

SystemVerilog中的关联数组
描述
关联数组实际上是一种查找表,内存空间直到被使用时才会分配,每个数据项都会有一个特定的“键(索引)”,索引的类型不局限于整型。
相对于一般的数组,关联数组的内存空间利用会更加充分,因为它是稀疏的,无需一开始就分配很大的内存空间。
当变量集合的大小未知或数据空间稀疏时,关联数组是比动态数组更好的选择。例如只需要使用到地址0和地址FF,关联数组可以只分配2个地址空间,而动态数组则需要分配256个地址空间。
打个比方,如果动态数组时内存,那么关联数组更像是一个具有“tag”的cache。
关联数组也是一种unpacked数组。
data_type array_id [index_type];
其中data_type是数组元素的数据类型。array_id是数组的名称。index_type是索引(或键)的数据类型。各种数据类型的索引示例如下:
//wildcard index. Can be indexed by any integral type int myArray[ * ]; //Array that stores 'bit [31:0]' at string type index. bit [31:0] myArray[ string ]; //Array that stores 'string' at string type index. string myArray [ string ]; // Array that stores 'int' at Class type index int myArray [ class ]; //Array that stores 'logic' type at integer type index logic myArray[ integer ]; typedef bit signed [7:0] mByte; int myArray [mByte]; //'bit signed' index
比较特别的是以class作为索引类型的联合数组。
module assoc_arr;
class AB;
int a;
int b;
endclass
int arr[AB]; //Associative array 'arr' with class 'AB' as index
AB obj, obj1;
initial begin
obj = new();
obj1= new();
arr[obj]=20; //Store 20 at the object handle index 'obj'
$display("%0d",arr[obj]);
arr[obj1]=10; //Store 10 at the object handle index 'obj1'
$display("%0d",arr[obj1]);
end
endmodule
仿真log:
20 10 V C S S i m u l a t i o n R e p o r t
声明类“AB”,并使用它作为关联数组中的索引
int arr[AB]
声明两个AB类型的对象(obj和obj1),并实例化,赋值以这两个对象为索引的联合数组值。
arr[obj] = 20; arr[obj1] = 10;
String Index – Example
下面是一个以字符串为索引类型的联合数组示例:
module assoc_arr;
integer St [string] = '{"Peter":26, "Paul":24, "Mary":22};
integer data;
initial
begin
$display("St=",St);
$display("data stored at Peter = %0d",St["Peter"]);
$display("data stored at Paul = %0d",St["Paul"]);
$display("data stored at Mary = %0d",St["Mary"]);
St["mike"] = 20; //new data stored at new index "mike"
data = St["mike"]; //retrieve data stored at index "mike"
$display("data stored at mike = %0d",data);
$display("St=",St);
end
endmodule
仿真log:
run -all;
# KERNEL: St='{"Mary":22, "Paul":24, "Peter":26}
# KERNEL: data stored at Peter = 26
# KERNEL: data stored at Paul = 24
# KERNEL: data stored at Mary = 22
# KERNEL: data stored at mike = 20
# KERNEL: St='{"Mary":22, "Paul":24, "Peter":26, "mike":20}
# KERNEL: Simulation has fnished.
声明关联数组“St”,并对其进行初始化:
integer St [string] = '{"Peter":26, "Paul":24, "Mary":22};
意味着将26存储在索引“Peter”中,24存储在索引中
“Paul”,22存储在索引“Mary”中。
2. 分别打印数组。
3. 在新索引“mike”中添加新数据。注意,这个数据项的内存此时才开始分配。
Associative Array Methods
下面是关联数组提供的一些方法。
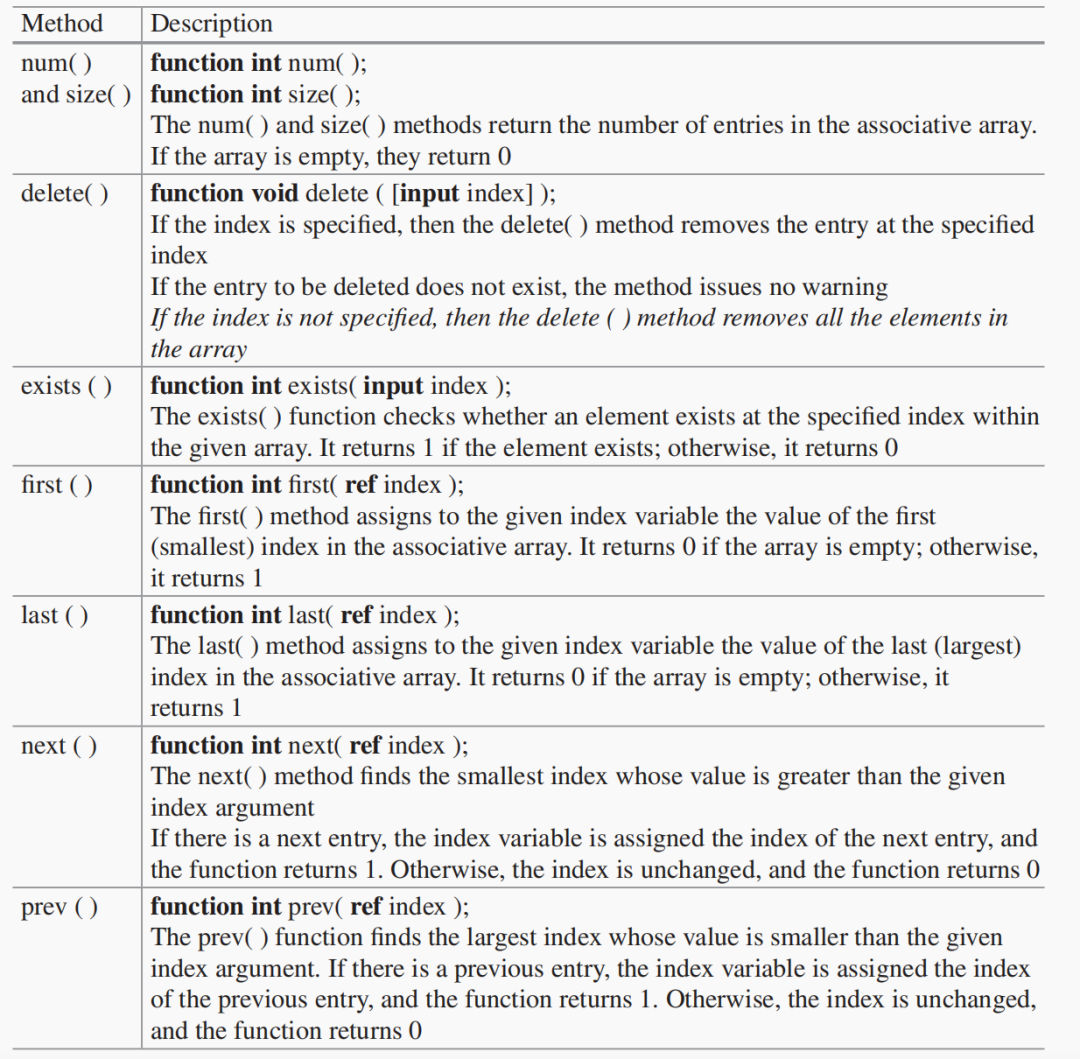
module assoc_arr;
int temp, imem[int];
integer St [string] = '{"Peter":20, "Paul":22, "Mary":23};
initial
begin
if(St.exists( "Peter") ) $display(" Index Peter exists ");
//Assign data to imem[int]
imem[ 2'd3 ] = 1;
imem[ 16'hffff ] = 2;
imem[ 4'b1000 ] = 3;
$display( " imem has %0d entries", imem.num );
if(imem.exists( 4'b1000)) $display("Index 4b'1000
exist)");
imem.delete(4'b1000);
if(imem.exists( 4'b1000)) $display("Index 4b'1000
exists)");
else $display(" Index 4b'1000 does not exist");
imem[ 4'b1000 ] = 3;
if(imem.first(temp)) $display(" First entry is at index
%0d ",temp);
if(imem.next(temp)) $display(" Next entry is at index
%0b ",temp);
if(imem.last(temp)) $display(" Last entry is at index
%0h",temp);
imem.delete( ); //delete all entries
$display(" imem has %0d entries", imem.num );
$display(" imem = %p", imem);
end
endmodule
仿真log:
Index Peter exists
imem has 3 entries
Index 4b'1000 exists
Index 4b'1000 does not exist
First entry is at index 3
Next entry is at index 1000
Last entry is at index ffff
imem has 0 entries
imem = '{}
V C S Simulation Report
声明了两个关联数组
int imem[int];
integer St [string] = '{"Peter":20, "Paul":22, "Mary":23};
使用.exists()判断某个索引对应的数据元素是否存在。
使用.num(),获取该联合数组具有的元素个数
使用.delete()删除特定索引对应的元素。如果不指定索引,则所有的元素都会被删除。
使用方法first()、next()和last()访问某个联合数组元素
First entry is at index 3 Next entry is at index 1000 Last entry is at index ffff
Associative Array – Default Value
可以在关联数组声明时为其指定默认值。
module assoc_arr;
string words [int] = '{default: "hello"};
initial begin
$display("words = %p", words['hffff]); //default
$display("words = %p", words[0]); //default
$display("words = %p", words[1000]); //default
words['hffff] = "goodbye";
$display("words = %p", words);
$display("words = %p", words[100]); //default
end
endmodule
仿真log:
words = "hello"
words = "hello"
words = "hello"
words = '{0xffff:"goodbye"}
words = "hello"
V C S S i m u l a t i o n R e p o r t
数组“words”的初始化默认值是“hello”,当我们访问索引“hffff”、“0”和“1000”时,都会打印默认值“hello”。
我们为index ' hffff分配一个字符串值" goodbye "。
Creating a Dynamic Array of Associative Arrays
关联数组也可以是动态数组中的元素,如下示例:
module assoc_arr;
//Create a dynamic array whose elements are associative arrays
int games [ ] [string];
initial begin
//Create a dynamic array with size of 3 elements
games = new [3];
//Initialize the associative array inside each dynamic
//array element
games [0] = '{ "football" : 10,"baseball" : 20,"hututu":70 };
games [1] = '{ "cricket" : 30, "ice hockey" : 40 };
games [2] = '{ "soccer" : 50, "rugby" : 60 };
// Iterate through each element of dynamic array
foreach (games[element])
// Iterate through each index of the current element in
// dynamic array
foreach (games[element][index])
$display ("games[%0d][%s] = %0d", element, index,
games[element][index]);
end
endmodule
仿真log:
games[0][baseball] = 20 games[0][football] = 10 games[0][hututu] = 70 games[1][cricket] = 30 games[1][ice hockey] = 40 games[2][rugby] = 60 games[2][soccer] = 50 V C S S i m u l a t i o n R e p o r t
审核编辑:汤梓红
-
随机抽取SV数组中的一个元素方法实现2024-03-21 1977
-
带你了解SystemVerilog中的关联数组2023-06-09 9057
-
使用SystemVerilog解决数组问题2023-03-08 2272
-
网络和变量的未压缩数组2023-02-09 1310
-
SystemVerilog中可以嵌套的数据结构2022-11-03 2492
-
SystemVerilog中的操作方法2022-10-31 4250
-
SystemVerilog动态数组的大小更改展示2022-10-21 2253
-
SystemVerilog中数组的赋值、索引和切片2022-10-20 6390
-
PHP数组排序2020-11-04 1585
-
基于本体的软件工程关联数据的自动构建2017-12-22 862
-
基于社交网络和关联数据的服务网络构建方法2017-12-06 1126
-
转一篇Systemverilog的一个牛人总结2015-08-27 13541
全部0条评论

快来发表一下你的评论吧 !

