
资料下载

为Raspberry Pi创建七段显示驱动程序
描述
背景
这篇博文旨在作为我深入研究在 Raspberry Pi 上使用 Windows IoT 进行软件和硬件开发的一系列博文中的第一篇。
介绍
在 Raspberry Pi 上做任何其他事情之前,我决定开始的第一个任务是显示输出,这样我就可以看到我的应用程序完成的任何处理的结果。七段显示器是显示基本数字输出的一种简单方式,无论是温度、湿度还是计时器。
七段显示器可以有一个或多个数字,并带有共阳极或共阴极电路。共阳极显示器的每个段都有一个共享输入,每个段都有自己的输出,而共阴极显示器的每个段都有一个单独的输入和一个公共输出。
具有多于一个数字的显示器,每个数字将有一个阳极或一个阴极,但段输入/输出是共享的。由于一次只能显示一个数字,要显示多位数字,每个数字及其段必须非常快速地打开和关闭,给人眼的印象是所有需要的数字都在连续显示。
下面的解决方案是使用 4 位 7 段共阴极显示器编写的,但该库是有意编写的,以允许它通过 GPIO 输出用于任意位数的 7 段共阴极显示器。
先决条件
- 运行 Windows IoT 的树莓派。
- 8 x 220 欧姆电阻器。
- 7段共阴极显示。我在这个演示中使用了 5641AS,但任何都可以工作,只需相应地更改引脚即可。
- 面包板。
- 连接线。
熔化图
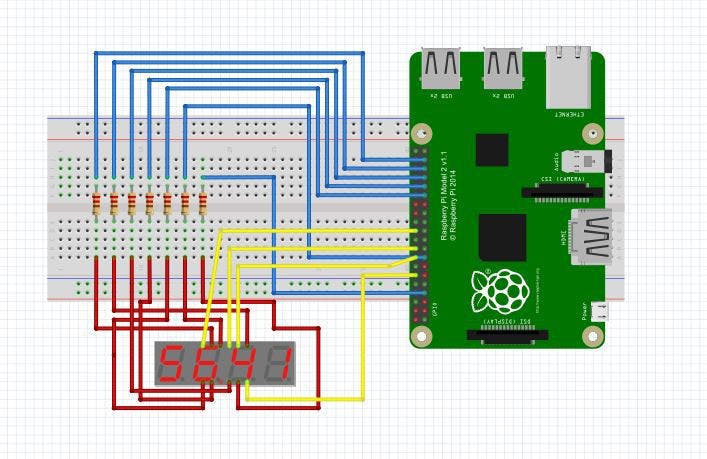
七段显示图
编写此代码时使用的显示器是 5641AS,它有 12 个引脚,从左下角逆时针方向排列。数据表可以在谷歌上找到,但引脚布局如下:
- 乙
- 丁
- 小数点
- C
- G
- 数字 4
- 乙
- 数字 3
- 数字 2
- F
- 一种
- 数字 1
代码
GitHub [上面的链接] 上提供了完整的解决方案,但可以分为 3 个主要部分,初始化、构建输出和显示输出。
初始化
要设置显示器,我们需要知道哪些输出引脚将驱动段,哪些将驱动显示器。虽然段数是固定的(7 或 8,包括小数点),但显示屏上可用的位数可能会有所不同,具体取决于所使用的显示屏。在此示例中,我们有 4 位数字,因此我们需要提供 4 个额外的 pin 号码并对其进行初始化。
这些段是显式传递的,并且任何剩余的引脚都假定为每个显示器一个,通过 params 参数传递。每个显示链接输出引脚和段输出都设置为高电平,这意味着没有电压差,也没有电流流过。因此,所有显示都将关闭。
public Display(int segA, int segB, int segC, int segD, int segE, int segF, int segG, params int[] displayPins)
{
this.Displays = new GpioPin[displayPins.Length];
for (int i = 0; i < displayPins.Length; i++)
{
GpioPin pin = GpioController.GetDefault().OpenPin(displayPins[i]);
pin.Write(GpioPinValue.High);
pin.SetDriveMode(GpioPinDriveMode.Output);
this.Displays[i] = pin;
}
this.SetupOutputPin(ref this.PinSegA, segA);
this.SetupOutputPin(ref this.PinSegB, segB);
this.SetupOutputPin(ref this.PinSegC, segC);
this.SetupOutputPin(ref this.PinSegD, segD);
this.SetupOutputPin(ref this.PinSegE, segE);
this.SetupOutputPin(ref this.PinSegF, segF);
this.SetupOutputPin(ref this.PinSegG, segG);
this.cts = new CancellationTokenSource();
this.token = new CancellationToken();
}
private void SetupOutputPin(ref GpioPin pin, int pinNo)
{
pin = GpioController.GetDefault().OpenPin(pinNo);
pin.Write(GpioPinValue.High);
pin.SetDriveMode(GpioPinDriveMode.Output);
}
构建输出
为了为消费者提供一种设置要显示的值的简便方法,我们将在库中完成这项工作。假设我们要显示 1234 整数,那么我们需要将单个数字拆分为一个由单个数字组成的数组,数组的长度小于或等于我们可以显示的位数,这取决于我们是否're 显示前导零。
在下面的代码中,我们首先运行一些检查以确保我们有一个有效的数字来显示,并且有足够的数字来显示它。然后我们通过 %10 [模数] 计算将它分解成单独的数字。
public void DisplayNumber(int number, bool displayLeadingZero = true)
{
this.displayNo = number;
this.displayLeadingZero = displayLeadingZero;
if (this.displayNo < 0)
{
throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException("Number cannot be negative");
}
int checkMax = 1;
for(int i = 0; i < this.DisplayDigits.Length; i++)
{
checkMax = checkMax * 10;
}
if(number >= checkMax)
{
throw new ArgumentException("Cannot display numbers greater than " + (checkMax - 1).ToString());
}
if (this.displayNo == 0)
{
this.Blank();
if(this.DisplayDigits.Length > 0)
{
this.DisplayDigits[0] = 0;
}
}
else
{
List<int> listOfInts = new List<int>();
while (this.displayNo > 0)
{
listOfInts.Add(this.displayNo % 10);
this.displayNo = this.displayNo / 10;
}
if (displayLeadingZero)
{
while (listOfInts.Count < this.Displays.Length)
{
listOfInts.Add(0);
}
}
else
{
while (listOfInts.Count < this.Displays.Length)
{
listOfInts.Add(10);
}
}
this.DisplayDigits = listOfInts.ToArray();
}
显示输出
为了以足够快的速度在输出显示器上显示数字以欺骗眼睛认为所有显示器同时打开,我们必须创建一个永久循环,其唯一工作是依次打开和关闭每个显示器。这是通过“开始”方法完成的,该方法只是启动一个循环,并显示先前计算的数组中的数字。如果数组更新,显示会自动更新。
private void Start()
{
if (running)
{
return;
}
running = true;
Task.Factory.StartNew(() =>
{
while (!this.cts.IsCancellationRequested)
{
if (this.DisplayDigits == null)
{
this.Blank();
}
int[] arrDigs = this.DisplayDigits;
for (int i = 0; i < arrDigs.Length; i++)
{
this.SetDisplay(this.Displays[i], arrDigs[i]);
}
}
}, token);
}
设置显示功能关闭所有显示[设置为高],然后根据数字将显示特定数字所需的段设置为高/低,然后将显示引脚设置为低,允许电流流动个位数。这轮流通过每个数字依次打开和关闭每个数字。这种情况发生的速度比眼睛能察觉的要快,给人的印象是所有数字都同时打开。
private void SetDisplay(GpioPin displayPin, int value)
{
this.ClearDisplay();
switch (value)
{
case 0:
this.SetHigh(new GpioPin[] { this.PinSegA, this.PinSegB, this.PinSegC, this.PinSegD, this.PinSegE, this.PinSegF });
this.SetLow(new GpioPin[] { this.PinSegG });
break;
case 1:
this.SetHigh(new GpioPin[] { this.PinSegB, this.PinSegC });
this.SetLow(new GpioPin[] { this.PinSegA, this.PinSegD, this.PinSegE, this.PinSegF, this.PinSegG });
break;
case 2:
this.SetHigh(new GpioPin[] { this.PinSegA, this.PinSegB, this.PinSegD, this.PinSegE, this.PinSegG });
this.SetLow(new GpioPin[] { this.PinSegC, this.PinSegF });
break;
case 3:
this.SetHigh(new GpioPin[] { this.PinSegA, this.PinSegB, this.PinSegC, this.PinSegD, this.PinSegG });
this.SetLow(new GpioPin[] { this.PinSegE, this.PinSegF });
break;
case 4:
this.SetHigh(new GpioPin[] { this.PinSegB, this.PinSegC, this.PinSegF, this.PinSegG });
this.SetLow(new GpioPin[] { this.PinSegA, this.PinSegD, this.PinSegE });
break;
case 5:
this.SetHigh(new GpioPin[] { this.PinSegA, this.PinSegC, this.PinSegD, this.PinSegF, this.PinSegG });
this.SetLow(new GpioPin[] { this.PinSegB, this.PinSegE });
break;
case 6:
this.SetHigh(new GpioPin[] { this.PinSegA, this.PinSegC, this.PinSegD, this.PinSegE, this.PinSegF, this.PinSegG });
this.SetLow(new GpioPin[] { this.PinSegB });
break;
case 7:
this.SetHigh(new GpioPin[] { this.PinSegA, this.PinSegB, this.PinSegC });
this.SetLow(new GpioPin[] { this.PinSegD, this.PinSegE, this.PinSegF, this.PinSegG });
break;
case 8:
this.SetHigh(new GpioPin[] { this.PinSegA, this.PinSegB, this.PinSegC, this.PinSegD, this.PinSegE, this.PinSegF, this.PinSegG });
break;
case 9:
this.SetHigh(new GpioPin[] { this.PinSegA, this.PinSegB, this.PinSegC, this.PinSegD, this.PinSegF, this.PinSegG });
this.SetLow(new GpioPin[] { this.PinSegE });
break;
case 10: // Clear Display
this.SetLow(new GpioPin[] { this.PinSegA, this.PinSegB, this.PinSegC, this.PinSegD, this.PinSegE, this.PinSegF, this.PinSegG });
break;
default:
this.SetLow(new GpioPin[] { this.PinSegA, this.PinSegB, this.PinSegC, this.PinSegD, this.PinSegE, this.PinSegF, this.PinSegG });
break;
}
this.SetLow(new GpioPin[] { displayPin });
}
包括演示应用程序在内的完整代码清单可通过页面顶部的链接获得。
未来发展
目前,输出仅限于完整的正整数。未来的改进可能包括显示小数或负数,或一些字母数字字符(例如用于温度显示的 C 或 F)。
声明:本文内容及配图由入驻作者撰写或者入驻合作网站授权转载。文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表电子发烧友网立场。文章及其配图仅供工程师学习之用,如有内容侵权或者其他违规问题,请联系本站处理。 举报投诉
- 相关下载
- 相关文章





