
资料下载

用Arduino库来读取DHT11湿度和温度传感器数据
描述
介绍
在这个项目中,我开发了一个 Arduino 库来读取 DHT11 湿度和温度传感器生成的数据,并使用 AZDelivery ESP8266 ESP-12F NodeMCU Lua Amica V2 将其连续发送到 ThingSpeak 云服务。
有许多库可以用来读取 DHT11 传感器数据。那么,为什么要重新发明轮子呢?只是为了了解事物的运作方式并可能改进它们的乐趣。
我使用逻辑分析仪和 DHT11 传感器数据表来了解协议并为传感器开发自己的库。DHT11 温度和湿度传感器
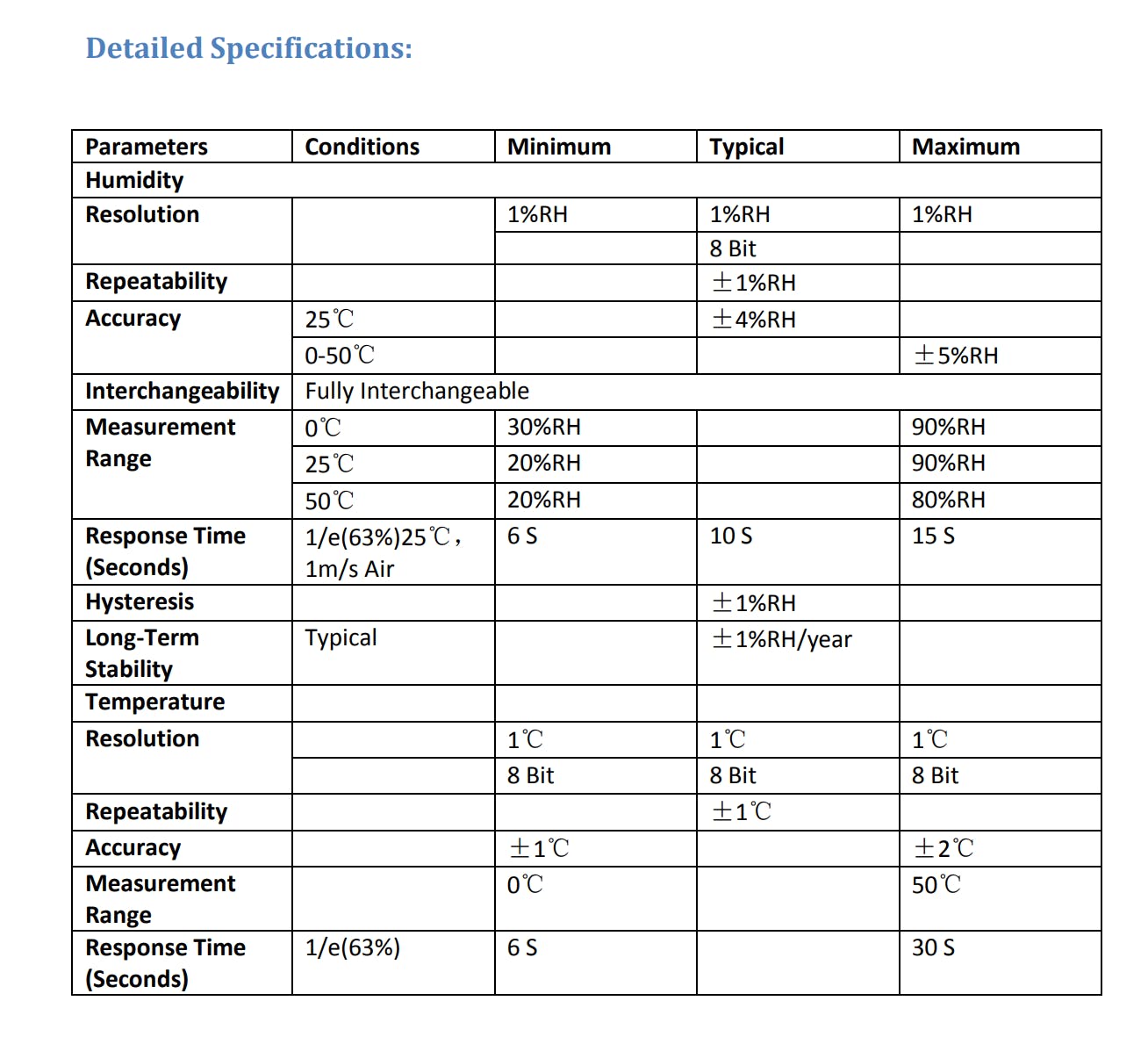
DHT11 温度和湿度传感器具有温度和湿度传感器复合体,具有校准的数字信号输出。采用独有的数字信号采集技术和温湿度传感技术,确保高可靠性和出色的长期稳定性。该传感器包括一个电阻式湿度测量元件和一个NTC温度测量元件,并连接到一个高性能8位微控制器,具有卓越的品质、快速的响应、抗干扰能力和成本效益。
PINOUT 和 MCU 连接
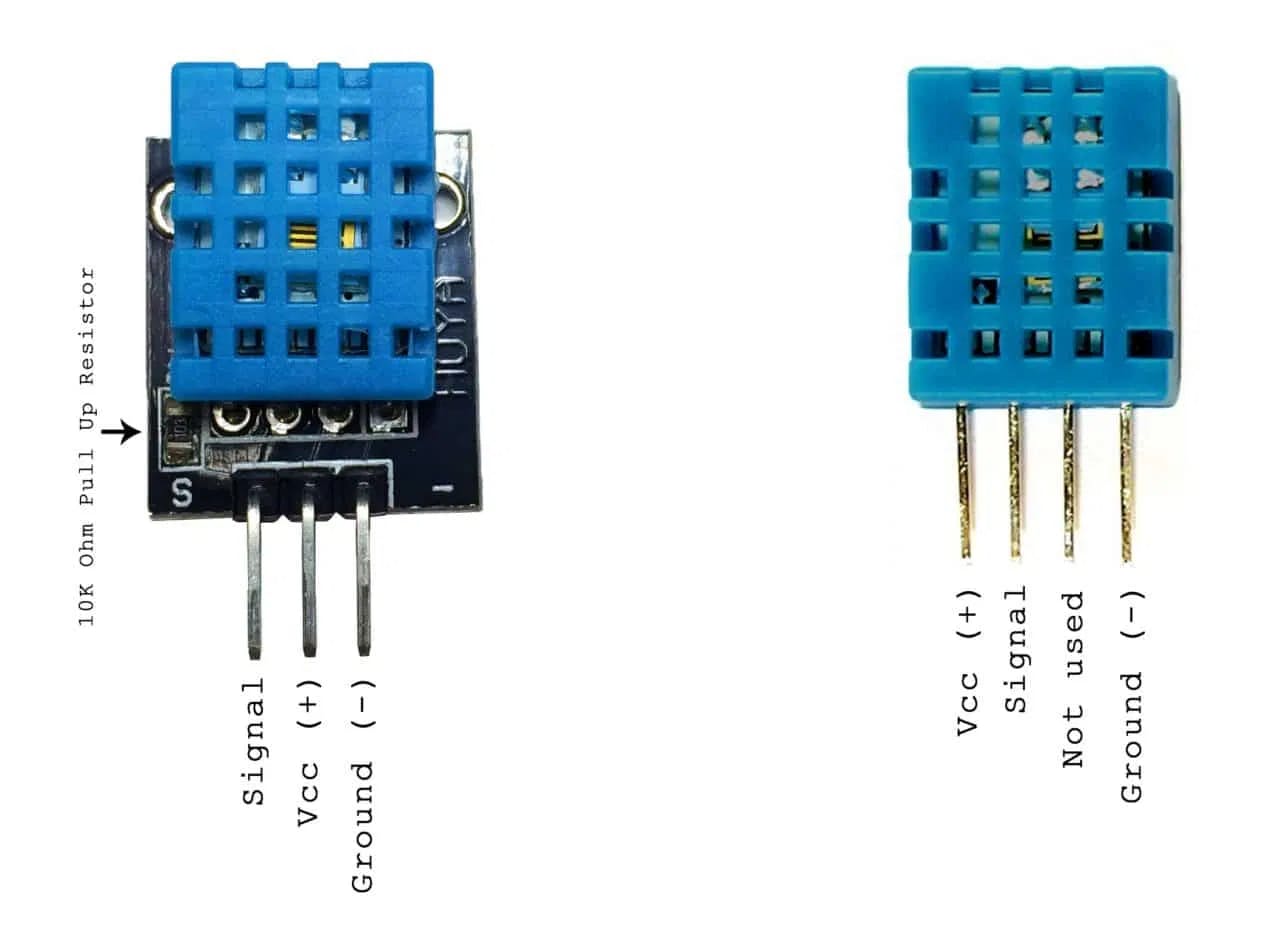
MCU 到 DHT11 连接
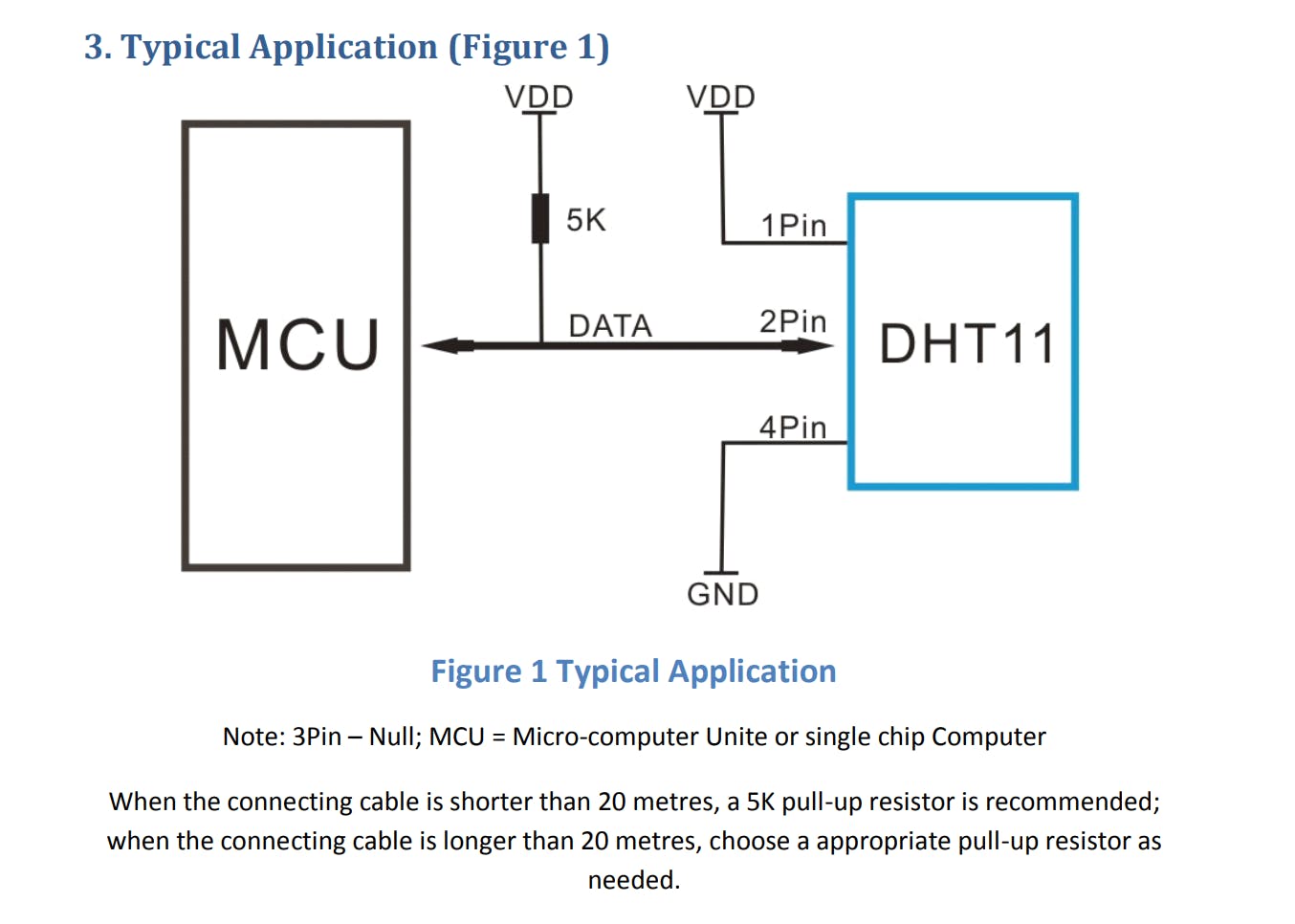
使用的分线模块已经有一个 10 KOhm 的上拉电阻。

DHT11 数据引脚连接到 D1 (GPIO5)
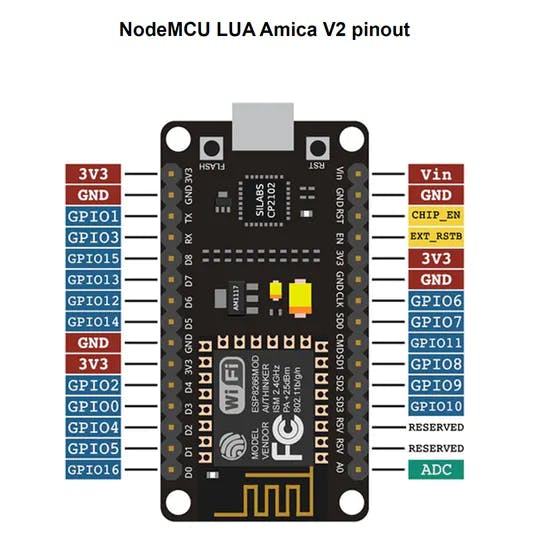
GPIO 0-15 都有一个内置的上拉电阻器,如果直接使用 DHT11 而不是分线器,我们可以使用它。
有关如何在我的NodeMCU Amica V2 路试中设置此模块的更多信息
AZ Delivery NodeMCU V2 路试,作者:Enrique Albertos。
https://www.hackster.io/javagoza/nodemcu-amica-v2-road-test-2e8bff
MCU 到 DHT11 通信
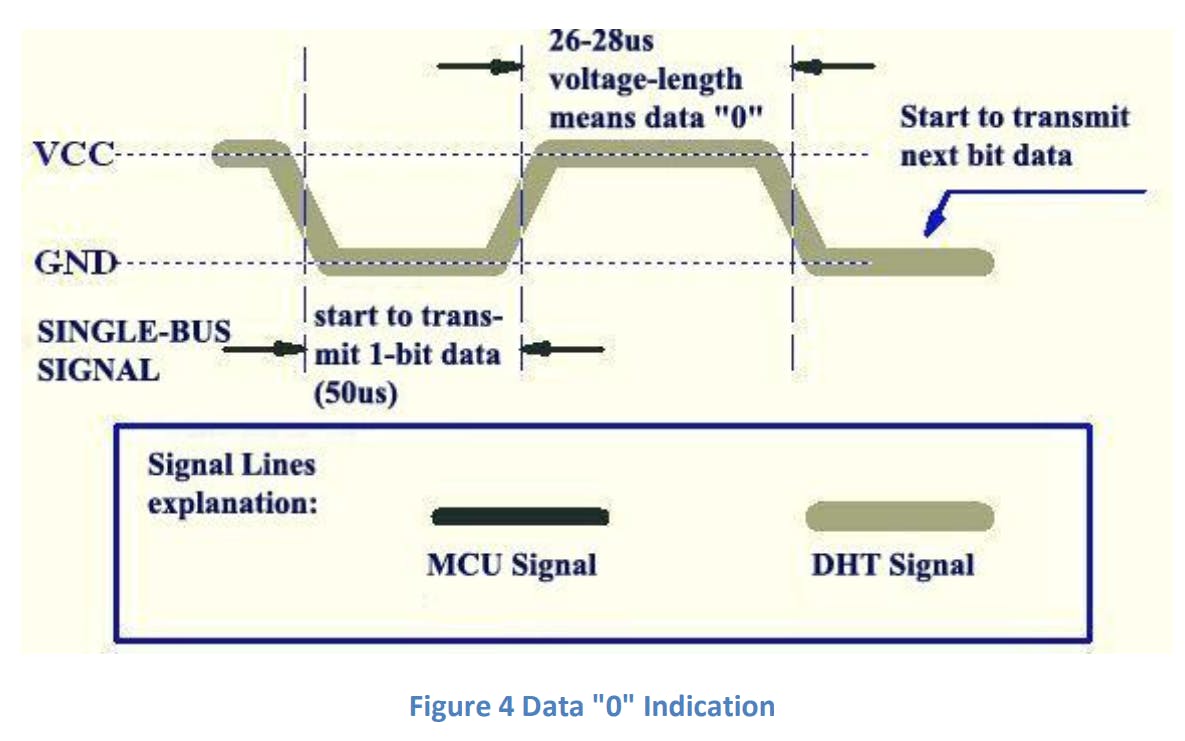
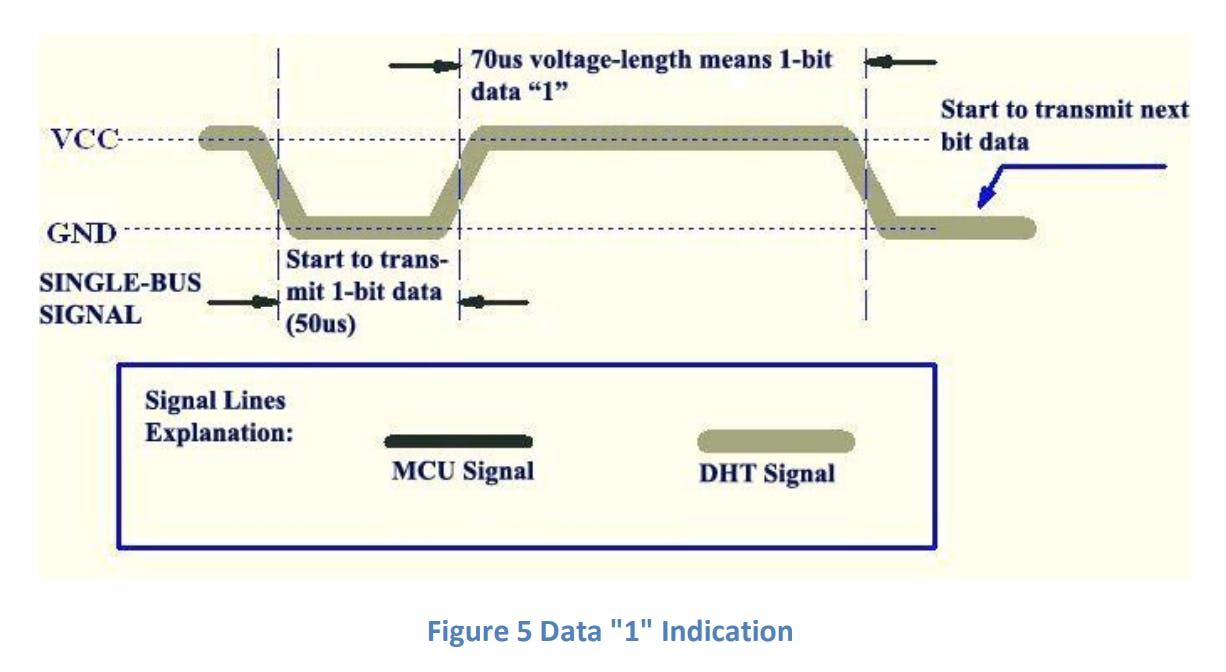
DHT11 单总线数据格式
单总线数据格式用于 MCU 和 DHT11 传感器之间的通信和同步。一个通信过程大约是4ms。数据由小数部分和整数部分组成。一次完整的数据传输为 40 位,传感器先发送高位数据。
数据格式:
8 bit integral RH data + 8 bit decimal RH data + 8 bit integral T data + 8 bit decimal T data + 8 bit checksum.
如果数据传输正确,校验和应该是:
8 bit integral RH data + 8 bit decimal RH data + 8 bit integral T data + 8 bit decimal T data
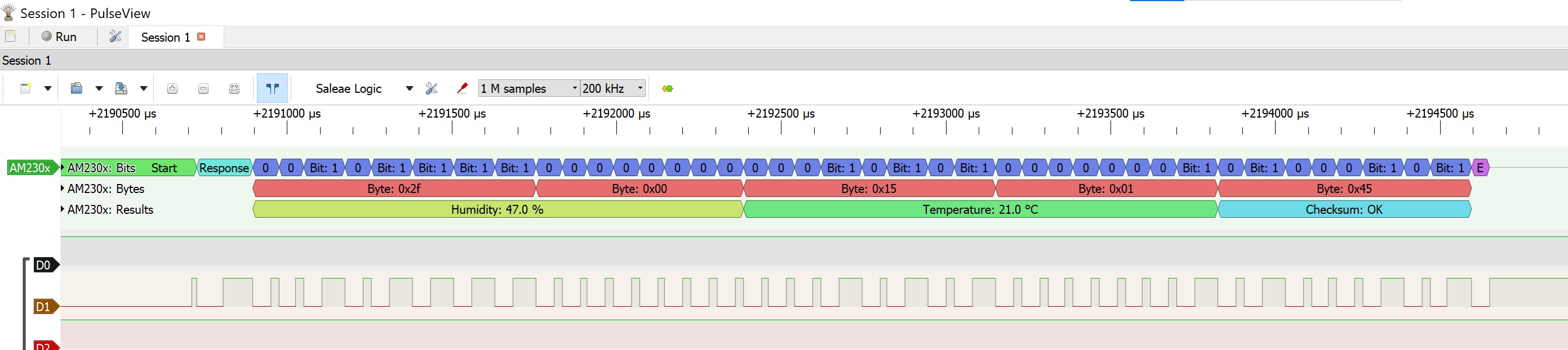
PulseView 和逻辑分析仪
PulseView 是 libsigrok 和 libsigrok 解码库的图形前端,允许访问各种设备和协议解码器,让您记录、分析、处理和导出模拟和逻辑数据。
逻辑分析仪
我们正在使用 AZ-Delivery 的这款廉价逻辑分析仪来监视 MCU 和 AZ Delivery NodeMCU 8266 Amica 模块之间的通信。
逻辑分析仪有 8 个并行输入 (0-5 V),每秒最多允许 2400 万个测量步骤。对于数字信号,采样速度必须比带宽快 4 倍。这意味着带宽是采样率的四分之一。
- 最大数字采样率:24 MSPS
- 最大数字带宽:6 MHz
这足以监视这种简单的通信所需的 200 Khz。
脉冲视图
安装后,您会在开始菜单中找到一个名为 Zadig 的程序。默认情况下,Windows 识别的某些设备将安装 PulseView 无法使用的驱动程序。Zadig 的目的是让您更改 Windows 用于特定设备的驱动程序 - 对于大多数设备,您需要选择 WinUSB 以将它们与 PulseView 或原始专有 Windows 驱动程序一起使用以将其与您访问设备的任何其他软件一起使用和。
新会话
- 打开一个新会话
- 选择您要使用的设备:
- 点击“运行”获取信号数据(设置了则等待触发)
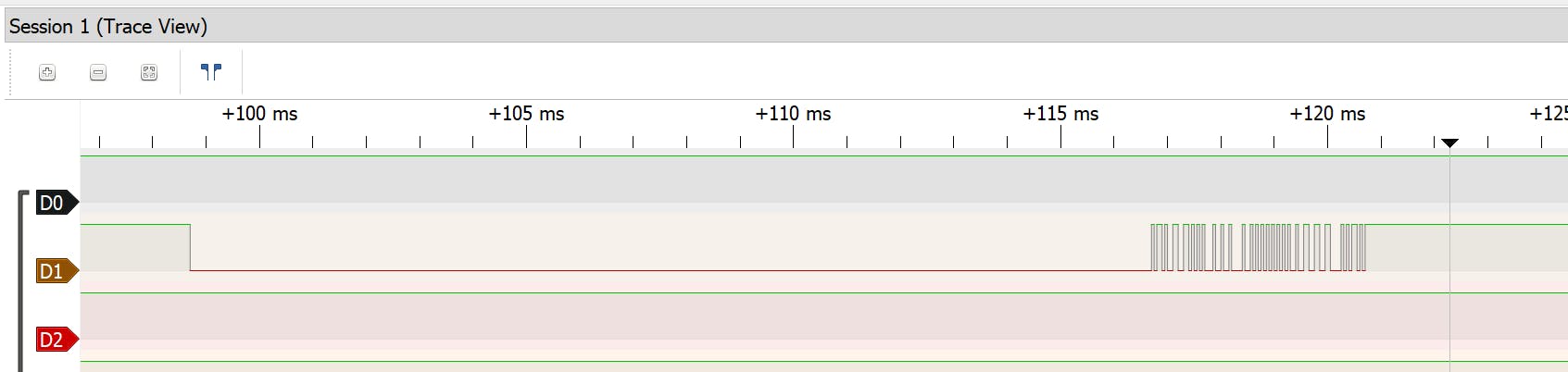
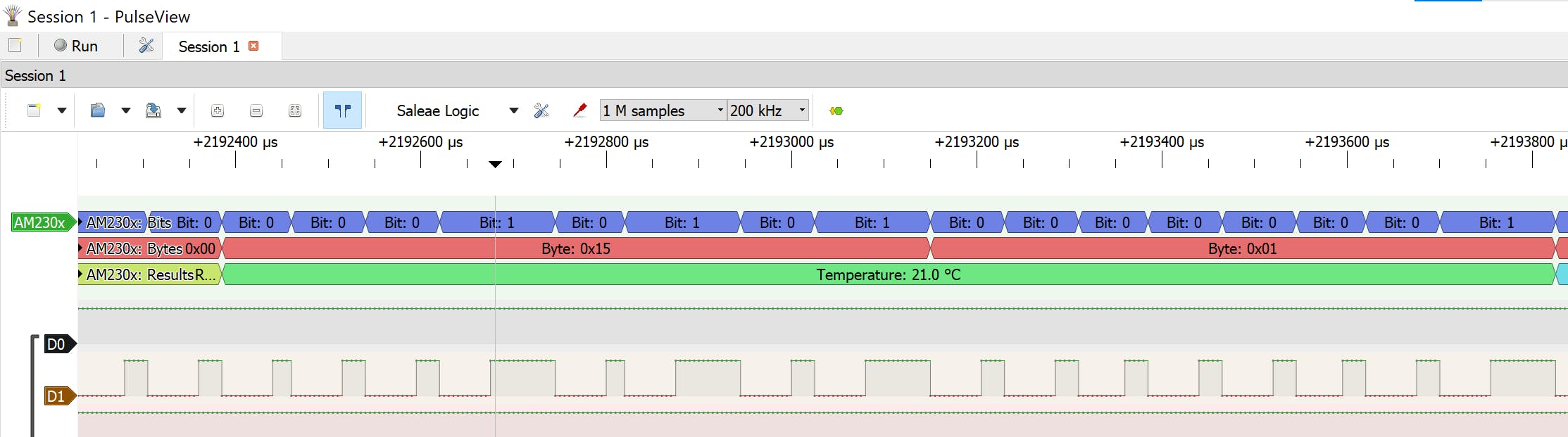
放大直到看到信号,MCU 和 DHT11 之间的通信大约需要 135 毫秒。
这是向传感器请求数据时的位流。
DHT11单线通讯协议解码器
Pulseview 带有一个 DHT11 协议解码器。让我们使用它。
添加解码器并将其关联到串行数据线。D1 在我们的例子中。
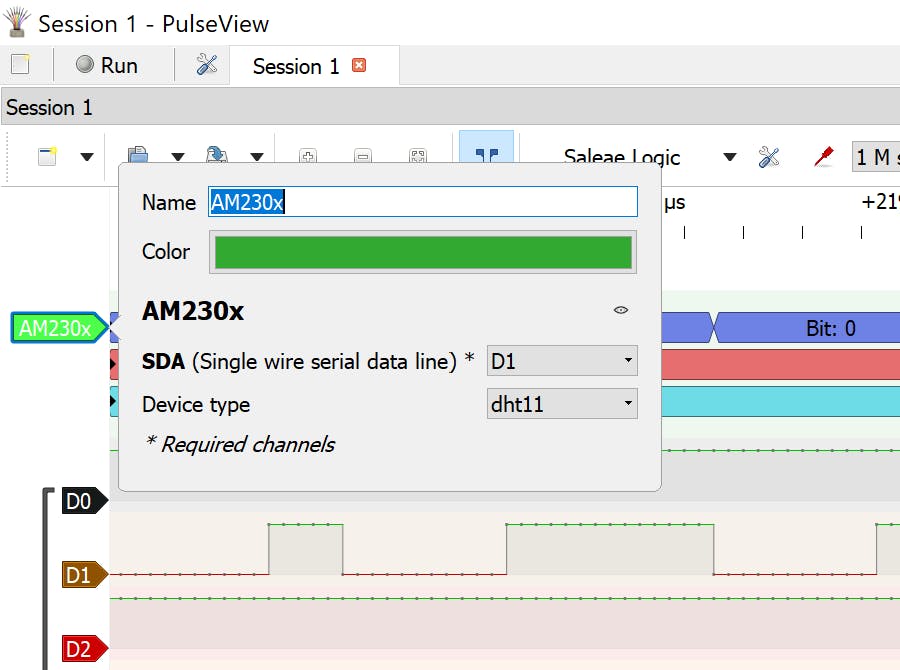
该解码器处理傲松 AM230x/DHTxx/RHTxx 系列数字湿度和温度传感器使用的专有单线通信协议。
采样率:建议使用至少200 kHz的采样率来正确检测协议的所有元素。
选项:
AM230x 和 DHTxx/RHTxx 数字湿度和温度传感器使用相同的单线协议,测量值的编码不同。因此,必须使用选项“设备”来正确解码各个传感器的通信。“ dht11 设备类型”用于我们的目的。
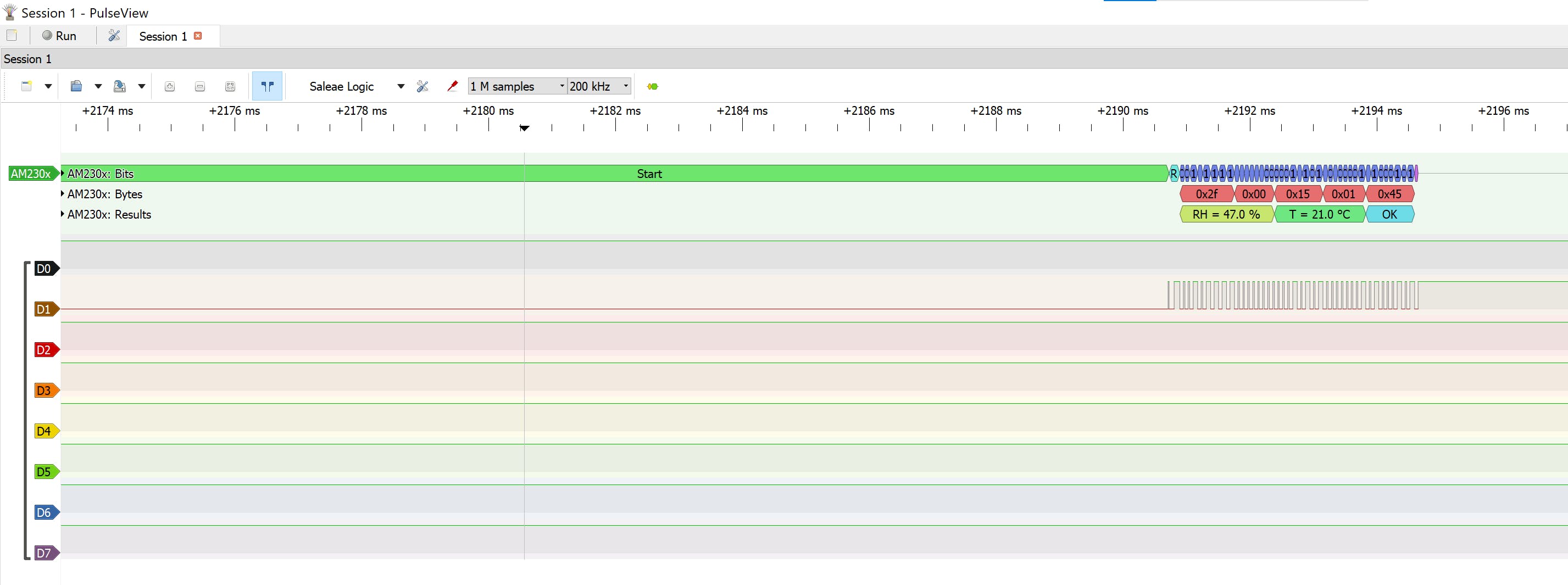
缩放以查看解码数据

相对湿度 %
8 位积分 RH 数据 + 8 位十进制 RH 数据
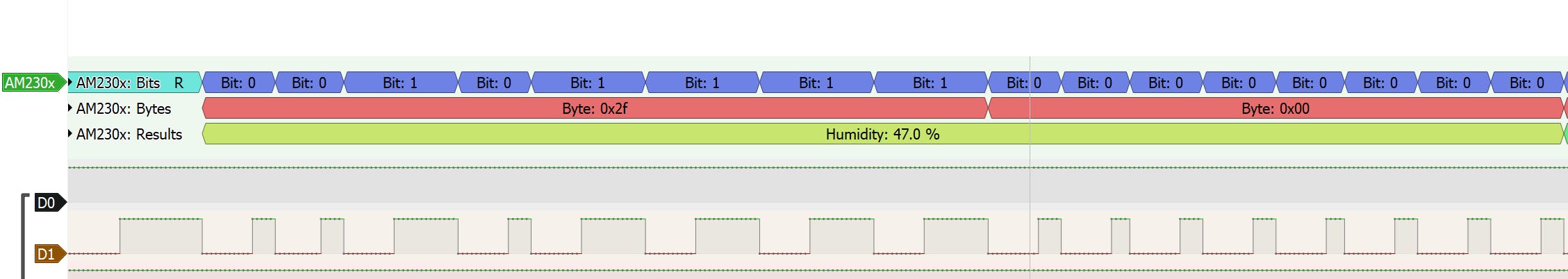
温度
8位整数T数据+8位十进制T数据
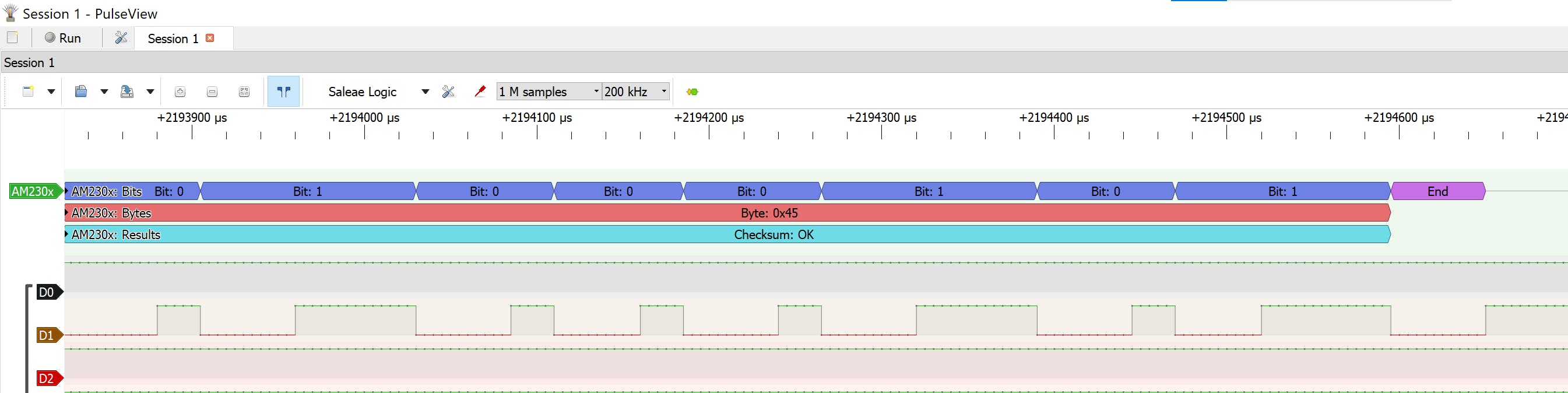
校验和
8 位积分 RH 数据 + 8 位十进制 RH 数据 + 8 位积分 T 数据 + 8 位十进制 T 数据
使用 ESP8266 内核为 Arduino 读取传感器数据
我们有几种方法来读取数据并处理 DHT11 使用的专有单线通信协议:
- 盲循环:等待固定的时间,并假设 I/O 将在该固定延迟过去之前完成。此方法不适合我们读取传感器数据,因为 0s 和 1s 时序不同,您可能会失去同步,但我们将使用它来启动信号到 DHT,因为这是使 DHT11 从低电平变化的盲信号-power-consumption mode 到 running-mode。
- 忙等待同步或轮询。检查完成状态的 I/O 状态的软件循环。这可能是我们读取 DHT11 发送数据的第一个候选者,因为系统非常简单,实时响应并不重要。
- 中断。使用硬件导致特殊的软件执行。当输入设备有新数据时,硬件将请求并中断。软件中断服务将从输入设备中读取并保存在全局 RAM 中。为了简单起见,我们不会使用这种方法。
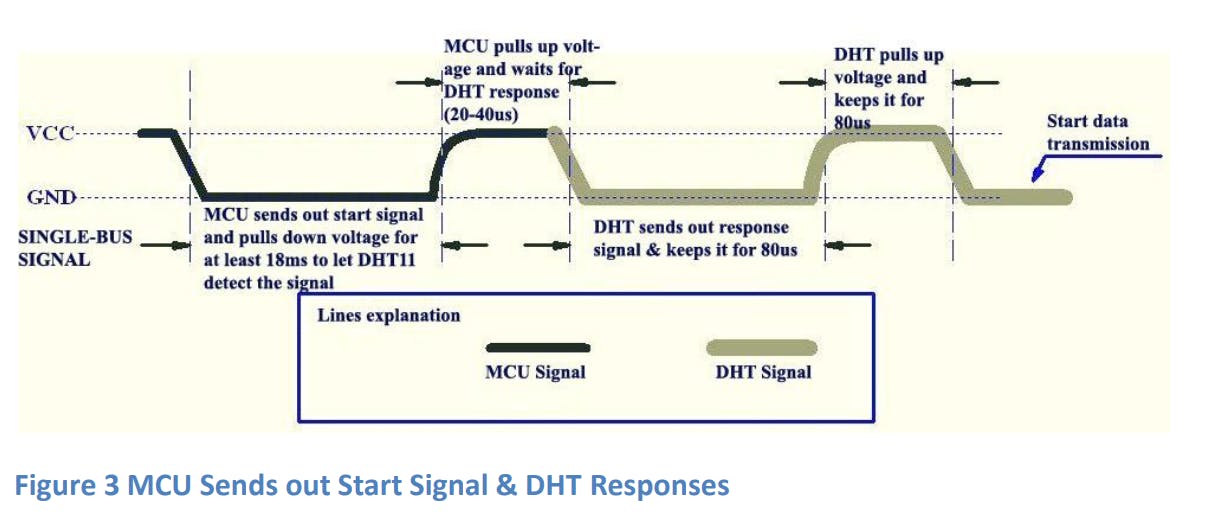
开始信号 - 盲循环
Data Single-bus free 状态为高电平。当 MCU 和 DHT11 开始通信时,MCU 程序会将 Data Single-bus 电压电平从高电平设置为低电平,这个过程必须至少需要 18 ms 才能确保 DHT 检测到 MCU 的信号,然后 MCU 会拉高电压并等待 20 -40 我们 DHT 的回应。
/**
MCU Sends Start Signal to DHT as this is a blind cycle that makes DHT11
to change from the low-power-consumption mode to the running-mode
Consists of a pulse of at least 18 ms voltage-length
@params void
@return true if there no problem
*/
boolean DHT11::sendStartSignal(void) {
digitalWrite(pin, LOW); // MCU Send start signal
pinMode(pin, OUTPUT);
delay(timeLengthWakeupSignal_ms); // at least 18 ms
// MCU Pulls up voltage
pinMode(pin, INPUT);
digitalWrite(pin, HIGH); // Switch to receive data
return true;
}
本项目使用的 DHT11 模块有一个 10K 的上拉电阻,所以我们不设置 INPUT_PULLUP。
DHT一旦检测到启动信号,就会发出一个低电平响应信号,持续80us。然后DHT程序将Data Single-bus电压电平由低到高并保持80us,为DHT发送数据做准备。
忙等待同步
然后我们将使用忙等待同步来检测以下脉冲沿,从 RAISING 到 FALLIN 以及从 FALLING 到 RAISING
/**
Waits until digital port changes to final state or timeout occurs
@param pin to check
@param state to wait for
@param maximum time to wait
@return the elapsed time to reach the final state if less than timeout
or the elapsed time that forced the timeout
*/
int DHT11::busyWait(const int pin, const int finalState, const int timeout) {
int elapsedTime = 0;
int startTime = micros();
while ( digitalRead(pin) != finalState && elapsedTime < timeout ) {
elapsedTime = micros() - startTime;
}
return elapsedTime;
}
忙于等待启动信号响应
首先等待启动信号响应
DHT一旦检测到启动信号,就会发出一个低电平响应信号,持续80us。所以我们将等待 DHT11 准备好。
/**
Once DHT detects the start signal, it will send out a low-voltage-level
response signal, which lasts 80us. So we will wait for the DHT11 to be ready.
@param void
@return true if there no problem
*/
boolean DHT11::waitForStartSignalResponse(void) {
return busyWait(pin, LOW, timeoutForStartData_us) < timeoutForStartData_us;
}
忙于等待起始位
然后等待起始位
/**
DHT sends out response signal and keeps it for 80 us
then DHT pulls up voltage and keeps it for 80 us
@param void
@return true if there no problem
*/
boolean DHT11::waitForStartBit(void) {
if ( busyWait(pin, HIGH, timeoutForResponseSignal_us) < timeoutForResponseSignal_us) { // DHT sends oit response signal and keeps it for 80 us
return (busyWait(pin, LOW, timeoutForStartData_us) < timeoutForStartData_us); // then DHT pulls up voltage and keeps it for 80 us
}
return false;
}
忙等待读取 40 位数据
最后读取 40 位数据
/*
Read the 40 bits in a Dht11 data record
@param pointer to the record to be actualized
@return true if there no problem
*/
boolean DHT11::readDht11DataRecord(DHT11::Dht11_data_type * dataRead)
{
uint8_t integralRh = readByte(pin, timeoutForStartToTransmitData_us, timeoutForData_us, zeroLength_us);
uint8_t decimalRh = readByte(pin, timeoutForStartToTransmitData_us, timeoutForData_us, zeroLength_us);
uint8_t integralTemp = readByte(pin, timeoutForStartToTransmitData_us, timeoutForData_us, zeroLength_us);
uint8_t decimalTemp = readByte(pin, timeoutForStartToTransmitData_us, timeoutForData_us, zeroLength_us);
uint8_t checksum = readByte(pin, timeoutForStartToTransmitData_us, timeoutForData_us, zeroLength_us);
// Verify checksum: integral RH + decimal RH + integral Temp data + decimal Temp data
if ( (integralRh + decimalRh + integralTemp + decimalTemp ) != checksum ) {
dataRead->error = ERROR_CHECKSUM;
dataRead->status = statusString[ERROR_CHECKSUM];
return false;
}
dataRead->error = ERROR_NONE;
dataRead->status = statusString[ERROR_NONE];
dataRead->temperature = (float)integralTemp + (float)decimalTemp / 10.0;
dataRead->humidity = (float)integralRh + (float)decimalRh / 10.0;
return true;
}
读取一个字节
如果检测到“1”位,则字节初始化为 b0000 0000,位位置使用 BIT_MASK 切换
const uint8_t BIT_MASK[] = {0x01, 0x02, 0x04, 0x08, 0x10, 0x20, 0x40, 0x80};
/*
Read 8 bits in a byte from the line
@param pointer to the record to be actualized
@param int pin,
@param int timeout For Start To Transmit Data in us
@param int timeout For Data in us,
@param int bit Zero Length in us
@return the read byte if any or FF if there is any problem reading
*/
uint8_t DHT11::readByte(const int pin,
const int timeoutForStartToTransmitData_us,
const int timeoutForData_us,
const int bitZeroLength_us) {
uint8_t data = 0;
for (int i = 7; i >= 0; i--) {
if (busyWait(pin, HIGH, timeoutForStartToTransmitData_us) < timeoutForStartToTransmitData_us) { // wait for RAISING
int bitLength = busyWait(pin, LOW, timeoutForData_us) ; // wait for FALLING
if (bitLength > timeoutForData_us) {
return 0xFF;
}
if (bitLength > bitZeroLength_us) { // 1 bit value, toggle bit
data |= BIT_MASK[i];
}
}
}
return data;
}
检查解决方案
- 创建 DHT11 对象
- 通话设置
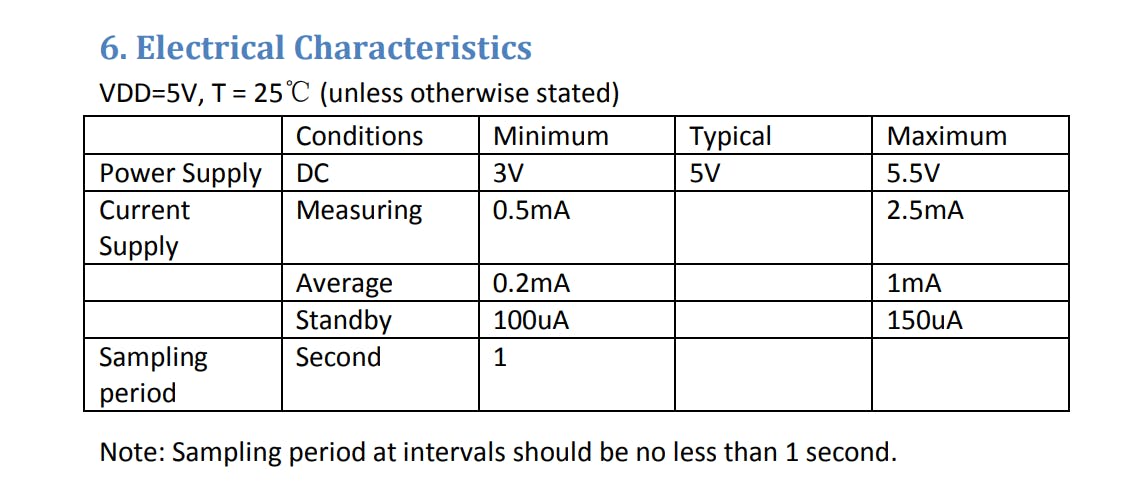
- 需要新讲座时调用 readSensor。注意:间隔采样周期应不少于 1 秒。
#include "DHT11.h"
DHT11 dht11; // DHT11 sensor
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(115200); // for debugging
Serial.println();
Serial.println("Status\tHumidity (%)\tTemperature (C)");
// Initialize DHT11 sensor
dht11.setup(D1); // sensor in D1
}
void loop()
{
DHT11::Dht11_data_type sensorData = dht11.readSensor();
logData(&sensorData);
// NOTE: Sampling periods at intervals should be no less than 1 second
delay(2000); // Wait 2000 milliseconds for the next reading
}
/*
* Logs sensor data to serial log
*
* @params void
* @retun void
*/
void logData(DHT11::Dht11_data_type *sensorData){
Serial.print(sensorData->status);/* status of communication */
Serial.print("\t");
Serial.print(sensorData->humidity, 0);
Serial.print("\t\t");
Serial.println(sensorData->temperature, 2);
}
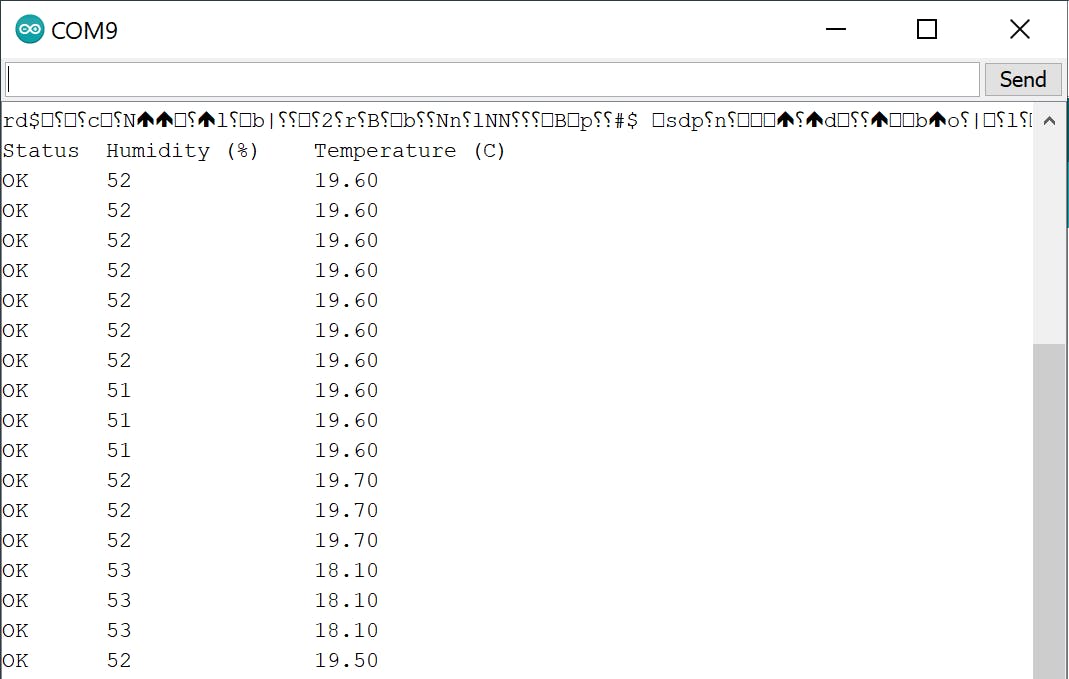
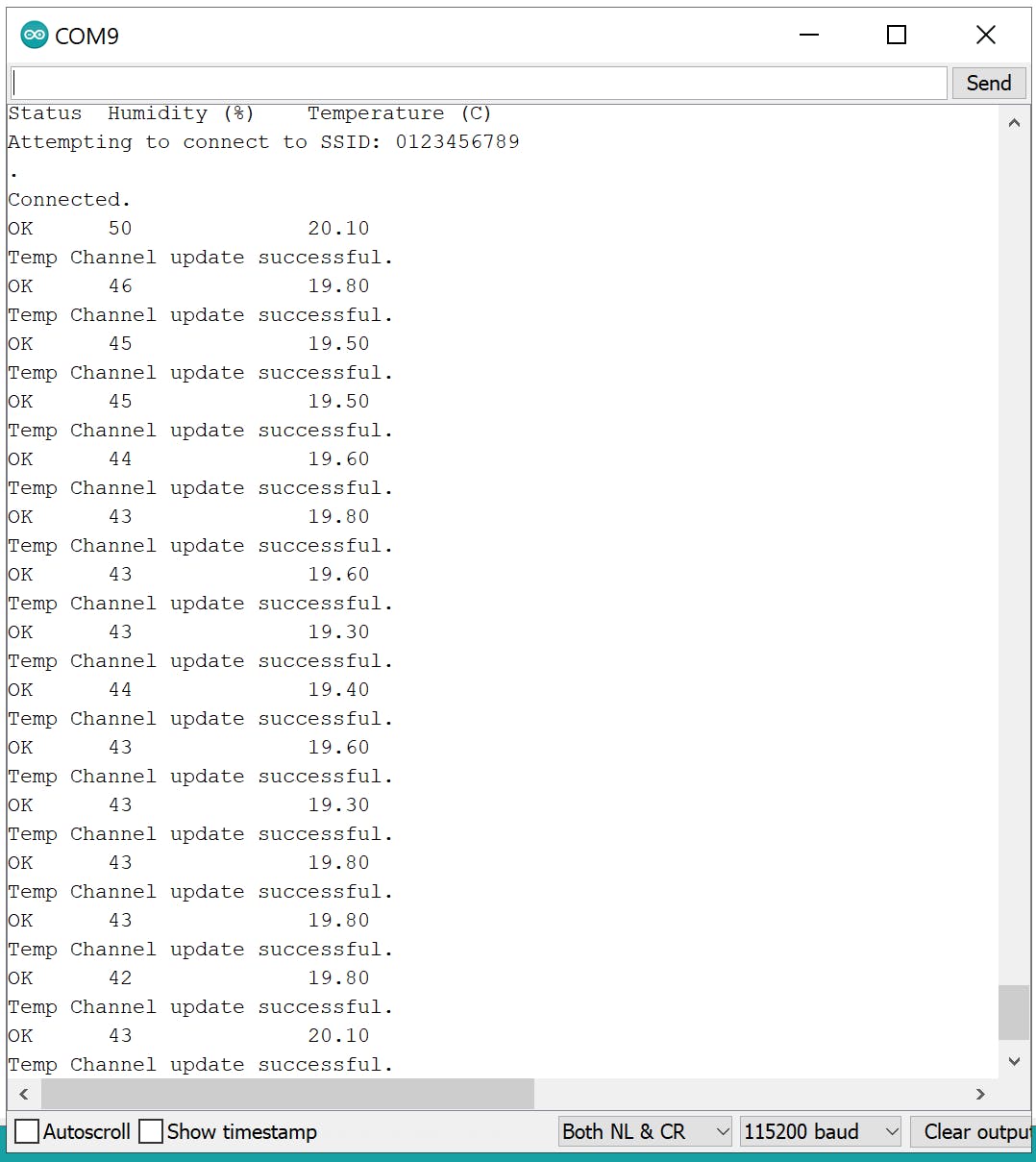
通过串口记录数据。
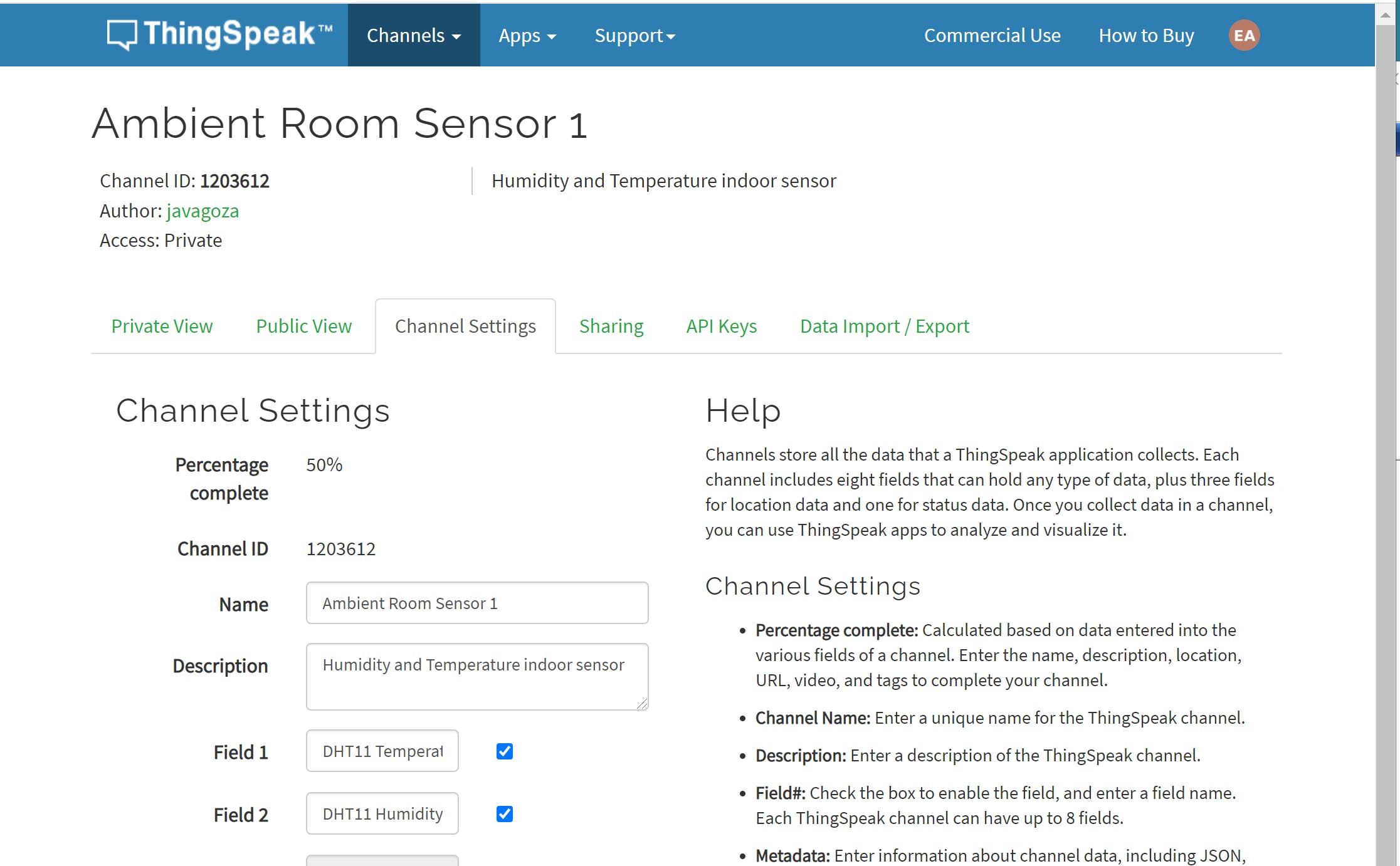
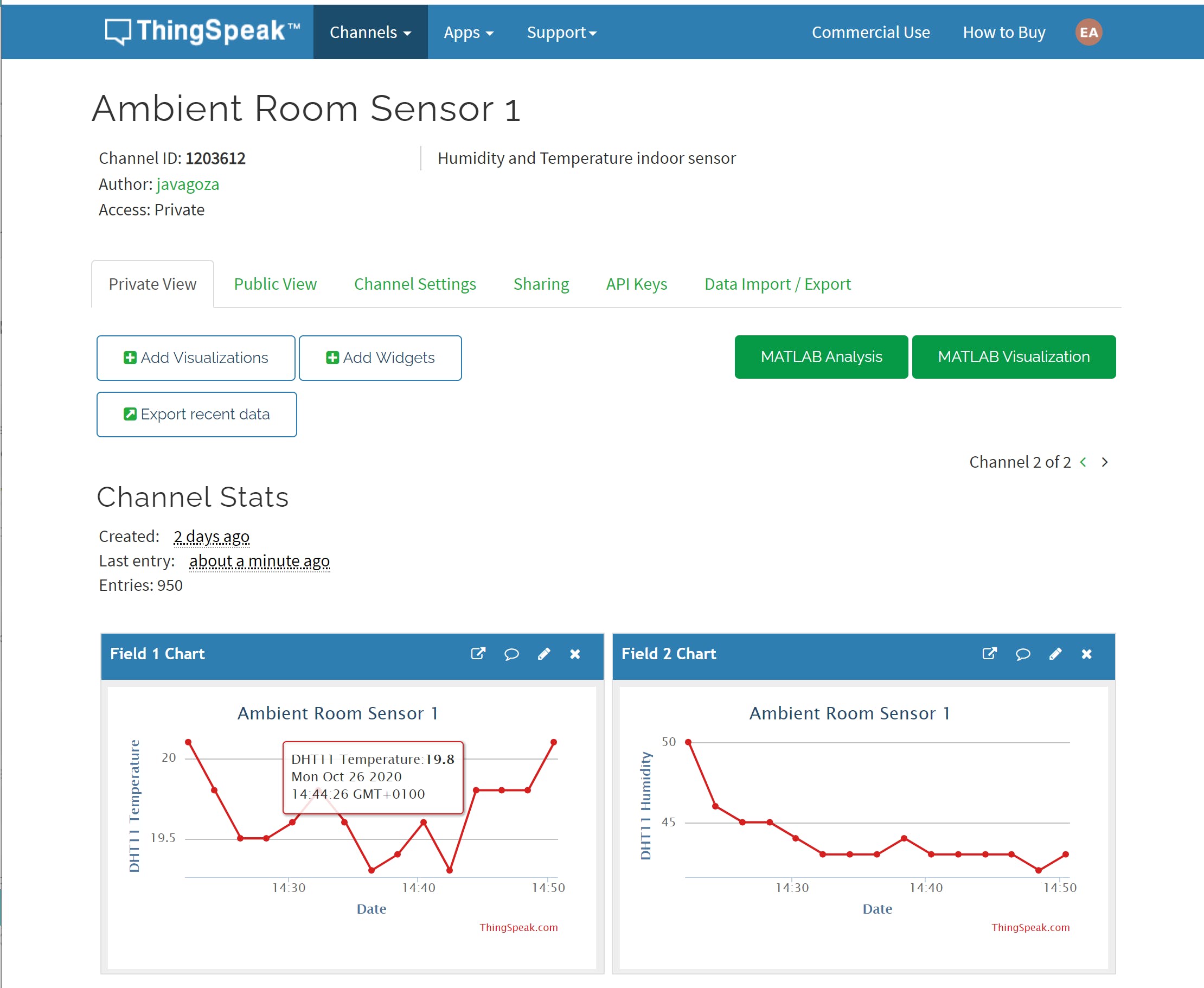
向 ThinkSpeak 发送数据
首先注册:
使用两个字段创建通道:
- 湿度
- 温度
在文件 secrets.h 中填写您的秘密数据
// Use this file to store all of the private credentials
// and connection details
#define SECRET_SSID "MySSID" // replace MySSID with your WiFi network name
#define SECRET_PASS "MyPassword" // replace MyPassword with your WiFi password
#define SECRET_CH_ID 0000000 // replace 0000000 with your channel number
#define SECRET_WRITE_APIKEY "XYZ" // replace XYZ with your channel write API Key
最终代码
主要代码:
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(115200); // for debugging
// Begin ThinkSpeak connection
WiFi.mode(WIFI_STA);
ThingSpeak.begin(client); // Initialize ThingSpeak
Serial.println();
Serial.println("Status\tHumidity (%)\tTemperature (C)");
// Initialize DHT11 sensor
dht11.setup(D1); // sensor in D1
}
void loop()
{
checkWifiConnection();
DHT11::Dht11_data_type sensorData = dht11.readSensor();
logData(&sensorData);
if (DHT11::ERROR_NONE == sensorData.error) {
sendDataToThingSpeak(&sensorData);
}
delay(120000); // Wait 120 seconds to update the channel again
}
检查WIFI连接
/*
* Check if wifi is connected
* if not reconnect
*
* @params void
* @retun void
*/
void checkWifiConnection(void) {
// Connect or reconnect to WiFi
if (WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED) {
Serial.print("Attempting to connect to SSID: ");
Serial.println(SECRET_SSID);
while (WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED) {
WiFi.begin(ssid, pass); // Connect to WPA/WPA2 network.
Serial.print(".");
int counter = 0;
// wait for connection established
while ((WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED ) && (counter < 10)) {
delay(1000);
counter++;
}
}
Serial.println("\nConnected.");
}
}
向 ThingSpeak 发送数据:
/*
* Sends sensor data to Thing speak
*
* @params sensor data record reference
* @retun void
*/
void sendDataToThingSpeak(DHT11::Dht11_data_type *sensorData) {
// Write to ThingSpeak. There are up to 8 fields in a channel, allowing you to store up to 8 different
// pieces of information in a channel. Here, we write to field 1.
ThingSpeak.setField(1, sensorData->temperature);
ThingSpeak.setField(2, sensorData->humidity);
int x = ThingSpeak.writeFields(myChannelNumber, myWriteAPIKey);
if (x == 200) {
Serial.println("Temp Channel update successful.");
}
else {
Serial.println("Problem updating temp channel. HTTP error code " + String(x));
}
}
日志记录
声明:本文内容及配图由入驻作者撰写或者入驻合作网站授权转载。文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表电子发烧友网立场。文章及其配图仅供工程师学习之用,如有内容侵权或者其他违规问题,请联系本站处理。 举报投诉
- 相关下载
- 相关文章





