and voltage are outside configured limits.
Fast charge is terminated by any of the following:
- Peak voltage detection (PVD)
- Negative delta voltage (-
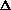 V)
V) - Maximum voltage
- Maximum temperature
- Maximum time
After fast charge, the bq2002E/G optionally tops-off and pulse-trickles the battery per the pre-configured limits. Fast charge may be inhibited using the INH pin. The bq2002E/G may also be placed in low-standby-power mode to reduce system power consumption. The bq2002E differs from the bq2002G only in that a slightly different set of fast-charge and top-off time limits is available. All differences between the two ICs are illustrated in Table 1.