
资料下载

用Arduino控制小型线性执行器
描述
此 Arduino 线性致动器教程展示了如何使用 Arduino 兼容板和各种输入传感器控制Firgelli 小型线性致动器,包括用于直接控制的滑块和旋转旋钮、用于增量移动的操纵杆以及具有预设位置的三个按钮(在代码中预设)每个位置都分配给一个按钮,因此当用户按下按钮时,小型线性执行器会移动到该位置)。
对于 Arduino 线性执行器项目,Firgelli 的小型线性执行器非常出色。这些线性执行器有一个内部控制器,允许它们像伺服一样操作。通过使用 Arduino 伺服库,我们可以简单地向执行器发送所需的位置,然后它移动到该位置。
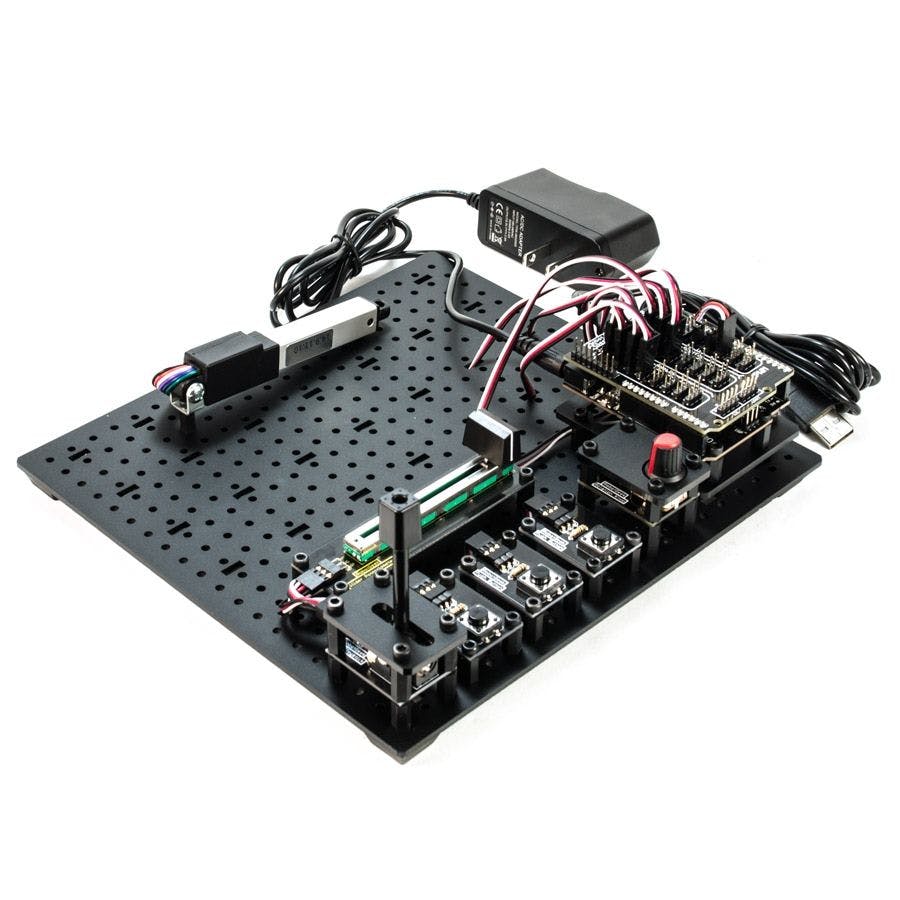
所有部件都可以在RobotGeek Arduino 线性执行器实验者套件中一起找到,或者单独获得。
第 1 步:接线
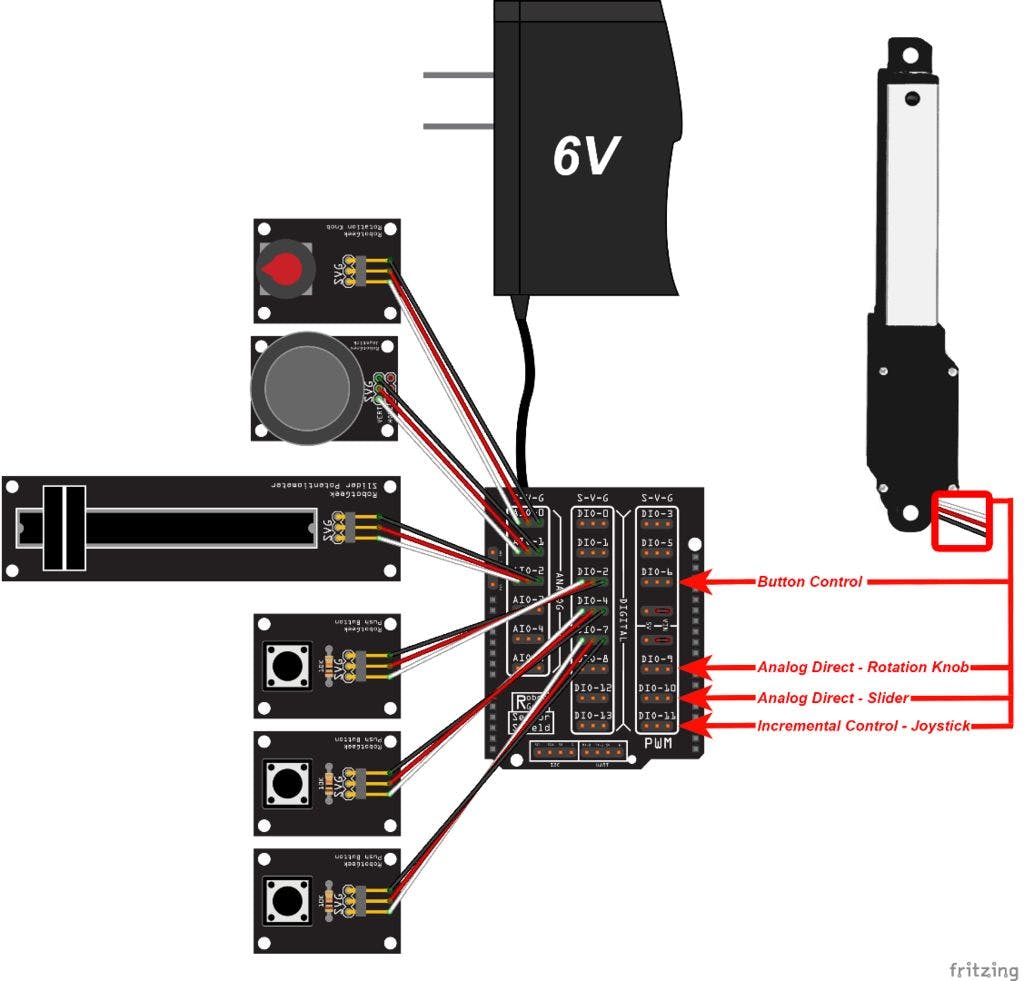
请注意,您必须将线性致动器物理插入不同的端口才能使用不同的控件移动它。如果您有多个线性执行器,您可以使用此代码同时控制多达 4 个。
第 2 步:将代码上传到您的 Arduino
您可以在RobotGeek 库和工具中的以下位置找到此演示代码:
RobotGeekSketches -> Demos -> LinearActuator -> linearActuatorExpDemo -> linearActuatorExpDemo.ino
这段代码将帮助我们完成接下来的三个部分。根据您正在学习的教程部分,您将被要求将线性致动器插入不同的引脚。
/***********************************************************************************
* RobotGeek Linear Actuator Experimenter's Kit Demo
* ________
* | \---------\___________________________
* __| | ||--------------------|__
* (o | FIRGELLI | o ||____________________| o)
* |__________________/--------------------------||
*
*
* The following sketch will allow you to control a Firgelli Linear actuator using
* the RobotGeek Slider, RobotGeek Knob, RobotGeek Joystick, and RobotGeek Pushbuttons
*
* http://www.robotgeek.com/robotgeek-experimenters-kit-linear-actuator
*
*
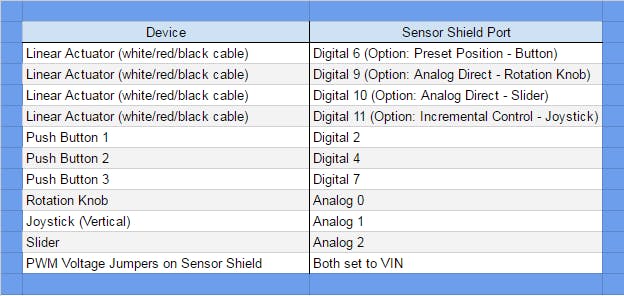
* Wiring
* Linear Actuator - Digital Pin 6, 9, 10, and/or 11
*
* Knob - Analog Pin 0
* Joystick - Analog Pin 1
* Slider - Analog Pin 2
*
* Pushbutton - Digital Pin 2
* Pushbutton - Digital Pin 4
* Pushbutton - Digital Pin 7
*
* Jumpers for pins 3/5/6 and 9/10/11 should be set to 'VIN'
*
*
* Control Behavior:
* Moving the slider or knob will move the linear actuator keeping absolute position.
* Moving the joystick will move the linear actuator incrementally.
* Pressing one of the buttons will move the linear actuator to a predetermined position.
*
***********************************************************************************/
//Includes
#include //Servo Library can be used for Firgelli Mini Linear Actuators
//Linear Actuator Pins
const int LINEARPIN_BUTTON = 6; //Linear Actuator on Digital Pin 6
const int LINEARPIN_KNOB = 9; //Linear Actuator on Digital Pin 9
const int LINEARPIN_SLIDER = 10; //Linear Actuator on Digital Pin 10
const int LINEARPIN_JOYSTICK = 11; //Linear Actuator on Digital Pin 11
//Analog Input Pins
const int KNOB_PIN = 0; //Knob on Analog Pin 0
const int JOYSTICK_PIN = 1; //Joystick (vertical) on Analog Pin 1
const int SLIDER_PIN = 2; //Slider on Analog Pin 2
//Digital Input Pins
const int BUTTON1_PIN = 2; //Button 1 on Digital Pin 2
const int BUTTON2_PIN = 4; //Button 2 on Digital Pin 4
const int BUTTON3_PIN = 7; //Button 3 on Digital Pin 7
//Generic deadband limits - not all joystics will center at 512, so these limits remove 'drift' from joysticks that are off-center.
const int DEADBAND_LOW = 482; //decrease this value if drift occurs, increase it to increase sensitivity around the center position
const int DEADBAND_HIGH = 542; //increase this value if drift occurs, decrease it to increase sensitivity around the center position
//Max/min pulse values in microseconds for the linear actuators
const int LINEAR_MIN = 1050;
const int LINEAR_MAX = 2000;
// variables will change:
int button1State = 0; // variable for reading the pushbutton status
int button2State = 0; // variable for reading the pushbutton status
int button3State = 0; // variable for reading the pushbutton status
Servo linearKnob, linearSlider, linearButton, linearJoystick; // create servo objects to control the linear actuators
int knobValue, sliderValue, joystickValue; //variables to hold the last reading from the analog pins. The value will be between 0 and 1023
int valueMapped; // the joystick values will be changed (or 'mapped') to new values to be sent to the linear actuator.
//variables for current positional value being sent to the linear actuator.
int linearValue_Knob = 1500;
int linearValue_Slider = 1500;
int linearValue_Button = 1500;
int linearValue_Joystick = 1500;
int speed = 2;
void setup()
{
//initialize linear actuators as servo objects
linearKnob.attach(LINEARPIN_KNOB); // attaches/activates the linear actuator as a servo object
linearSlider.attach(LINEARPIN_SLIDER); // attaches/activates the linear actuator as a servo object
linearButton.attach(LINEARPIN_BUTTON); // attaches/activates the linear actuator as a servo object
linearJoystick.attach(LINEARPIN_JOYSTICK); // attaches/activates the linear actuator as a servo object
//Analog pins do not need to be initialized
//use the writeMicroseconds to set the linear actuators to their default positions
linearKnob.writeMicroseconds(linearValue_Knob);
linearSlider.writeMicroseconds(linearValue_Slider);
linearButton.writeMicroseconds(linearValue_Button);
linearJoystick.writeMicroseconds(linearValue_Joystick);
}
void loop()
{
//Preset Positions for Button Control
// if the pushbutton is pressed set the linear value
button1State = digitalRead(BUTTON1_PIN);
if (button1State == HIGH) {
// set the position value
linearValue_Button = 1300;
}
button2State = digitalRead(BUTTON2_PIN);
if (button2State == HIGH) {
// set the position value
linearValue_Button = 1500;
}
button3State = digitalRead(BUTTON3_PIN);
if (button3State == HIGH) {
// set the position value
linearValue_Button = 1700;
}
//Analog Direct Control
//read the values from the analog sensors
knobValue = analogRead(KNOB_PIN);
sliderValue = analogRead(SLIDER_PIN);
linearValue_Knob = map(knobValue, 0, 1023, LINEAR_MAX, LINEAR_MIN); //Map analog value from the sensor to the linear actuator
linearValue_Slider = map(sliderValue, 0, 1023, LINEAR_MAX, LINEAR_MIN); //Map analog value from the sensor to the linear actuator
//Incremental Joystick Control
joystickValue = analogRead(JOYSTICK_PIN); //read the values from the joystick
//only update if the joystick is outside the deadzone (i.e. moved oustide the center position)
if(joystickValue > DEADBAND_HIGH || joystickValue < DEADBAND_LOW)
{
valueMapped = map(joystickValue, 0, 1023, speed, -speed); //Map analog value from native joystick value (0 to 1023) to incremental change (speed to -speed).
linearValue_Joystick = linearValue_Joystick + valueMapped; //add mapped joystick value to present Value
linearValue_Joystick = constrain(linearValue_Joystick, LINEAR_MIN, LINEAR_MAX); //
}
//Use the writeMicroseconds to set the linear actuator to its new position
linearKnob.writeMicroseconds(linearValue_Knob);
linearSlider.writeMicroseconds(linearValue_Slider);
linearButton.writeMicroseconds(linearValue_Button);
linearJoystick.writeMicroseconds(linearValue_Joystick);
delay(10);
}
第 3 步:模拟直接控制
对于本节:
要使用旋转旋钮,请将线性执行器插入Digital Pin 9
要使用滑块,请将线性执行器插入Digital Pin 10
那么这是怎么回事?我们正在将模拟传感器的绝对位置映射到执行器位置。这是有道理的,您将旋转旋钮或滑块移动到一个位置,并且线性执行器与该位置匹配。
想看废话吗?将操纵杆插入Analog Pin 0 ,将线性执行器插入Digital Pin 9 。操纵杆始终返回到中心位置,导致线性执行器匹配并返回到其中心值。如果您想使用操纵杆将线性致动器移动到中心以外的位置,那么这并不是那么有用,这将我们带到下一节。在继续之前,请确保将传感器恢复到原来的引脚。
如果您想要仅涵盖本教程这一部分的草图,可以在此处找到它。
第 4 步:增量控制
对于本节:
要使用操纵杆,请将线性执行器插入Digital Pin 11
那么这是怎么回事?这一次,我们不是直接映射到操纵杆的值,而是使用操纵杆来增加线性致动器的位置,这样我们就可以放开操纵杆,让线性致动器保持在上次放置的位置。
如果您想要仅涵盖本教程这一部分的草图,可以在此处找到它。
第 5 步:预设控件
对于本节:
要使用按钮,请将线性执行器插入Digital Pin 6
那么这是怎么回事?在这一部分中,我们使用按钮按下将线性执行器发送到预定义的位置。当您知道在输入定义的情况下您希望线性致动器处于什么位置时,这非常简单且非常有用。
如果您想要仅涵盖本教程这一部分的草图,可以在此处找到它。
第 6 步:下一步是什么?
现在您知道了三种控制直线推杆的方法。你能想到可以从中受益的项目吗?您有想要自动打开的盒子吗?您将如何使用线性致动器来做到这一点?人体的所有肌肉都是生物线性致动器。你能做一个模仿这个的机械臂吗?做一张可以倾斜的桌子怎么样?我们很想听听您的项目!去创造吧!
声明:本文内容及配图由入驻作者撰写或者入驻合作网站授权转载。文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表电子发烧友网立场。文章及其配图仅供工程师学习之用,如有内容侵权或者其他违规问题,请联系本站处理。 举报投诉
- 相关下载
- 相关文章





