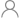
| Output options | Fixed Output |
| Iout (Max) (A) | 0.1 |
| Vin (Max) (V) | 35 |
| Vin (Min) (V) | 17.6 |
| Vout (Max) (V) | 15 |
| Vout (Min) (V) | 5 |
| Fixed output options (V) | 5, 12, 15 |
| Noise (uVrms) | 40 |
| Iq (Typ) (mA) | 4.5 |
| Thermal resistance θJA (°C/W) | 26 |
| Rating | Military |
| Load capacitance (Min) (μF) | 0 |
| Regulated outputs (#) | 1 |
| Accuracy (%) | 4 |
| PSRR @ 100 KHz (dB) | 40 |
| Dropout voltage (Vdo) (Typ) (mV) | 1500 |
| Operating temperature range (C) | -55 to 125 |
- Line Regulation of 0.04%/V
- Load Regulation of 0.01%/mA
- Output Voltage Tolerances of ±2% at Tj = 25°C and ±4% over the Temperature Range
- Output Current of 100 mA
- Internal Thermal Overload Protection
- Output Transistor Safe Area Protection
- Internal Short Circuit Current Limit
All trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
The LM140L series of three terminal positive regulators is available with several fixed output voltages making them useful in a wide range of applications. The LM140LA is an improved version of the LM78LXX series with a tighter output voltage tolerance (specified over the full military temperature range), higher ripple rejection, better regulation and lower quiescent current. The LM140LA regulators have ±2% VOUT specification, 0.04%/V line regulation, and 0.01%/mA load regulation. When used as a zener diode/resistor combination replacement, the LM140LA usually results in an effective output impedance improvement of two orders of magnitude, and lower quiescent current. These regulators can provide local on card regulation, eliminating the distribution problems associated with single point regulation. The voltages available allow the LM140LA to be used in logic systems, instrumentation, Hi-Fi, and other solid state electronic equipment. Although designed primarily as fixed voltage regulators, these devices can be used with external components to obtain adjustable voltages and currents.
With adequate heat sinking the regulator can deliver 100 mA output current. Current limiting is included to limit the peak output current to a safe value. Safe area protection for the output transistor is provided to limit internal power dissipation. If internal power dissipation becomes too high for the heat sinking provided, the thermal shut-down circuit takes over, preventing the IC from overheating.