

SystemVerilog中的操作方法
描述
SystemVerilog提供了几个内置方法来支持数组搜索、排序等功能。
Array Locator Methods
下表是数组定位方法,需要附带" with "子语句,基于给定的表达式上从现有数组中筛选出某些元素。所有满足给定表达式的元素都会返回到一个队列中:
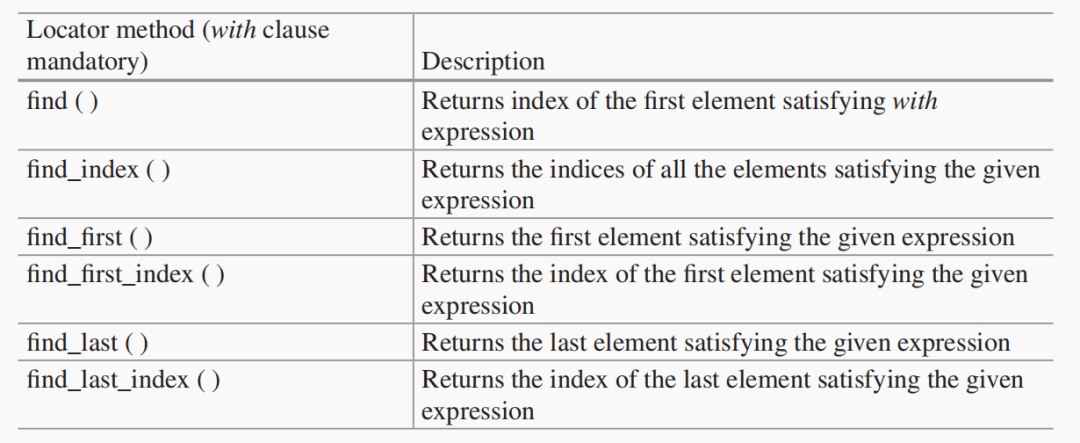
module arrayLocator;
string ques[$]; //queue of string type
int intA[int]; //associative array
int quei[$]; //queue of int type
int x;
initial begin
intA[1] = 3;
intA[2] = 2;
intA[3] = 6;
intA[4] = 7;
intA[5] = 3;
//returns all elements stratifying the 'with' expression
quei = intA.fnd( x ) with ( x > 5 );
$display("fnd(x)::quei=%0p",quei);
//returns all elements stratifying the 'with' expression
quei = intA.fnd( x ) with ( x < 5 );
$display("fnd(x)::quei=%0p",quei);
//returns the indices of all elements
//that satisfy the 'with' expression
//quei = intA.fnd_index with (item == 3);
quei = intA.fnd_index with (item > 1);
$display("fnd_index::quei=%0p",quei);
//returns the frst element satisfying 'with' expression
quei = intA.fnd_frst with (item > 3);
$display("fnd_frst::quei=%0p",quei);
//returns the frst element satisfying 'with' expression
end
endmodule
仿真log:
fnd(x)::quei='{6, 7}
fnd(x)::quei='{3, 2, 3}
fnd_index::quei='{1, 2, 3, 4, 5}
fnd_frst::quei='{6}
V C S S i m u l a t i o n R e p o r t
首先声明一些数组和队列。这些队列是必需的,因为需要作为数组方法的返回值。
给int数组“intA”的元素赋值。
使用fnd定位方法如下:
quei = intA.fnd( x ) with ( x > 5 );
$display("fnd(x)::quei=%0p",quei);
将返回所有>5的元素(6和7)
fnd(x)::quei='{6, 7}
再次使用fnd,返回所有<5的元素(3,2,3):
quei = intA.fnd( x ) with ( x < 5 );
$display("fnd(x)::quei=%0p",quei);
使用“fnd_index”,它将返回所有满足with表达式的元素的索引。
quei = intA.fnd_index with (item > 1);
$display("fnd_index::quei=%0p",quei);
“intA”数组中的元素是3,2,6,7,3。所有值都是>1,所以仿真打印
fnd_index::quei='{1, 2, 3, 4, 5}
使用with子句查找第一个>3的元素。
quei = intA.fnd_frst with (item > 3);
$display("fnd_frst::quei=%0p",quei);
所找到的值是6,所以会打印:
fnd_frst::quei='{6}
现在让我们看看其他可以不需要with子语句的定位方法。
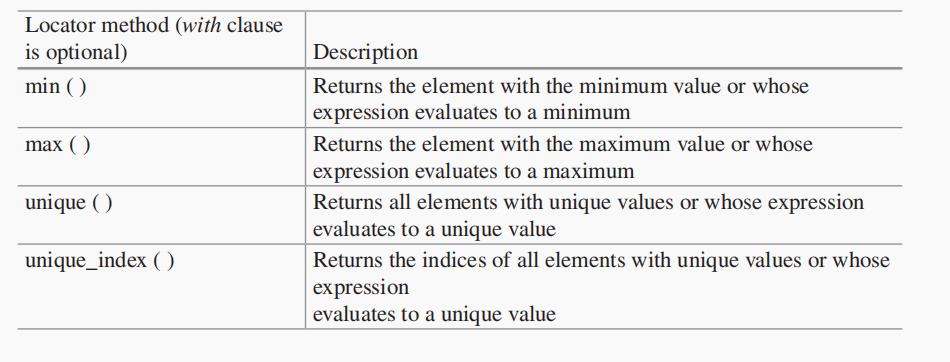
module arrayLocator;
string str[5] = '{"bob", "kim", "Derek", "bob", "kim"};
string ques[$]; //queue of strings
int intA[int]; //associative array
int quei[$]; //queue of int
int x;
initial begin
intA[1] = 3;
intA[2] = 2;
intA[3] = 6;
intA[4] = 7;
intA[5] = 3;
// Find smallest item
quei = intA.min;
$display("quei=%p",quei);
// Find string with largest numerical value in 'str'
ques = str.max;
$display("ques=%p",ques);
// Find all unique string elements in 'str'
ques = str.unique;
$display("ques=%p",ques);
// Find all unique indices in 'intA'
quei = intA.unique_index;
$display("quei=%p",quei);
end
endmodule
仿真log:
quei='{2}
ques='{"kim"}
ques='{"bob", "kim", "Derek"}
quei='{1, 2, 3, 4}
使用方法“min”在“intA”数组中查找值最小的元素:
// Find smallest item
quei = intA.min;
$display("quei=%p",quei);
“intA”的元素是3,2,6,7,3。最小的值是2,所以打印:
quei='{2}
我们使用max方法在字符串数组" str "中搜索数值最大的元素:
ques = str.max;
$display("ques=%p",ques);
“str”的值为“bob”、“kim”、“Derek”、“bob”和“kim”。所以最大的数值是“kim”:
ques='{"kim"}
接下来,我们查找字符串" str "中所有唯一的元素:
ques = str.unique;
$display("ques=%p",ques);
“str”的值为“bob”、“kim”、“Derek”、“bob”和“kim”。因为“bob”和“kim”是重复的,它们不是唯一的。因此,我们在仿真log中看到以下内容:
ques='{"bob", "kim", "Derek"}
最后,我们搜索数组" intA "中的所有唯一元素的下标:
quei = intA.unique_index;
$display("quei=%p",quei);
“intA”的元素是3,2,6,7,3。所以指标1 2 3 4处的值是独一无二的。索引5的最后一个值3是重复的。因此,仿真打印如下:
quei='{1, 2, 3, 4}
Array Ordering Methods
数组排序方法对数组的元素进行重新排序,但关联数组除外。
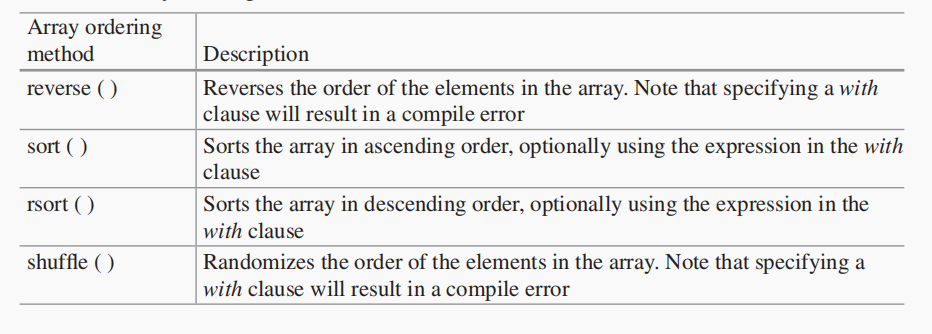
module arrayOrder;
string str[5] = '{"bob", "george", "ringo", "john",
"paul"};
int intA[8] = '{3,2,1,6,8,7,4,9};
initial begin
$display("BEFORE 'str' reverse: str=%p", str);
str.reverse;
$display("AFTER 'str' reverse: str=%p", str);
$display("BEFORE 'intA' sort: intA=%p", intA);
intA.sort;
$display("AFTER 'intA' sort: intA=%p",intA);
$display("BEFORE 'intA' rsort: intA=%p",intA);
intA.rsort;
$display("AFTER 'intA' rsort: intA=%p",intA);
$display("BEFORE 'intA' shuffe: intA=%p",intA);
intA.shuffe;
$display("AFTER 'intA' shuffe: intA=%p",intA);
end
endmodule
仿真log:
BEFORE 'str' reverse: str='{"bob", "george", "ringo", "john", "paul"}
AFTER 'str' reverse: str='{"paul", "john", "ringo", "george", "bob"}
BEFORE 'intA' sort: str='{3, 2, 1, 6, 8, 7, 4, 9}
AFTER 'intA' sort: intA='{1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 7, 8, 9}
BEFORE 'intA' rsort: intA='{1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 7, 8, 9}
AFTER 'intA' rsort: intA='{9, 8, 7, 6, 4, 3, 2, 1}
BEFORE 'intA' shuffe: intA='{9, 8, 7, 6, 4, 3, 2, 1}
AFTER 'intA' shuffe: intA='{2, 4, 1, 6, 7, 3, 9, 8}
V C S S i m u l a t i o n R e p o r t
3.5.3阵列约简方法
数组约简方法应用于任意解包装的整数值数组
将数组缩减为单个值。可以使用可选的with子句来指定
约简方法中使用的值。这些方法返回一个相同的值
类型作为数组元素类型。表3.5描述了阵列缩减方法。
下面是一个例子:
Array Reduction Methods
数组约简方法应用于任意整数值数组,将数组计算为单个值。可以使用可选的with子句来指定约简方法中使用的值。
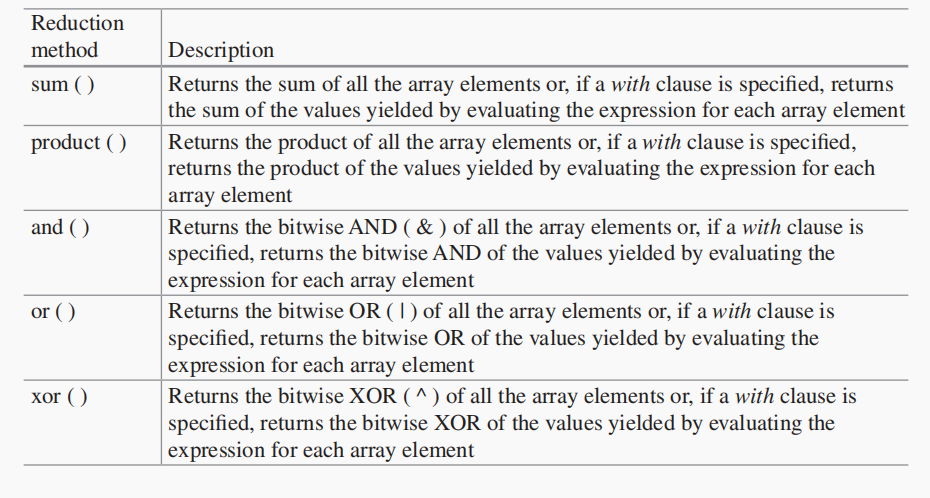
module arrayReduction;
int intA[4] = '{4,3,2,1};
logic [7:0] intB [2][2] = '{ '{1,2}, '{3,4} };
int y;
initial begin
y = intA.sum;
$display("intA.sum = %0d",y); //sum = 10 (4+3+2+1)
y = intA.sum with ( item + 1);
$display("intA.sum = %0d",y); //sum=14 (5+4+3+2)
//y = intB.sum; //Compile ERROR
//y = intB.sum with (item.sum); //OK
y = intB.sum with (item.sum with (item)); //OK
$display("intB.sum = %0d",y); //sum = 10 (1+2+3+4)
//y = intB.xor; //Compile Error
//y = intB.xor(item) with (item > 0); //Compile Error
y = intB.xor(item) with (item.xor); //OK
$display("intB.xor = %0h",y); //xor = 4 (1^2^3^4)
y = intA.product;
$display("intA.product = %0d",y); //product = 24 (4*3*2*1)
y = intA.product(item) with (item + 1);
$display("intA.product = %0d",y); //product = 120 (5*4*3*2)
y = intA.and;
$display("intA.and = %0h",y); //'and' = 0 (4&3&2&1)
y = intA.or;
$display("intA.or = %0h",y); //'or' = 7 (4 || 3 || 2 || 1)
end
endmodule
仿真log:
intA.sum = 10 intA.sum = 14 intB.sum = 10 intB.xor = 4 intA.product = 24 intA.product = 120 intA.and = 0 intA.or = 7 V C S S i m u l a t i o n R e p o r t
约简运算符只适用于一维数组,如果你试着在二维数组上使用约简运算符,将得到一个编译错误。
Error-[IMDARMC] Illegal MDA reduction method call
审核编辑:汤梓红
-
GPIO引脚操作方法概述2022-01-20 1093
-
RK3288的GPIO操作方法是什么2022-03-09 1805
-
PCB应力应变测试操作方法2023-06-12 2454
-
控温/恒温烙铁操作方法及使用说明2009-04-18 9549
-
EWB的基本操作方法2010-03-05 27933
-
智能仪表组态操作方法评述2011-07-21 819
-
工业烤箱操作方法及异常现象排除2011-08-23 3916
-
iphone远程控制电脑的操作方法2012-02-18 14609
-
PROTEL铺铜操作方法2016-03-11 1336
-
独立按键操作方法2016-03-21 758
-
Altium designer阻值图输出的详细操作方法2017-01-08 1533
-
电子测力计的操作方法2019-04-17 3147
-
光幕传感器工作原理及操作方法2019-10-12 10715
-
AD18操作方法2022-03-28 1541
-
multisim的基本界面与操作方法2025-06-24 205
全部0条评论

快来发表一下你的评论吧 !

